
Getty Images
Bitcoin halving explained: Everything you need to know
Since its 2009 inception, bitcoin surged from $0 to a peak of $69,000 in Nov. 2021. To control supply, a halving event happens to limit mining rewards and slow bitcoin creation.
Approximately every four years, the Bitcoin cryptocurrency community braces for a major event known as -- the halving. The most recent bitcoin halving event occurred on April 19, 2024.
Bitcoin is among the most highly valued and widely traded forms of cryptocurrency in the world. In 2024, bitcoin continued to increase in value reaching new highs as investors flocked to the digital currency. Among the drivers for the increased demand and price of bitcoin is the easier availability of bitcoin as an investment class, with the debut of Bitcoin cryptocurrency exchange-traded funds.
With the increased access and popularity of Bitcoin, the halving event of 2024 arguably received more public interest and media coverage than any prior halving event.
What is Bitcoin halving?
With Bitcoin halving the reward for a bitcoin mining operation is cut in half.
Bitcoin mining is the process that creates new bitcoin tokens. During mining, a miner solves a cryptographic operation, and then the miner is offered a reward. After Bitcoin halving, the miner is given 50% fewer tokens for a successful operation than before the halving event.
Bitcoin halving is a core element of how cryptocurrency operates and is intended to help regulate the availability of new bitcoin. The primary goal of the halving is to slow the pace of bitcoin creation. By slowing the pace, the basic idea is that the scarcity of bitcoin tokens will increase.
Bitcoin's creator Satoshi Nakamoto built the concept of halving when creating Bitcoin. Nakamoto created halving because the supply was capped at 21 million tokens.
About the Bitcoin network
The Bitcoin network is based on blockchain technology, which is comprised of a decentralized and distributed network of nodes.
Nodes on the Bitcoin network contain transaction history and are responsible for validating new transactions. A block on the Bitcoin network is a group of transactions that bitcoin miners verify by solving a cryptographic algorithm. The process used in the Bitcoin network to verify blocks is a consensus algorithm known as proof of work (PoW).
The miner that solves the PoW adds the next block to the blockchain and as a reward is issued newly minted bitcoin. As of April 19, 2024, the reward is 3.125 bitcoin. At Bitcoin's creation, the reward was 50 bitcoin per block, so since its inception, bitcoin has been halved four times.
How does Bitcoin halving work?
Here's how the Bitcoin halving works:
Reaching the halving threshold
The Bitcoin protocol includes a rule that after every 210,000 blocks are mined, the reward for mining a new block is halved. To date, it has taken roughly four years to reach the threshold.
Triggering the halving
Once the 210,000th block from the last halving event is added to the blockchain, the Bitcoin network automatically triggers the halving event. This is a feature embedded within the Bitcoin protocol.
Reducing the block reward
After the halving event is triggered, the block reward for miners is cut in half. For example, after the first halving in 2012, the reward went from 50 to 25 bitcoin tokens.
Continuing the cycle
The cycle of mining and halving continues, with the next halving event anticipated after another 210,000 blocks are mined. This predictable and transparent supply schedule is one of the defining features of Bitcoin.
Effects of Bitcoin halving
The Bitcoin halving event has numerous effects including the following:
- Demand. Halving reduces the rate at which new bitcoin are released into circulation, which can limit supply and increase demand for existing bitcoin.
- Investing. The increased demand, driven by constrained supply, could potentially increase the value of bitcoin, making it an even more lucrative investment.
- Mining. For miners, the halving can functionally reduce the incentive for mining new blocks since the reward is decreased. As a result, there could be a consolidation in bitcoin mining as smaller miners drop out of the market.
- Inflation. The halving has the goal of attempting to control inflation by reducing Bitcoin's supply over time. By reducing the reward, the idea is that Bitcoin's inflation rate decreases over time. Though with the dramatic spike in Bitcoin valuation in fiat currency, it's unclear what impact the 2024 halving will have on inflation
- Environment. The halving might indirectly influence the environmental impact of bitcoin mining. As rewards decrease, miners are incentivized to seek more energy-efficient mining practices.
History of Bitcoin halving
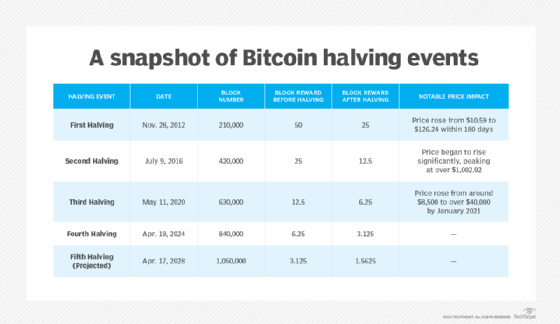
Bitcoin halving has been occurring at predictable four-year intervals ever since the first halving in November 2012.
Future of Bitcoin
The future price of bitcoin is likely to continue fluctuating as cryptocurrency value can be volatile and speculative as an investment instrument. In the short term, investor interest remains high thanks in part to the introduction of Bitcoin spot ETFs in January 2024. With the cryptocurrency ETFs, it became easier for investors to gain exposure to bitcoin's price movements through regulated financial products.
The future of Bitcoin will include more halving events for decades yet to come.
The next halving event is currently expected to occur in April 2028. The overall process of halving is set to continue until around the year 2140. At that point, all 21 million bitcoin are expected to be mined. After 2140, miners will solely earn transaction fees for their participation in processing transactions.
Sean Michael Kerner is an IT consultant, technology enthusiast and tinkerer. He has pulled Token Ring, configured NetWare and has been known to compile his own Linux kernel. He consults with industry and media organizations on technology issues.







