OLED TV (organic light-emitting diode television)
What is an OLED TV (organic light-emitting diode television)?
An OLED TV (organic light-emitting diode television) is a type of display technology that uses OLEDs to render images on the panels used for TV screens. An OLED TV differs in important ways from other types of light-emitting diode (LED) technologies because OLED does not require backlighting or a liquid crystal display (LCD) to render images.
An OLED panel uses organic -- i.e., carbon-based -- substances as semiconductor material to display images. The panel is created by sandwiching thin films of organic materials between multiple layers of semiconductor material. The panel typically includes cathode, anode and conductive layers, often along with other types of layers. When electrical current is applied to the layers, the organic material glows with its own light, a process referred to as electroluminescence.
The layers sit on a substrate made up of a material such as glass or plastic. The substrate provides a foundation for the panel.
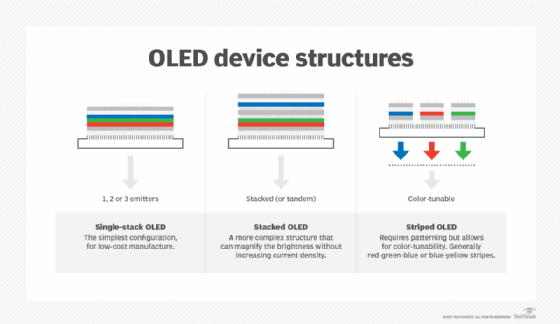
The display's colors are determined by the types of organic materials used for the layers and how those materials are arranged. TV manufacturers use different methods to render colors and enhance images. However, the underlying principles are the same:
- Each pixel emits its own light.
- Pixels can be controlled individually.
- Pixels can be turned on or off at an individual level.
- The amount of current determines the pixel's brightness.
Steven Van Slyke and Ching W. Tang pioneered OLED technology in the 1980s when working at Kodak. However, the world did not see the first commercial OLED TV until 2007 when Sony introduced its XEL-1 TV, which had only an 11-inch display. Since then, OLED TVs have gotten bigger, better and easier to manufacture, resulting in a wider variety of TVs at more affordable prices.
Many vendors now sell OLED TVs, including LG, Samsung, Sony, Panasonic and Vizio. LG Display, an LG subsidiary, is the world leader in OLED panel production. Many of today's OLED TVs use LG panels, even if the TV itself is sold under a different brand.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of OLED TVs?
Because the pixels in an OLED TV panel emit their own light and can be controlled individually, they hold several advantages over other TV display technologies:
- OLED pixels do not require backlighting, resulting in panels that are thinner and lighter than other display technologies.
- The lack of backlighting means that OLED TVs require less power to operate, compared to other LED technologies.
- Because light does not need to pass through an LCD layer, OLED displays support a wider viewing angle. The image does not lose color or contrast if viewers sit off to the side, away from the screen's center.
- OLED TVs support much faster refresh rates than other LED technologies, with the latest models delivering rates up to 240 hertz.
- OLED TVs typically offer better picture quality than other technologies, rendering colors with greater accuracy, displaying highlights more precisely and offering true black images.
- Because of the high picture quality, OLED technology makes it possible to create TV panels that offer contrast ratios up to 1,000,000-to-1.

Despite the benefits of OLED TVs, the technology also comes with several challenges. First, OLED TVs are not as bright as many LED TVs. This can be a disadvantage in brightly lit rooms or rooms with lots of windows. For many viewers, however, this might not be a concern because the difference is typically not highly significant. In addition, the picture's overall quality is high enough to mitigate some of the concerns around brightness. Vendors have also been taking steps to beef up brightness, so it is becoming less of an issue.
OLED TVs are more susceptible to burn-in and image retention than other LED technologies. Burn-in can permanently damage the panel, and retention can temporarily affect the image, although it typically goes away after a few minutes of regular usage. That said, manufacturers have made improvements in recent years to help mitigate the problem and reduce its likelihood.
Perhaps one of the biggest drawbacks of OLED TVs is cost. Since their introduction, they have been substantially more expensive than other display technologies, especially when they first hit the market. Although prices have been dropping as the technology and manufacturing techniques mature, OLED TVs are still pricier than the rest of the TV market, especially the high-end models. For some buyers, however, the superior quality is worth the investment.
Today, OLED TVs are available to consumers in a broad range of prices and sizes, from several hundred dollars for some in the 43-inch class to more than $25,000 for devices in the 90-inch range.
The growing interest in OLED has led to several variations. For example, Samsung now offers quantum dot OLED TVs, a technology that incorporates quantum dots into its TVs to help improve picture quality even more. Another emerging market is the flexible OLED panel, a type of OLED display that is malleable enough to be folded or rolled up. Manufacturers are also working on transparent OLED panels, which make it possible to display images on a transparent material.
Learn about setting up and troubleshooting multiple thin client monitors, and read about 4K video resolution in the enterprise.
