OpenFlow
What is OpenFlow?
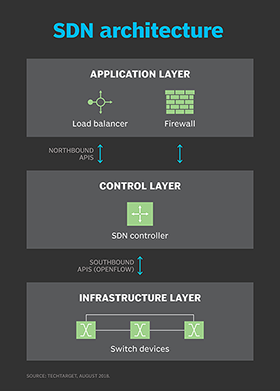
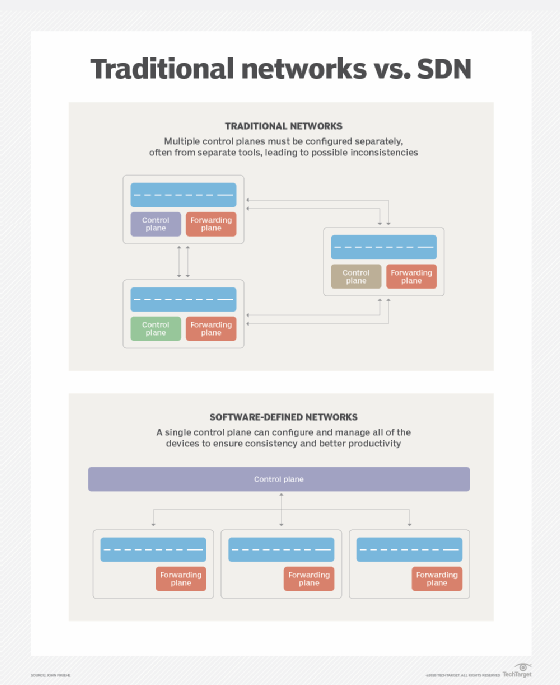
OpenFlow, an open source standard supported by many vendors, is the first software defined networking (SDN) control protocol. It separates the control plane (decision-making) from the forwarding plane (packet routing).
OpenFlow is currently in version 1.5 of the specification. It is maintained by the Open Network Foundation.
OpenFlow is a network control protocol. Network traffic does not go through the OpenFlow protocol. Instead, OpenFlow sends the control signals that tell the network switches how to route the network traffic.
In traditional network design, each switch would contain a routing table that it used to decide how to route each packet. This routing table is largely static; it would be updated by the administrator individually on each router.
In OpenFlow, an SDN controller is the control plane. The SDN controller contains the logic and does the decision-making for how the network traffic should flow between the switches. The SDN controller establishes a connection to each switch to pass messages. This connection uses Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and is often encrypted with Transport Layer Security (TLS). It uses port 6653 with earlier versions using 6633.
The controller sends commands to the OpenFlow switches, which handle the network data. The OpenFlow commands change the switch's flow routing table. The flow table is the OpenFlow equivalent of the routing and MAC address forwarding tables. It contains all the instructions for how the switch will handle network traffic.
The flow table contains many rows of flow entries which tell the switch how to handle each packet. The flow entries can use each OSI layer of a packet, including MAC address match, IP address match, protocol match or port match. These rules can be multilevel and combined to create complex rules. This level of flexibility allows each OpenFlow switch to act as a basic firewall as well. Switches can forward packets that do not match any rules to the SDN controller for the controller to inspect and create a new flow rule for it.
Flow tables can be delivered proactively or reactively. In proactive delivery the controller sends the flow table to all switches. In reactive mode the controller only sends new flow entries when requested by the switch. This can help to reduce the amount of data stored on each switch and improve performance.
The OpenFlow SDN controller can communicate with higher-level applications. These higher-level applications contain the business logic and can be configured more easily by a technician. This is then put on a northbound interface API to the controller. The controller then makes the flow rules.
What are the advantages of OpenFlow?
OpenFlow is an open source SDN technology. It is supported by many vendors and providers. Some switches can use either OpenFlow rules or its own internal ones. It can be used in an entirely virtualized network environment to control virtual switches in cloud computing.
The SDN nature of OpenFlow allows for quick response to changes and failures. It is also highly flexible and can manage highly complex rules.
To illustrate the use of OpenFlow, imagine a campus area network (CAN) with many buildings, switches and two internet connections. For normal operation, the network traffic flows through the closest connections to get to its destination. If a link connecting two buildings goes down, the switches can report the connection status to the controller, which then sends new flow rules out to the affected switches with a new forwarding path. If an internet connection goes down it can also route any internet-bound traffic over the good link. A large CAN with many different types of devices could also quickly become full of unwanted traffic, but it would be expensive to put a firewall between each building or even each floor within a building. The flow rules could be set to drop unwanted traffic such as broadcast requests or Apple Bonjour so they don't go out to the entire network and quickly overwhelm it.
Explore the story of SDN, including control planes, OpenFlow protocol and disaggregation. Learn what SDN data center controllers do in a network and about 10 important components of SDN controllers. Check out 12 common network protocols and their functions.
