The Three Ways (The Phoenix Project)
The Three Ways is a set of business principles that encourage organizations to value a corporate culture in which feedback loops are short, everyone understands how different parts of the business interrelate and all employees are encouraged to seek knowledge that will help the company meet business goals.
The Three Ways was first introduced in a popular business/IT book called The Phoenix Project. The Phoenix Project's narrative story line shows the reader through the character's eyes that bad things can happen when product owners, software developers, IT operations, quality assurance (QA) and security teams fail to work together as a cohesive unit.
The concept of the Three Ways is introduced by a mysterious all-knowing character in the book named Erik Reid. It provides the other characters with a framework for implementing DevOps and building a culture in which people, process and technology are aligned and working towards the same goal: providing value to customers.
The Phoenix Project, which is published by IT Revolution, has an accompanying reference work called The DevOps Handbook. It provides a more in-depth explanation of The Three Ways and information about how the principles can be used to create best practices.
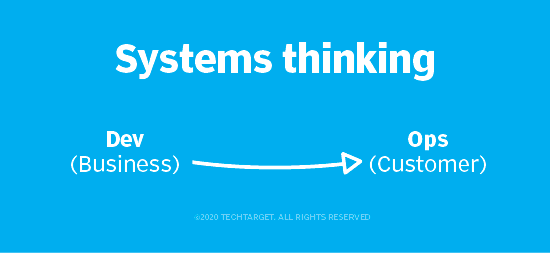
The First Way: Systems thinking and the principles of flow
Systems thinking places value on looking at the big picture. Global performance should be prioritized over local performance, and rather than focusing on the individual performance of employees, teams or departments, organizations should focus on creating a smooth flow of work: from Business → Development → Operations → Customer.
Examples of systems thinking include:
- Reducing work in progress
- Removing project constraints and bottlenecks;
- Making sure to not pass any known defect to another department or work center;
- Continually trying to find ways to simplify and improve workflow.
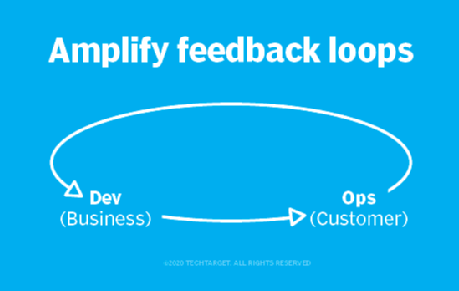
The Second Way: Feedback loops and the need for amplification
The Second Way places value on providing and receiving quick feedback on a continual basis. The aim is to improve work quality while also preventing repeat problems.
When feedback loops are amplified, mistakes can quickly be identified and fixed. When feedback loops are continual, it's less likely that important information will be lost due to staffing changes.
Examples of amplifying feedback loops include:
- Introducing shift left testing in order to get feedback as early as possible;
- Reducing work in progress to create faster workflows and get feedback as soon as possible;
- Understanding and responding to all customers interactions;
- Embedding knowledge where it is needed;
- Creating quality at the source.
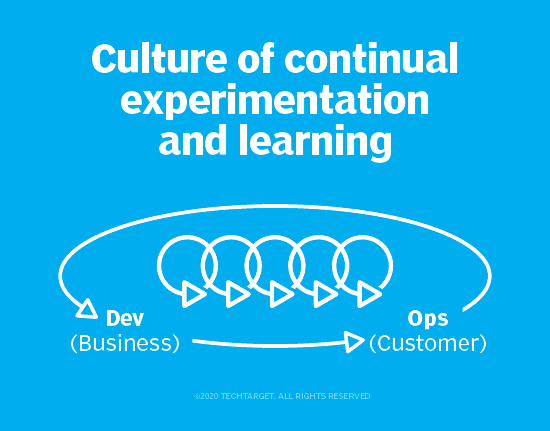
The Third Way: Creating a culture of continual experimentation and learning
The Third Way is about building a healthy organizational culture that encourages continual learning and experimentation amongst employees. Specifically, this means recognizing the importance of practice and repetition, and accepting risk-taking and making mistakes as part of the learning process.
Examples of a culture of continual learning and experimentation include:
- Encouraging a safe culture of failure that uses both successes and failures as learning examples;
- Making time to improve daily work processes;
- Providing opportunities for long-term employee growth; and
- Rewarding calculated risks.
Quiz Yourself!
1. What do you call a technique or methodology that reliably leads to a desired result?
Answer
2. What do you call the collection of values, beliefs, ethics and attitudes that characterize an organization and guide its practices?
Answer
3. QA is the systematic process of determining whether a product or service meets specified requirements. What does QA stand for?
Answer
4. In IT project management, ________ is an operational philosophy that promotes better communication and collaboration among business owners, IT Operations, software developers, QA testers and InfoSec staff members.
Answer
5. What type of innovation involves a series of small improvements made to a company's existing products, services or processes?
a. incremental
b. innovative
Answer
