project constraint
What is a project constraint?
A constraint in project management is any restriction that defines a project's limitations. For example, a project's scope is the limit of what the project is expected to accomplish.
The three most significant project planning and management constraints are time, cost and scope. They are sometimes known as the triple constraint or the project management triangle or the iron triangle.
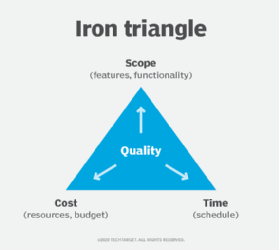
In the project management triangle, dependencies are assumed where making a change to one project constraint will affect one or both of the others. For example, increasing the scope of a project is likely to extend the project timeline and require more money.
That reality is also expressed as the pick two principle. It maintains that for any given set of three desired qualities or expectations -- such as good, fast and cheap -- it is likely that only two can coexist. For example, a product might be delivered quickly and inexpensively, but the quality will suffer.
The 3 most important project constraints
Most of what's involved in a project is defined by its schedule, cost and scope. The project schedule deals with time constraints. It specifies the time frame and time management criteria according to which the deliverables and tasks must be delivered. This includes the final deadline for completion.
Project cost is sometimes stated as resources and finances. Cost constraints involve the financial limitations of the resources allocated to the project budget and the overall limit on the total amount that can be spent. A project's scope involves the goals, deliverables and tasks that define the project.
Other project constraints
In addition to time, cost and scope constraints, other common project issues must be considered in the course of a project lifecycle. These include the following:
- Staffing. The qualifications of potential team members must be considered when assembling a project team. The project lead is a particularly important position, requiring leadership capabilities along with other skills specific to the project. In addition to the project lead, other team members might need special skills, such as expertise in artificial intelligence, to support the project. It might also be necessary to replace a team member if someone becomes unavailable, so maintaining a cadre of suitable backup candidates is advisable.
- Quality. Delivering quality results is a primary requirement for any project. The level of quality assurance should be defined early in the project lifecycle, as quality constraints affect other project constraints.
- Communication. Project team members must communicate regularly with each other, as well as with project stakeholders and senior management. Periodic status reports are essential.
- Benefits. Another important constraint that should be established early in the project lifecycle is defining the benefits of the project. This is another way to define the end game, or the overall results of a project that the project sponsors specified.
- Methodology. The way work is to be performed, or the project management methodology, must be defined up front. It should be periodically reviewed to ensure it's keeping the project on time and within budget and preventing scope creep.
- Risks. Virtually any project, no matter how large or small or complex, has risks that can affect its successful completion. Internal project risks include the potential for loss of staff or funding. External risks are things such as supply chain disruptions and difficulties with project management software. Risk assessment and risk management are key activities to ensure project success.
Managing project constraints
Project constraints are part of all projects. Their management ensures a project's timely completion with the desired quality, functionality and cost management.
The process of managing constraints starts with accepting the fact that constraints exist and play major roles in the project. The following are steps and best practices to deal with the constraints of project management:
- Identify the likely constraints when developing the project plan.
- Establish buffer zones and holding areas that can be used when changes in constraints occur.
- Regularly monitor constraints as part of the overall project management plan.
- Communicate any changes to constraints to the appropriate individuals and teams.
- Manage how tasks are assigned and performed.
- Be prepared to review and modify project constraints when circumstances require changes.
- Have an emergency plan to address unexpected changes to the project.
- Review how project constraints affected the stakeholder and customer satisfaction following its completion.
Find out about five ways to keep IT project planning on track and deal with project constraints.
