deep web
What is the deep web?
The deep web is an umbrella term for parts of the internet not fully accessible using standard search engines such as Google, Bing and Yahoo. The contents of the deep web range from pages that were not indexed by search engines, paywalled sites, private databases and the dark web.
Every search engine uses bots to crawl the web and add the new content they find to the search engine's index. It isn't known how large the deep web is, but many experts estimate that search engines crawl and index less than 1% of all the content that can be accessed over the internet. The searchable content of the web is referred to as the surface web.
Much of the content of the deep web is legitimate and noncriminal in nature. Deep web content includes email messages, chat messages, private content on social media sites, electronic bank statements, electronic health records (EHR) and other content that is accessible one way or another over the internet.
Any website that is paywalled, such as the text of news articles or educational content site that requires a subscription, is also blocked from search engine bots. Fee-for-service sites like Netflix are also not crawled by the bots.
For that reason, there are some advantages to the deep web. For starters, much of the content on the deep web is irrelevant and would only make searches that much more difficult. And there's also a privacy issue; no one would want Google bots crawling their Netflix viewings or Fidelity Investments account.
Deep web vs. dark web
The terms deep web and dark web are sometimes used interchangeably, but they are not the same. The dark web is a segment of the larger deep web and similarly refers to anything on the internet that is not indexed by and, therefore, accessible via a search engine like Google.
While the deep web is full of legal and legitimate content like paywalled publications, databases and academic journals and research, the dark web is much more disreputable. The dark web is the scene of many illegal activities, including black markets for stolen credit cards and personal information, firearms, malware, prostitution, sex trafficking and drugs. Cyber attack services, like access to botnets that can conduct distributed denial-of-service attacks, are also available.
The dark web is full of illegal marketplaces and forums where criminal activity is advertised and discussed. Some examples include Empire Market, Dream Market and Nightmare Market.
One drug dealing website called Silk Road became so famous it was routinely cited as an example of the dark web in mainstream media reports. Its owner was eventually arrested and sentenced to life in prison with no chance for parole.
The only type of illegal products not found on the major dark web markets is explicit child exploitation material. Pedophiles have their own dark web sites and forums separate from the places where cocaine and credit cards are sold.

How to access the deep web
Although the deep web's information isn't indexed by regular search engines, it can often still be accessed.
Accessing content on the deep web is relatively safe, and most internet users do it all the time. Logging into Gmail or LinkedIn, or signing in to the Wall Street Journal are just a few examples of accessing data on a deep web site.
User accounts on the deep web contain a lot of personal information that criminals might value -- that's why access to much of the deep web is restricted.
The deep web, including the dark web, will never come to users. Spam and phishing attacks may originate from a dark web marketplace, but a user has to download something infected from that marketplace to release malware. An attack would not originate from the dark web site itself.
The dark web is intentionally hidden and requires specific technologies -- like the Tor browser and the Invisible Internet Project (I2P) network -- to gain access. Both tools have legitimate uses. Tor will protect your IP when visiting websites and I2P is a proxy network that can help journalists reporting from dangerous territories.
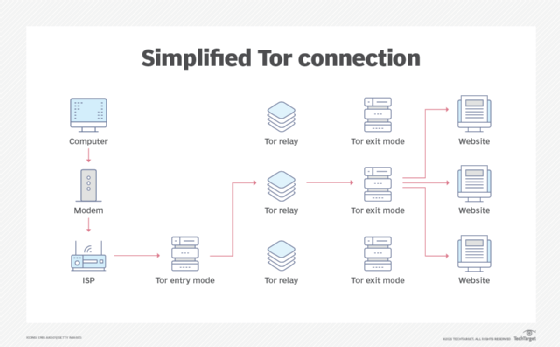
Users cannot access a dark web marketplace without the Tor browser. And while it's based on the Mozilla Firefox browser, Tor is not as well maintained and has page rendering issues.
There is one legitimate reason to peruse the dark web. With all the discussions related to hacking and exploit trading on the dark web, it is a great place to see where yet-unknown vulnerabilities are being discussed. By monitoring the dark web, users might gain the advantage of knowing where exploits are before they become widespread threats.
