historical data
What is historical data?
Historical data, in a broad context, is data collected about past events and circumstances pertaining to a particular subject.
By definition, historical data includes most data generated either manually or automatically within an enterprise. Sources, among a great number of possibilities, include press releases, log files, financial reports, project and product documentation and email and other communications.
How is historical data used and why is it important?
In a business context, historical data is used to make important strategic decisions about the present and future. Managers use historical data to track organizational performance over time, identify areas of improvement and make predictions about future trends.
Businesses are collecting more data than ever and often storing it for longer, both for their own purposes and to satisfy compliance requirements.

Historical data can answer important questions such as the following:
- What were our sales last quarter?
- How many customer complaints did we receive last year?
- How has our website traffic changed over the past six months?
Organizations should have a plan in place for collecting, storing and managing historical data. This will ensure that historical data is available when needed and can be easily accessed and analyzed.
How is historical data stored?
Historical data can be stored in a variety of ways, including databases, spreadsheets and text files. It is important to choose a storage method that is efficient and scalable so historical data can be easily accessed and analyzed.
When choosing a storage method for historical data, it is important to consider the following questions:
- How much data will need to be stored?
- How often will the data need to be accessed?
- Who will need to access the data?
- What type of analysis will be performed on the data?
There are many options available for storing historical data. The best option for a particular organization depends on the specific needs and requirements.
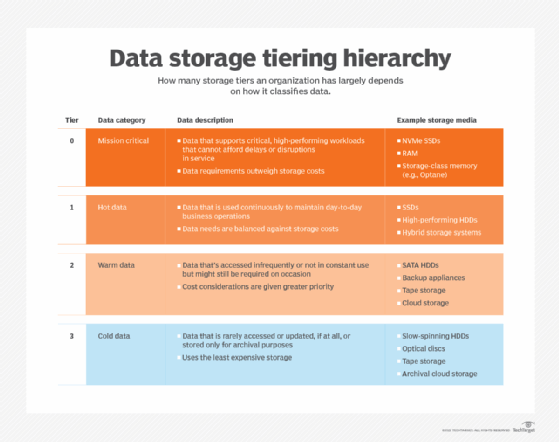
Storage capacities have increased significantly in recent years and cloud storage has taken much of the burden of storage administration from many enterprises.
However, for large organizations with strict compliance requirements and privacy controls there are also options to store historical data in a private server or data center.
How long should you retain historical data?
The answer to this question depends on the organization and the type of data being collected.
Some organizations are required by law or regulation to retain historical data for a certain period of time. For example, businesses in the financial services industry are subject to Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) rules, which require the retention of business records for varying lengths of time depending on the type of record.
Other organizations may have internal policies for how long historical data should be retained. For example, a company may keep financial records for seven years or customer service records for five years.
It is important to consult with legal and compliance teams to determine how long historical data needs to be retained. Once a decision has been made, it is important to have a plan in place for how historical data will be stored and managed over time
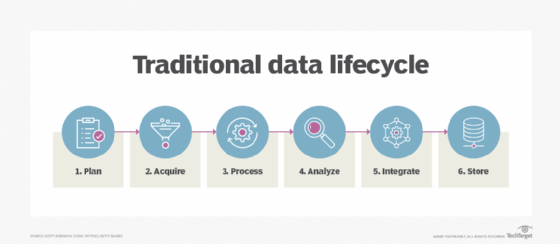
Because data storage requires resources to maintain, data lifecycle management (DLM) is recommended to ensure that data is not maintained without good reason or for longer than necessary and that it is properly archived or disposed of as appropriate.
Learn how to develop and implement a data storage plan, explore 2 storage tiering strategies for modern media and see how to effectively plan cloud storage scalability.