memristor
What is a memristor?
A memristor is an electrical component that limits or regulates the flow of electrical current in a circuit and remembers the amount of charge that has previously flowed through it. Memristors are important for many real-world applications. One reason is that they are non-volatile, meaning that they retain memory without power, enabling extended use even if power is unavailable or goes out.
The term memristor is a combination of the terms memory and resistor. It is a non-volatile electronic memory device for which resistance can be programmed and then stored. This characteristic makes memristors useful for data storage.
Also, because memristors are non-volatile, they remember their resistor state even if they lose power. Memristors are an attractive memory option for a number of reasons, including the following:
- They work faster than many solid-state storage technologies.
- They require less energy to operate.
- Depending on the design, they can store a lot of data in a small area.
- They are immune to the damaging effects on memory of radiation.
What does a memristor do?
A memristor is a passive circuit element, like resistors, capacitors and inductors. That said, unlike other passive elements, memristors are nonlinear devices since the relationship between current and voltage is not a simple straight line but rather a curve. Also, since the memristor cannot amplify signals or inject power into circuits, it is unlike active elements, such as transistors.
Memristors provide a memory solution that combines the best of RAM and flash memory. RAM offers fast data access but loses data if power is lost. Flash memory devices, like USB drives, are non-volatile and can store information when not powered. However, they work slower than RAM. Fast, reliable, non-volatile memristors provide the benefits of RAM and flash memory without the associated drawbacks.
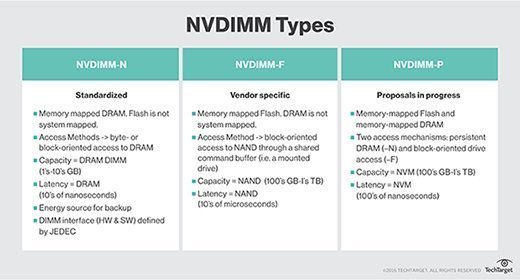
Memristors, which are considered to be a subcategory of resistive RAM, are one of several storage technologies that have been predicted to replace flash memory. If the storage hierarchy could be flattened by replacing dynamic RAM and hard disk drives with memristors, it would theoretically be possible to create analog computers capable of carrying out calculations on the same chips that store data.
Memristor structure
Memristors have a simple structure. A single device consists of two metal electrodes with a thin metal-oxide film -- often titanium dioxide -- between them. Unlike a resistor that has a fixed resistance, a memristor has voltage-dependent resistance. That means that, by restricting the amount of oxygen available and by supplying current-carrying, negatively charged mobile electrons, it is possible to change the material's resistance.
The memristor's material must have a resistance that can reversibly change with voltage. The resistance can either increase or decrease by changing the polarity of the applied voltage. In other words, the memristor's resistance depends on the charge flowing through it. The changing resistance gives the device its memory properties and enables it to hold data.
How does a memristor work?
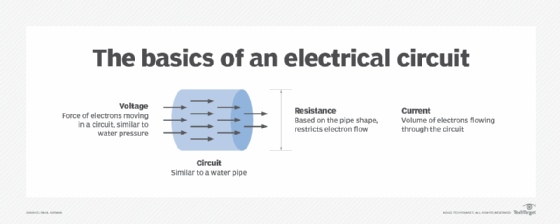
A memristor is often compared to an adjustable pipe that carries water. When the water flows in one direction, the pipe's diameter expands and enables the water to flow faster, but when the water flows in the opposite direction, the pipe's diameter contracts and slows down the water's flow. If the water is shut off, the pipe retains its diameter until the water is turned back on.
When a memristor's power is shut off, the memristor retains its resistance value. This means that, if power to a computer were cut off with a hard shutdown, all the applications and files that were open before the shutdown would still be available when the computer was restarted.
History of memristors
The original concept for memristors was conceived in 1971 by Professor Leon Chua at the University of California, Berkeley in his paper, "Memristor -- The Missing Circuit Element." According to Chua, a memristor is a nonlinear, passive, two-terminal electrical component that linked electric charge and magnetic flux. He framed his theory in terms of equations about electric circuits that link four quantities: voltage, current, charge and magnetic flux. However, he didn't explain the structure or material of the as-yet nonexistent memristor.
It wasn't until 2008 that scientists at HP Labs built the first working memristor by applying Chua's theories in the real world. They did so by changing the resistance between a conducting and a less-conducting state in a thin-film device.
This device consisted of two metal electrodes separated by a thin film of an electric metal-oxide insulator called titanium dioxide, or titania. When voltage is applied to the device's terminals, an electric current flows through it. The movement of this current through the titania film alters the device's overall resistance and gives it a memory that enables the device to store data.
Since those early days, the definition of memristor has been broadened to include any form of non-volatile memory that is based on resistance switching, which increases the flow of current in one direction and decreases the flow of current in the opposite direction.
New memristors are now available that offer the following:
- High levels of endurance.
- High levels of retention.
- Ultra-high-density crossbar arrays.
- Nanometer-level scalability, meaning a thin film and a small memristor.
Explore the differences between flash memory vs. RAM.
