What is a uniform resource identifier (URI)?
A uniform resource identifier (URI) is a character sequence that identifies a logical (abstract) or physical resource -- usually, but not always, connected to the internet. The strings of characters incorporated in a URI, such as a scheme name and a file path, serve as identifiers.
URIs can identify different types of resources, including the following:
- Electronic documents.
- Webpages.
- Images.
- Information sources with a consistent purpose.

A uniform resource locator (URL), or web address, is the most common form of URI. It is used for unambiguously identifying and locating websites or other web-connected resources.
What is the purpose of a URI?
URIs distinguish one resource from another; they matter most on the world wide web. URIs enable internet protocols to facilitate interactions between and among resources such as binary data, photos, videos, and text.
URIs label each of these resources. This then allows internet protocols to identify the resources that need to be fetched so users can access them as they browse the internet.
Besides identifying and fetching web resources, URIs are also used in the following cases:
- A user opens an email client.
- A user wants to send text messages.
- JavaScript is to be executed.
What is an example of a uniform resource identifier?
A URI is merely a sequence of specific characters that identify a particular resource on the internet. These characters change depending on the resource type.
For example, a URI that specifies access to a remote computer can look like this:
telnet://192.0.2.16:80
However, a URI that specifies an e-book on the TechTarget website might look like this:
http://www.techtarget.com/ white-paper-ebook/educating-customers-on-genai-using-content-to-build-engagement-for-ai-enhanced-services/
A blog'sblog's URI could take the form:
https://www.techtarget.com/blog/this-is-the-blog-title
A URI can also specify a phone number:
tel:+1-617-431-XXXX
Or it might specify an email address:
mailto: [email protected]
What is a file URI?
A file URI is used to identify a file on a host computer. It always has this syntax:
file://host/path
Here, host refers to the fully qualified domain name of a system. If the host name is not specified, it is assumed to be localhost. This refers to the system on which the URL is being interpreted. The URI can also contain an empty hostname.
The path is a hierarchical directory path and refers to a file's location on that system. In the URI syntax, a single slash always separates the host name and path name. no host name is specified, the URI syntax will be file:/path. If the directory includes subdirectories, they can be included in the syntax with additional slashes.
Here are some examples of file URIs:
- In UNIX: file://localhost/etc/fstab.
- In Windows: file://localhost/c:/WINDOWS/clock.avi.
How uniform resource identifiers work
A URI provides a simple, extensible way to identify internet resources. Since they provide uniformity, different types of resource identifiers can be used in the same context, regardless of the mechanisms used to access those resources. The resource identifiers can also be reused in different contexts.
Suppose a user wants to access an e-book on www.techtarget.com via a browser like Google Chrome. The e-book is associated with a specific URI. Here's how it will work:
- The user enters into Chrome's address bar the URI: https://www.techtarget.com/white-paper-ebook/educating-customers-on-genai-using-content-to-build-engagement-for-ai-enhanced-services/.
- Chrome will identify the various components of the URI.
- Chrome will send a request to the TechTarget server.
- The server will display the resource content on the user's device.
In this case, the resource is an e-book so the user will see a form like Figure 1 to download it.
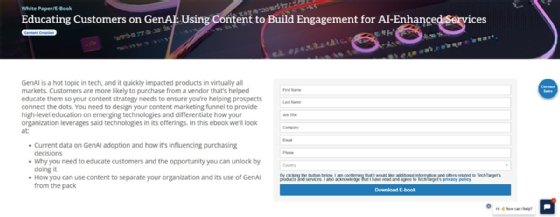
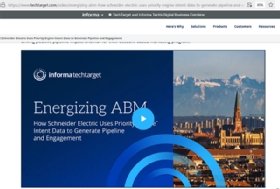
If the required resource is a video, its URI will be different. However, the way it works will be the same. When the server fetches the resource, it will be displayed on the browser screen as shown in Figure 2.
Uniform resource identifier syntax
The generic form of any URI scheme is:
scheme://authority:port/URL path?URL query#URL fragment
Most URIs contain some or all of these elements: scheme name, authority, file path, query, and fragment. In the TechTarget e-book example, the syntax can be broken down in the following way:
- Scheme: http://.
- Authority: www.techtarget.com.
- URL path: white-paper-ebook/educating-customers-on-genai-using-content-to-build-engagement-for-ai-enhanced-services/.
In the URI, the file path may be empty. As long as the scheme name is provided, the URI will do its job of distinguishing one resource from another. In addition, port, query, and fragment are optional components. They are not visible in the TechTarget ebook URI.
Here is a breakdown of the primary elements of a URI.
Scheme (not optional)
Within the URI, the first element is the scheme name. Schemes are case-insensitive and separated from the rest of the object by a colon. The scheme establishes the concrete syntax and indicates which protocols the browser must use for that URI.
Ideally, URI schemes should be registered with Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) although nonregistered schemes can also be used.
Example:
If the URI is telnet://192.0.2.16:80, the scheme name is "telnet."
Authority (not optional)
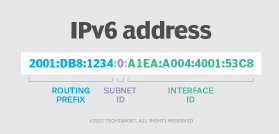
The URI's authority component is composed of multiple parts: a host consisting of either a registered name or an IP address, an optional authentication section and an optional port number.
The authentication section contains the username and password, separated by a colon, and followed by the symbol for at (@). After the @ comes the hostname, followed by a colon and then a port number. IPv4 addresses are commonly in a dot-decimal notation, and IPv6 addresses, which need to be in brackets, are typically in hexadecimal form.
The path containing data is notated by a sequence of segments separated by slashes. These slashes imply a hierarchical structure. The path begins with a single slash, whether or not an authority is present. However, the path cannot start with a double slash. This part of the syntax might closely resemble a particular file path but does not always imply a relation to that file system path.
In the previous URI example (telnet://192.0.2.16:80), a scheme name is present. The numbers after the double slash constitute the authority. Because no characters come after the slash, it indicates that the path is empty.
In the case of web resources, the authority is the URI's host name or domain name (website). It can also be an IP address. It indicates which web server is being requested.
Path (not optional)
The URI path is the specific location of the requested resource on the domain'sdomain's web server. It may look something like this: file:///C:/Users/Blogs/Documents/ revolutionizing-content-with-intent-driven-insights/.txt.
Here, everything after "file:///" points to the specific document.
Query (optional)
The query contains a string of nonhierarchical data. It is often a sequence of attribute-value pairs separated by a delimiter, such as an ampersand (&) or semicolon. A question mark separates the query from the part that comes before it.
The string represents some operation applied to a queryable object by the URI.
Example:
In the URI foo://techtarget.com:8042/over/there?name=parrot#beak, the query is "name=parrot#beak".
However, because this part of the syntax is optional, it might not always be present.
Fragment (optional)
The fragment contains an identifier that provides direction to a secondary resource. A hash (#) separates it from the preceding part of the URI.
If the primary resource is a Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) document or article, the fragment can be an ID attribute of a specific element of that resource. In this case, a web browser will scroll this particular element into view.
However, if the fragment ID is void, it indicates that the URI refers to the whole object. In this case, the hash sign might be omitted.
Port (optional)
A URI can also include a port number. However, this is usually omitted if the web server uses the standard ports of the HTTP (80) or HTTPs (443) protocol. If other ports are used, they must be specified for the browser to be able to fetch the required resources.
The need for a universal syntax
Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the world wide web, first documented URIs in June 1994 in Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) RFC 1630. In creating this document, Berners-Lee's main goal was to define a universal syntax for identifying and accessing objects on the world wide web.
According to Berners-Lee, multiple protocols and systems are used for document search and retrieval. To enable global access of these documents, even with different data formats, a universal set of names and addresses in all name spaces is essential. This set will allow the object names in different spaces to be treated in a common manner, allowing the access of those objects using both existing and future/proposed protocols. It was this aim that led to the development of URIs.
Today, URIs and their generic syntax are defined in the IETF RFC 3986. Published in January 2005, RFC 3986 defines the generic URI syntax for the internet and security considerations for using URIs on the internet. RFC 3986 uses the term resource in a general sense, which means resources identified by URIs do not have to be accessible on the internet.
Uniform resource identifier resolution and references
Two additional aspects of URIs are resolution and references.
URI resolution is one of a few common operations performed on URIs that are also URLs. It involves determining the proper data access method and parameters needed to locate and retrieve the resource the URI represents.
A URI reference is used to determine common usage for a URI and might appear as a full URI, part of a full URI, or an empty string. If there is a fragment identifier, it will identify part of the resource referred to by the rest of the URI.
A URI reference can be a URI and a relative reference. In this case, the URI reference's prefix does not match the syntax of a scheme followed by its colon separator. To determine which components are present and whether the reference is relative, each of the URI components is parsed for its subparts and validation.
Types of uniform resource identifiers
URLs, uniform resource names (URNs) and uniform resource characteristics (URC) are three types of URIs.
Uniform resource locator (URL)
A URL is used to identify and locate webpages.
A URI identifies a resource but does not imply or guarantee access to it. A URL, however, identifies the resource and specifies how it can be accessed or where it is located. This is why a URL contains unique components, such as the protocol, domain and/or subdomain, and other URI components.
A URL is a subset of URIs. This means all URLs are URIs. However, not all URIs are URLs. A URL begins by stating the protocol that should be used to access and locate the logical or physical resource on a particular network. Therefore, the following applies to URLs:
- If the resource is a webpage, the URL starts with the protocol HTTP or HTTPS.
- If the resource is a file, the URL begins with the protocol FTP.
- For an email address, the URL starts with the protocol "mailto."
A URL is a location-dependent URI that may or may not be persistent. This means that if the resource's location changes, the URL also changes to reflect and point to the new location.
URL examples:
- https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/URI-Uniform-Resource-Identifier.
- https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc3986.
- https://www.w3.org/Addressing/URL/uri-spec.html.
Uniform resource name (URN)
Like a URL, a URN identifies a resource. But unlike a URL, a URN is location-independent and persistent, meaning it always identifies the same resource over time. A URN continues to persist even when the resource no longer exists or becomes unavailable.
A URN does not state which protocol should be used to locate and access the resource. Instead, it labels the resource with a persistent, location-independent and unique identifier.
A URN has three components:
- The label "urn."
- A colon.
- A character string as the unique identifier.
URN examples (provided by IETF RFC 2986):
- urn:oasis:names:specification:docbook:dtd:xml:4.1.2.
- urn:example:animal:ferret:nose.
Uniform resource characteristics (URC)
URCs are metadata that describe a particular resource. This metadata usually takes the form of attribute/value pairs. It might refer to various properties of a resource, such as the following:
- Author name.
- Publisher name.
- Encoding.
- Copyright status.
- Access restrictions.
Readable by both humans and computers, URCs are meant to describe a resource to represent its knowledge.
URI vs. URL
Although often used interchangeably, the terms URI and URL are different. A URI identifies a specific resource, while a URL is a special type of URI that both identifies a resource and specifies how it can be accessed. In other words, URIs are resource identifiers, while URLs are resource locators.
The analogy of a person's name and address can explain this difference. In this case, the name would be like the URI because it identifies the person. However, it doesn't explain how the person can be found or where they live. For this, the address is required, just as a URL would be when talking about resources on the internet.
Moreover, a URI can be used to identify and differentiate from each other various types of files and resources, including HTML and Extensible Markup Language (XML). However, URLs can only be used to identify and locate webpages and resources. If a protocol, such as FTP or HTTPS, is present or implied for a domain, it is called a URL, even though it is also a URI.
These differences notwithstanding, URIs and URLs have one important commonality: syntax. Like URIs, URLs also include a scheme (protocol), domain and path. The other sections, like query and fragment that are optional in URIs, are also optional in URLs.
Networking enables the internet to function, relying on several key protocols. These essential network protocols facilitate communication and connection across the internet. Learn about the common network protocols and their functions.