CAVE (Cave Automatic Virtual Environment)
What is CAVE?
CAVE (Cave Automatic Virtual Environment) is a virtual reality (VR) environment consisting of a cube-shaped VR room or a room-scale area in which the walls, floors and ceilings are projection screens. The user may wear a VR headset or heads-up display and interacts through input devices such as wands, joysticks or data gloves.
In a CAVE system, room-sized computer graphics, motion-tracking technology and stereoscopic displays create an immersive virtual reality environment for one or more users. A CAVE is contained within a larger room that is completely dark when in use.
Three-dimensional (3D) images within the VR CAVE appear to float in mid-air. The viewer's headgear is synchronized with the projectors, and they can walk around an image to study it from all angles. Sensors within the room provide a tracking system to monitor the viewer's position and align the perspective correctly.

How CAVEs work
VR rooms are one way to deliver a virtual reality experience. A newer technology, room-scale VR, uses hardware and software to provide a VR experience within a cleared area.
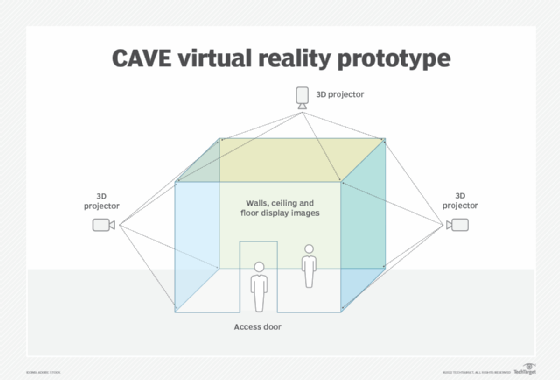
Figure 1 below is a prototype of a CAVE that could serve as an electronic visualization laboratory. Its walls, ceiling and floor are covered in material that can display images and computer graphics that various rear-projection systems, overhead lights and other display technologies generate. In this environment, VR glasses might not be required, depending on the experience and technology used. External to the room is a control device, such as a laptop computer with VR software, to prepare and deliver the program.
Speakers can be used inside or outside the CAVE. A haptic system can also be used to provide touch or tactile sensation and make the immersive environment even more real.
What are the benefits of CAVE technology?
CAVE VR environments can be entertaining and useful when demonstrating technology to senior management or products to customers. They are used in various contexts, including training surgeons and call center reps.
VR systems provide the following benefits:
- Data analysis. They make data visualization easier to understand in real time.
- Immersion. A participant's entire body and consciousness are engaged in the information delivery process.
- Detailed view. High-resolution, 3D images, simulations and displays enhance the level of detail provided. This is particularly useful in product development and research.
- Ease of use. Realistic experiences are possible without using devices like VR head-mounted displays.
- Enhanced data. The systems can capture interactions among project team members or with customers, including body language, eye motions and other physical indicators of how they perceive the experience.
The origin of CAVE technology
A research team led by Carolina Cruz-Neira, Daniel J. Sandin and Thomas A. DeFanti developed the first CAVE at the University of Illinois at Chicago. They demonstrated it at the 1992 SIGGRAPH conference.
Today, CAVEs are used for research in a range of disciplines, including archaeology, architecture, art, biology, engineering, geometry, geology, medicine and healthcare, meteorology and physics.
Many universities have CAVEs. In May 2007, researchers from the University of Calgary in Alberta, Canada, created the CAVEman, the first 4D human atlas. 4D includes the three spatial dimensions plus time, which enables researchers to simulate the progression of a disease or the effects of a treatment over time.
Because the word cave appears in the name, CAVE is what is called a recursive acronym. The name alludes to Plato's allegory in which prisoners confined to a cave interpreted external events from the shadows and echoes experienced within the cave. Most interpretations of the allegory center around the idea that our perception of reality is not reality but rather a construct of reality created by our minds.
Into the future: The Star Trek CAVE
Anyone who has watched the science fiction TV series Star Trek:The Next Generation has probably seen the holodeck. This fictional holographic simulation room is potentially a futuristic use of CAVE technology. When entering the Star Trek holodeck, at least one participant must describe the desired virtual world scenario to the ship's computer, which then processes the requirements into a 3D visualization experience.
The fictional system goes beyond projecting images onto screens and viewing them. USS Enterprise crew members can interact with one another and with simulated 3D participants that have all characteristics of live beings. And just like individuals leaving a VR room, people in the holodeck must tell the ship's computer to end the simulation to end the experience.
See how some organizations are using virtual reality technology today.
