augmented reality gaming (AR gaming)
What is augmented reality (AR) gaming?
Augmented reality gaming (AR gaming) is the real-time integration of virtual game elements with the physical environment of the player. Augmented reality games detect the real world and then overlay game visuals and audio using sensors such as cameras, microphones and global positioning system (GPS). Mixed reality (MR) and extended reality (XR) gaming takes this a step further by allowing for real-time feedback between the physical environment and the game.
Augmented reality gaming vs. virtual reality gaming
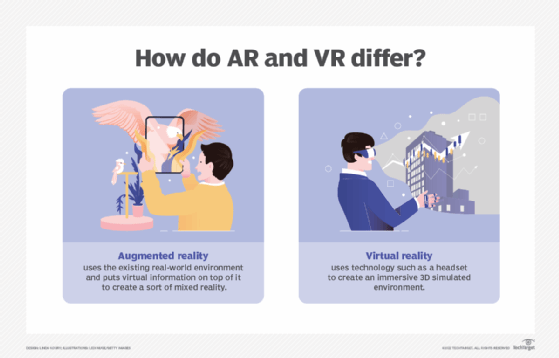
The main difference between virtual reality (VR) games and AR games is that in virtual reality, the user is visually cut off from the real world, whereas in AR, the user can still see and navigate real-world locations. This means that VR requires a dedicated headset as well as a clear playing space.
AR games can be played from a smartphone or a dedicated headset. A headset can provide a fully immersive experience by displaying game visuals in three dimensions from the player's point of view. These high-fidelity headsets, primarily the Microsoft HoloLens and the Meta Quest Pro, are currently expensive and in short supply. Because it does not require expensive dedicated hardware, smartphone-based AR gaming is much more popular. These games, however, are much less immersive, frequently simply overlaying some simple game graphics over a live camera feed while tracking location with GPS and other sensors.
Examples of augmented reality gaming
An early AR game is Zombies, Run! which was released in 2012. It would use audio cues based on GPS data to give runners out in the real world scores and the feeling of being chased.
The first AR game with broad appeal was Ingress made by Niantic Inc. It used OpenStreetMap data and the user's GPS location to allow players to capture or defend real-world points of interest.
Pokémon Go was released by Niantic in 2016 and became a major hit, propelling AR gaming to a mass market audience. Pokémon Go took the location and capturing concepts proven by Ingress and added the popular Pokémon franchise intellectual properties (IP) and a live view of the real-world camera with the fantastical element of a Pokémon in it. The popularity of Pokémon Go has led to the release of other AR games, such as Angry Birds AR: Isle of Pigs, Harry Potter: Wizards Unite and Jurassic World Alive.
Gamification may be used in augmented reality games to encourage healthy behaviors. For instance, incorporating a score and obstacles to overcome into a workout session.
In AR gaming, QR codes or fiducial tags can be used to anchor virtual objects to the real world. These can inform the game about the correct location, rotation and scale of the scene, allowing it to apply computer graphics in a realistic manner. For example, a card game may have markers on it so that when viewed through the game app, the characters appear to be standing on the cards in 3D.
Mixed reality gaming
Mixed reality (MR), also known as extended reality (XR) or hybrid reality in gaming, is augmented reality taken to the next level, with full real-time interaction between the game and the real world. In an AR game, if the player reached out to physically touch the virtual element, the game would not react and the person's hand would pass through; in an MR game, the virtual element may move or be knocked by the person's hand.
Because the real world is so messy and difficult for a computer to understand, mixed reality gaming is currently very limited. It is hoped that as machine vision, artificial intelligence (AI) and hardware become more available and capable, meaningful MR implementation will become easier.
Imagine a simple augmented reality game based on the children's pastime of "the floor is made of lava." The game would designate which areas of the floor were safe to walk on and which were not. AR would be unable to take into account real-world furniture or other objects. An MR game, for example, could recognize if a pillow was placed on the floor to create a safe place to step. While this is simple for a human to understand, it is difficult for a computer to distinguish between a pillow and the floor. Not to mention the various types of floor covering, pillow patterns or the use of a blanket instead of a pillow.
Future of augmented reality gaming
The wild success of Pokémon Go has demonstrated that the public is willing to engage in AR gaming. But current limitations in smartphone and headset technology limit augmented reality games.
Mobile processors and displays are expected to become more capable, and high-speed 5G internet will allow large amounts of data to be streamed to support high-fidelity AR gaming. The next generation of VR headsets, including a potential Apple headset or Magic Leap 2, may also have broad market appeal, introducing AR games to a new audience.

See how AI and augmented reality blur lines between virtual and reality and the benefits of immersive learning with AR and VR.
