digital footprint
What is a digital footprint?
A digital footprint -- sometimes called a digital shadow -- is the body of data that an individual creates through their actions online. Almost every online activity leaves some form of digital trace.
A digital footprint is relatively permanent, and once the data is public -- or even semipublic, as may be the case with social media -- the owner has little control over how it is used by others. For that reason, a major focus of digital footprint management is caution about online activities to control the data that can be gathered in the first place.
What are the consequences of a digital footprint?
Digital footprints are visible to a variety of entities, including the following:
- data brokers
- advertisers
- phone carriers
- internet providers
- employers
- cybercriminals
- hackers
- peers
- co-workers
A digital footprint helps people online identify the person that it belongs to. There are several effects of having a visible online identity, including the following:
- Access control. Providing information online lets users gain access to different applications and services. For example, people can use their email address, name and other information about them to create social media accounts, log in to a banking application or subscribe to an online publication.
- Online reputation. The information a person posts, says or otherwise leaves online influences how others perceive them. Seeing someone's browsing history, likes on social media platforms or online shopping history provides information about their personality and interests. This is often a benign consequence of digital footprints, but a visible reputation can be bad if the digital traces reflect poorly on the person. For example, an employer might see a derisive social media post that somebody made and choose not to hire that person.
- Targeted advertising. Marketers can use someone's digital footprint to market to that person based on their digital twin or digital identity. An internet user leaves digital traces that provide preference insights. Behavioral targeting uses these inferences to feed the user advertisements.
- Hacking. A hacker could use information from a user's digital footprint to exploit them through identity theft or attack other computer systems. Exposed usernames and passwords could give hackers access to user accounts, and visible email addresses could be used to construct spear phishing campaigns.
These negative consequences can affect entire companies, as well as individuals. Companies need to manage their digital footprint and be aware of how their employees represent themselves online by doing the following:
- identifying internet-facing infrastructure to determine the contents of the attack surface;
- auditing the assets contained in internet-facing infrastructure; and
- performing standard security processes, such as vulnerability testing and patch management.
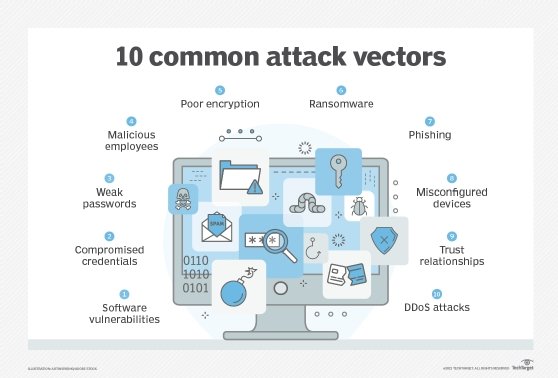
Types of digital footprint
Digital footprints are broken down into two types:
- Active digital footprints consist of data a user leaves intentionally. The user is also aware of the digital trace they leave behind because they have deliberately submitted information. An example of this would be a social media post or phone call. In both cases, they leave a digital history that they are aware of.
- Passive digital footprints are composed of data a user leaves behind unintentionally on the internet. Website visits and actions, searches and online purchases are among the online activities that add passive data traces to a digital footprint. Passive footprints are harder to track and manage because they can be collected without user consent. When a hacker collects data about a targeted system, it is known as footprinting.
Examples of digital footprint
Virtually any data that can be associated with a person's identity can be included in their digital footprint.
Examples of data that could be included in a digital footprint are the following:
- biometric data
- geolocation data
- IP addresses
- Yelp reviews
- passwords and login information
- subscriptions
- health information
- fitness data
- phone numbers
- license plate numbers
- social posts
- phone calls
- email addresses
- usernames
- passwords
- search history
- sensor data
- payment details
- credit card numbers
- downloads
- purchase history
- cookies
- images from surveillance devices
Activities that can generate data that appears in a digital footprint include the following:
- online banking
- social media
- reading the news
- fitness trackers
- health care apps
How to reduce digital footprint
Oversharing online is the easiest way to create an unmanageable digital footprint. To reduce a digital footprint to a more manageable size and protect their information, users can do the following:
- Check footprint online. Users can search their own names on Google or another search engine to see what comes up. Have I Been Pwned is another service that tells users if their sensitive data is public.
- Delete old accounts. Old social media accounts hold information that may not reflect the user anymore.
- Share only what is necessary. Avoid oversharing on social media -- even in more private social media features, such as messenger apps. Think of posting anywhere on social as permanently publishing something. Even after deleting, there is still a record of the post somewhere.
- Use a virtual private network (VPN). A VPN can help protect digital footprints by masking IP addresses and making online activity harder to trace.
- Visit secure websites. Websites with encryption add an extra layer of safety and online privacy while browsing. Users can tell a website is secure by looking at the URL to see if it begins with https rather than http.
- Adjust application privacy settings. Go through application privacy settings to opt out of settings that share more information than desired.
- Compartmentalize business and personal accounts. If possible, try and use separate accounts to limit visibility at work and control online perception.
- Practice cyber hygiene. Learn how to avoid common phishing or malware attacks that could proliferate personal data. Regularly clean up and back up data to avoid data breaches.
Background checking tools
Employers can use a variety of tools to check someone's background. A few examples are the following:
- MOSINT. MOSINT is an open source intelligence (OSINT) tool for email addresses. It lets the user gather information about a given email. Employers can use MOSINT to verify if an email exists and find related domains, social accounts, phone numbers and pastebin information.
- Nexfil. Nexfil lets employers find profiles by username on the web. An employer can enter the username and scan the internet for accounts with matching usernames.
- Maigret. Maigret is another OSINT tool that companies can use to find websites associated with a particular username.
While individuals would generally be concerned with managing their own digital footprint, enterprises have multiple identity types to consider. Learn how companies manage three types of digital identity on the internet in their cybersecurity strategies.