logical implication
What is logical implication?
Logical implication is a type of relationship between two statements or sentences. The relation translates verbally into "logically implies" or the logical connective "if/then" and is symbolized by a double-lined arrow pointing toward the right (=>).
In logic, implication is relationship between different propositions where the second proposition is a logical consequence of the first. For instance, if A and B represent semantic statements, then AB means "A implies B" or "If A, then B." The word "implies" is used in the strongest possible sense.
How does logical implication work?
As an example of logical implication, suppose the sentences A and B are assigned as follows:
A = The sky is overcast.
B = The sun is not visible.
In the above example, AB is a true statement, assuming we are at the surface of the earth, below the cloud layer. However, the statement BA is not necessarily true because it might be a clear night. In this case, logical implication does not work both ways. However, the sense of logical implication is reversed if the negation of both statements is used. That is, (AB) = (-B-A)
Using the above sentences as examples, we can say that if the sun is visible, then the sky is not overcast. This conditional statement is always true. In fact, there is logical equivalence between the two statements AB and -B-A.
How is logical implication used?
Use of logical implication is important when determining how a system processes data and generates responses when inquiries are introduced. When designing a system, it is important to identify the following logical operations:
- how the system should process data;
- how data analytics should be applied; and
- how the system should arrive at decision points.
This typically means that flow diagrams, decision trees or other mechanisms are used to identify the necessary conditions for how a system should perform.
The way the system handles its duties usually means decisions are being made. The compound statement of the form "if this, then that" implies a decision point in the decision-making process.
Flow diagrams are composed of decision points along with various processes. In a flow diagram, a decision point could have more than one choice, which is where the logical implication process is important. The process also provides a way to test decision points before putting them into a production system.
Why is logical implication important?
Complex systems have many decision points. Each of them must be analyzed and tested to ensure the process flow is efficient and generates the desired results. This is an important way to use logical implication.
When designing a system, the software engineer or developer defines the steps that perform the desired activities using the fewest number of decision points, which are also referred to as logic gates. Typically, the goal is to optimize processing speed while maximizing the system's efficiency and reliability.
How to write a logical implication statement
An implication is based on the "if this, then that" model. A typical statement uses the following format:
A => B
The above is read as "A implies B" and is true when A and B are true, when A is false and B is true, and is false when A is true and B is false. These options are typically included in a truth table.
A flowchart diagram usually starts with a process, such as "Computer won't turn on." A decision point is typically shown in a diamond-shaped box as shown in Figure 1.
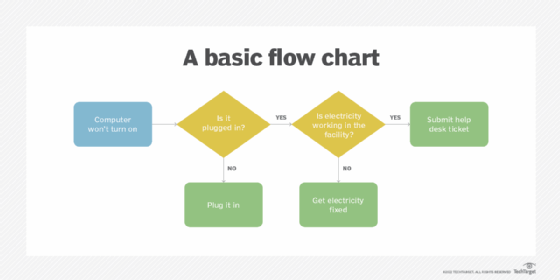
When a process flow reaches a certain point, the logical implication of the various choices must be examined. The decision point then becomes the juncture where the formal logic flow continues to the next process. In the example, those processes would be "Plug it in," "Get electricity fixed" or "Submit help desk ticket."
It's important to understand the term logical implication when working with flowcharts and business process modeling. Learn more about business process modeling notation.
