superconductivity
What is superconductivity?
Superconductivity is the ability of certain materials to conduct a direct electric current (DC) with practically zero resistance. This capacity produces interesting and potentially useful effects. For a material to behave as a superconductor, low temperatures are required.
What is the background on superconductivity?
Superconductivity was first observed in 1911 by H. K. Onnes, a Dutch physicist. His experiment was conducted with elemental mercury at 4 degrees kelvin (approximately -452 degrees Fahrenheit), the temperature of liquid helium. Since then, some substances have been made to act as superconductors at higher temperatures, although the ideal material that can superconduct at room temperature remains elusive.
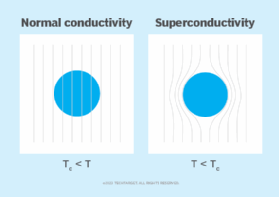
What is the difference between a conductor and a superconductor?
Conductors serve as carriers of electrons that move from one atom to another when voltage is applied, conducting electricity with little to no resistance. Most metals are considered good conductors. Pure elemental silver is one of the best electrical conductors. By contrast, non-metals such as wood do not conduct electricity and may be used as insulators to prevent getting an electrical shock, for example.
Superconductors are characterized by the absence of any kind of resistance to the flow of electrons. The conductive material must, however, be supercooled (e.g., using liquid nitrogen) to very low temperatures (e.g., around -253° C) to eliminate any resistance. The supercooling critical temperature is called the transition temperature and varies by the conductive materials being used.
How does superconductivity work?
When normally conductive elements and compounds with electromagnetic properties are cooled to low temperatures, they display two important properties of superconductors: they present no resistance to an electric current, and they generate a magnetic field. Thus they enter a superconducting state.
Since the discovery of superconductivity, research has identified many materials that can be turned into superconductors. However, the transition temperature varies for each material. A key challenge has been to develop materials that become superconductors at higher temperatures than absolute zero (-273.15° C or -459.67° F). Many materials, both single elements and compound elements, have demonstrated high temperature superconductivity. This makes it easier and more cost-effective to employ superconductors in a variety of applications.
A popular example of superconductivity is a cube or ball of metal floating above a superconductor. Superconductors do not normally like magnetic fields but will produce a field when another magnetic field is present. Assuming the magnetic charge in the cube/ball is opposite that of the superconductor, the two repel each other.
How are superconductors used?
Superconductors have been used in, or proposed for use in, a wide variety of applications. Examples include high-speed magnetic-levitation trains, magnetic resonance imaging equipment, ultra-high-speed computer chips, high-capacity digital memory chips, alternative energy storage systems, radio frequency filters, radio frequency amplifiers, sensitive visible light and infrared detectors, miniaturized wireless transmitting antennas, systems to detect submarines and underwater mines and gyroscopes for earth-orbiting satellites. The Josephson junction and the superconducting quantum interference device use superconductors.
Why is superconductivity important?
As more is discovered about superconductors, their applications will continue to grow in number as well as complexity. For now, scientists continue to grapple with making high-temperature superconductivity feasible. This will help with the design of new superconducting materials for advanced applications in the electric energy field. Since the cost for supercooling can be expensive, high-temperature superconductors will be more economically advantageous.
