
Getty Images
Apple lawsuit history explained
In March 2024, the DOJ filed a lawsuit against Apple, alleging its smartphone market monopoly. However, this isn't the first time Apple has seen legal action.
Apple is one of the most influential and successful technology companies of all time. However, along with this success, Apple has also faced numerous legal challenges.
On March 21, 2024, Apple was hit by an antitrust lawsuit filed by the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) alleging that the company had unlawfully exercised monopoly power with the iPhone in the smartphone market. The DOJ's action is intended to help open up the smartphone market and increase competition.
The 2024 lawsuit isn't the first such legal challenge that Apple has faced over its history as the company has had to deal with multiple lawsuits on a range of issues in the U.S. and in the EU.
What does the 2024 antitrust lawsuit allege?
The DOJ lawsuit alleges Apple violated Section 2 of the Sherman Antitrust Act by monopolizing and attempting to monopolize parts of the smartphone industry. The Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 is one of the foundational pieces of antitrust law in the U.S. and aims to prevent monopolies and encourage competition in open marketplaces.
"We allege that Apple has maintained monopoly power in the smartphone market, not simply by staying ahead of the competition on the merits, but by violating federal antitrust law," stated Attorney General Merrick B. Garland in a DOJ press release.
The 2024 DOJ lawsuit alleges that Apple's strategy relies on exclusionary, anticompetitive conduct that harms both consumers and developers. For consumers, this has resulted in fewer choices, higher prices and fees, lower quality smartphones, apps, and accessories, and less innovation from Apple and its competitors. The lawsuit also alleges that Apple has constructed its technology to extract more money from developers, content creators, artists, publishers, small businesses, and merchants.
Among the specific antitrust issues that the DOJ alleges Apple to be committing are the following:
- Monopoly power. Apple is accused of maintaining monopoly power in the smartphone market by making it harder for people to switch smartphones.
- Cross-platform messaging suppression. Apple is accused of suppressing cross-platform messaging, which has resulted in diminished functionality between iPhones and non-Apple devices.
- Third-party digital wallets and smartwatches limitations. The complaint includes allegations that Apple has limited the functionality of third-party digital wallets and smartwatches, which blocks competitors from the market.
- Blocking mobile cloud streaming services. Apple is also accused of blocking mobile cloud streaming services, which could have provided competition to its services.
- App store restrictions. The lawsuit touches on Apple's App Store restrictions as part of a broader pattern of anticompetitive behavior.
- Lack of interoperability with non-Apple devices. The complaint alleges a lack of interoperability with non-Apple devices, such as smartwatches.
History repeating -- Apple's other lawsuits
The 2024 DOJ antitrust lawsuit is not the first big lawsuit for Apple, and it's not the first time the DOJ has filed antitrust legal claims against Apple.
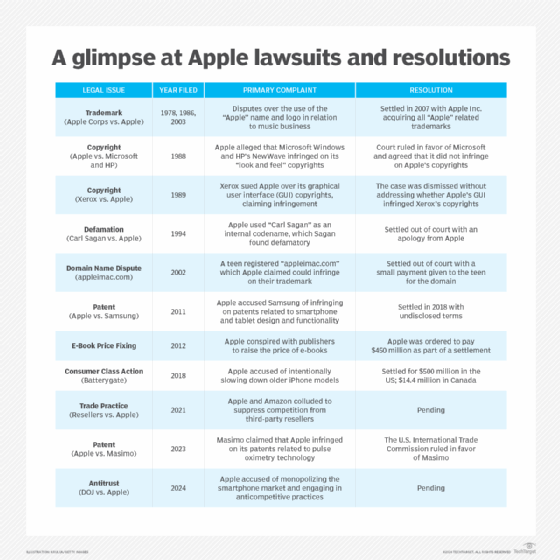
Apple faced two prior antitrust lawsuits from the DOJ. In 2010, the DOJ filed an antitrust lawsuit against Apple and other high-tech companies, including Google, Intel, Adobe, Intuit and Pixar related to work salaries. The lawsuit stated that the companies signed contracts with one another to limit their ability to compete with one another for competent workers, which prevented employees from getting better job opportunities.
Six years later in 2016, the DOJ issued its second antitrust claim against Apple, this time the issue was about e-book price fixing. Apple settled the 2016 case with the DOJ for $450 million in damages.
Apple has also faced consumer lawsuits over its battery health practices for its iPhone and the design of the butterfly keyboard on MacBook laptops which were prone to breaking. Other vendors -- such as Epic Games and Spotify -- have aimed at Apple over anticompetitive issues with the Apple App Store.
The EU has aimed at Apple over App Store issues, specifically related to music streaming.
Antitrust cases
Apple has dealt with multiple antitrust cases including the following:
- Apple iPod, iTunes antitrust litigation. In 2005, the Apple iPod iTunes antitrust litigation was about allegations that Apple committed unlawful acts in the sales of its iPod portable digital music player and online digital music files sold through its iTunes Music Store, in violation of federal and state antitrust laws.
- Apple and AT&T Mobility antitrust class action. Filed in 2007, the primary complaint in this case was that Apple and AT&T Mobility had entered into an exclusive agreement regarding the iPhone, which plaintiffs argued constituted a monopoly that violated antitrust laws.
- European antitrust probe. Starting in 2021, the primary complaint of the EU's antitrust probe was that Apple abused its dominant position in the market for the distribution of music streaming apps through its App Store.
- E-book price-fixing lawsuit. The 2016 e-book price-fixing lawsuit against Apple was centered around the complaint that Apple conspired with five major book publishers to raise the price of e-books.
- Epic Games lawsuit. The primary complaint in the Epic Games 2020 lawsuit relates to Apple's practices in the iOS App Store, which prevents the distribution of iOS apps through any means other than the App Store. The lawsuit also addresses the requirement for in-app purchases on iOS devices to use Apple's in-app payment processor.
Consumer class actions
Consumer class action lawsuits that Apple has faced include the following:
- Technical support class action. This lawsuit, initiated in 2016 as Maldonado v. Apple, Inc., is about allegations surrounding Apple's provision of technical support services under its AppleCare and AppleCare+ plans. Consumers alleged that Apple did not provide the level of service promised by AppleCare.
- iPod battery life class action. The Apple iPod battery life class action lawsuit was filed in the fall of 2003. The primary complaint was Apple misrepresented the capabilities of the iPod's built-in rechargeable battery.
- iPad and iPhone privacy class action. The Apple iPad and iPhone privacy class action stated Apple records users' mobile activity without their consent despite the privacy settings.
- iTunes price-switching class action. The primary complaint in the June 2009 iTunes price-switching class action was that Apple marketed and sold iTunes gift cards through the iTunes store with the promise that consumers could use the gift cards to purchase songs for $0.99 a song. However, after such gift cards were purchased, Apple raised the price of certain songs to $1.29.
- iPhone slowdown class action. Commonly known as "Batterygate," the iPhone slowdown class action was filed in 2018. The primary complaint is that iOS updates on certain iPhone models led to slowdowns and battery degradation.
- Siri eavesdropping class action. In January 2025, Apple agreed to pay $95 million in a class action lawsuit that alleged Apple used Siri to record conversations and share these conversations with advertisers. The lawsuit alleged Apple activated Siri secretly without user command and violated user privacy.
Trade practice
In the trade practice space, Apple faced a 2021 class action lawsuit.
The primary complaint was that Apple and Amazon entered into an agreement that effectively eliminated nearly all Apple resellers from Amazon Marketplace. The lack of competition from third-party resellers on Amazon's marketplace allegedly led to an inflation of iPhone and iPad prices.
Defamation
In the area of defamation, Apple has also faced legal challenges.
The Apple libel dispute with Carl Sagan began in 1994 when he filed a lawsuit. The primary complaint was that Apple had used Carl Sagan's name as an internal codename ("Carl Sagan") for its Power Macintosh 7100 project. The codename was intended as a humorous internal reference to Sagan's catchphrase "billions and billions," suggesting that the product would generate significant revenue for Apple.
In response, Apple changed the codename to BHA for Butt-Head Astronomer. Sagan found this new codename to be defamatory and sued Apple for libel.
Trademark
Apple has also faced numerous legal issues related to trademarks including the following:
- Apple Music trademark cancellation. The Apple Music trademark cancellation dispute involved a legal battle between Apple Inc. and jazz musician Charles Bertini over the use of the "Apple Music" trademark. The lawsuit was filed in 2016 when Bertini, who has used the "Apple Jazz" branding for his concerts since 1985, opposed Apple Inc.'s federal registration of "Apple Music."
- Apple Corps. The Apple Corps trademark dispute with Apple includes a series of legal battles that began in 1978. The primary complaint from Apple Corps, the company founded by music group The Beatles, was that Apple Computer's use of the name "Apple" and its logo infringed on Apple Corps' trademark rights.
Domain name disputes
Apple has faced several domain name disputes over the years, involving various domain names that were seen as infringing on Apple's trademarks.
In 2002, Apple dealt with a dispute over the domain: appleimac.com. In 2005 there was a domain name dispute over the itunes.co.uk domain. Then, in 2012, there was a dispute over the iPhone5.com domain.
Copyright
Apple has been involved in several copyright disputes with a pair of particularly notable ones early in the company's existence.
- Apple vs. Microsoft and Hewlett-Packard. In 1988, Apple filed a lawsuit against Microsoft and Hewlett-Packard alleging that Microsoft Windows and HP violated Apple's copyrights, particularly focusing on the use of overlapping and resizable windows in Windows 2.0.
- Xerox vs. Apple Computer. In 1989, Xerox sued Apple over its graphical user interface (GUI) copyrights, claiming that Apple's GUI infringed Xerox's copyrights.
Patent
Apple has faced several patent disputes over the years involving different technologies and competitors. Among the most notable are:
- Apple vs. Samsung. The dispute began in 2011 with Apple accusing Samsung of infringing on its patents related to the design and functionality of smartphones and tablet computers.
- Apple vs. Masimo. Originally filed in 2023, the dispute with Masimo stated that Apple infringed on Masimo's patents with the blood oxygen sensor technology used in Apple's smartwatches.
How did Apple respond to these lawsuits?
In nearly all cases, some form of settlement has been reached, often involving some form of financial penalty. Here are some notable outcomes.
What the latest lawsuit could mean for the future of smartphones?
If successful, the 2024 DOJ vs Apple antitrust lawsuit could have a profound impact on the future of the smartphone market.
The basis of the legal complaint is that Apple's ecosystem is closed and doesn't promote competition. If the DOJ wins the case, the potential outcome is that Apple will be forced to be more open, enabling significantly more competition in the smartphone market.
Being more open would have an impact on interoperability, especially with messaging. Apple has held a tight grip on its users with the iMessage service and a DOJ win would change that dynamic.
The DOJ's lawsuit also touches on the high fees Apple charges developers for app subscriptions or in-app purchases, which are then often passed on to consumers. Changes to these practices could lead to lower prices for apps and services, making digital purchases less expensive for consumers.
Sean Michael Kerner is an IT consultant, technology enthusiast and tinkerer. He has pulled Token Ring, configured NetWare and has been known to compile his own Linux kernel. He consults with industry and media organizations on technology issues.





