
What is a server?
A server is a computer program or device that provides a service to another computer program and its user, also known as the client. In a data center, the physical computer that a server program runs on is also frequently referred to as a server. That machine might be a dedicated server or it might be used for other purposes.
In the client-server model, a server program fulfills requests from client programs, which might be running on the same computer or other computers. A given application in a computer system might function as a client that makes requests for services from other programs and as a server fulfilling requests from other programs.
How servers work
The term server can refer to a physical machine, a virtual machine (VM) or software that's performing server services. Servers work in various ways, depending on how the word server is being used. Server operating systems (OSes), such as Microsoft Windows Server 2022, typically process client requests for service within the network and facilitate the linkages with the requested resources. Servers configured for specific services handle access to specialized resources, such as printer drivers, or to applications, such as file storage, respectively.
Physical and virtual servers
A physical server is simply a computer that's used to run server software. The differences between a server and a desktop computer are discussed in the next section.
A virtual server is a virtual representation of a physical server. Like a physical server, a virtual server includes its own OS and applications. These are kept separate from any other virtual servers running on the physical server.
The process of creating VMs involves installing a lightweight software component called a hypervisor onto a physical server. The hypervisor's job is to enable the physical server to function as a virtualization host. The virtualization host makes the physical server's hardware resources -- such as central processing unit (CPU) time, memory, storage and network bandwidth -- available to one or more virtual machines.
An administrative console lets admins allocate hardware resources to each virtual server. This drives down hardware costs, because a single physical server can run multiple virtual servers as opposed to each workload needing its own physical server.
Server software
At a minimum, a server requires two software components: an operating system and an application. The OS acts as a platform for running the server application. It provides access to computer networks and to the underlying hardware resources, such as storage devices. It also provides the dependency services the application needs.
The OS makes it possible for the server application to process client requests. For example, the server's Internet Protocol (IP) address and fully qualified domain name are assigned at the OS level.
Cloud servers vs. in-house servers
As with most cloud services, cloud servers provide a flexible and scalable environment. They eliminate the need for floor space and equipment racks to house hardware servers. They can be a cost-effective option for small and midsize businesses. However, organizations lose some control over cloud servers.
By contrast, organizations retain total control over in-house servers and their resources, but in-house servers also require space to house them; heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) facilities; and physical security to prevent unauthorized access to devices. This option is likely to be used for enterprise applications, where dozens or even hundreds of servers are deployed in one or more data centers.
A hybrid configuration, with a mix of on-site and cloud server resources, is another option.
Desktop computers vs. servers
There are similarities and differences between how desktop computers and servers work. Most servers are based on x86/x64 CPUs and can run the same code as an x86/x64 desktop computer. Unlike most desktop and laptop computers, physical servers often include multiple CPU sockets and error-correcting memory. Servers also generally support a far greater quantity of memory than most desktop computers.
Because server hardware typically runs mission-critical workloads, server hardware manufacturers and service providers design servers to support components with redundancy. A server might be equipped with redundant power supplies and redundant network interfaces. These redundant components enable a server to continue to function even if a key component fails.
Server hardware also differs from desktop hardware in its form factor. Modern desktop computers often exist as mini towers, designed to be placed under a desk, or laptop computers with self-contained components. Most servers are designed to be rack mounted. Rack mount systems have a 1U, 2U or 4U form factor, depending on how much rack space they occupy -- for example, a 2U server takes up twice as much rack space as a 1U server.

Another key difference between desktop computers and servers is the operating system. Desktop OSes, such as Windows 10 and Windows 11, might be able to perform some serverlike functionality, but they aren't designed or licensed to take the place of a server OS.
Some Windows 10 and 11 editions include Hyper-V, Microsoft's VM platform. Windows 10 and 11 as well as Windows Server 2022 can run Hyper-V. However, the desktop OSes' hypervisor is intended to be primarily used for development of VMs, whereas the version included with Windows Server 2022 is designed for running production virtual servers.
An organization could conceivably run a virtual server on top of Windows 10 or 11 Hyper-V, but there are licensing issues to consider. Additionally, Windows Server 2022 Hyper-V includes resiliency features that aren't present in the Windows 10 and 11 version. For example, Windows Server 2022 supports VM replication, storage pools deployed from multiple disk systems, and integration with Microsoft Azure for cloud-based recovery and resilience features.
Similarly, Windows 10 and 11 Hyper-V can make files available to devices on a local area network. Windows Server 2022, on the other hand, can be configured to act as a full-featured file server with a Resilient File System to protect data from being corrupted. In large organizations, a Windows Server 2022 distributed file system and block-level replication can be created across a server farm to provide better performance, scalability and resilience.
Types of servers
Servers are often categorized in terms of their purpose. A few examples of servers available include the following:
- Web server. A web server is a computer program that serves requested Hypertext Markup Language webpages or files. In this case, a web browser acts as the client.
- Application server. This type of server provides the business logic for an application program in a computer in a distributed network.
- Domain Name System server. A critical component for internet activity, the DNS server translates domain names into IP addresses.
- Proxy server. Proxy server software acts as an intermediary between an endpoint device, such as a computer, and another server from which a user or client is requesting a service.
- Game server. These servers support the deployment of various computer games and similar applications.
- Mail server. These applications receive incoming emails from local users -- people within the same domain -- and remote senders, and forward outgoing emails for delivery.
- Virtual server. This is a program running on a shared server that's configured in such a way that it seems to each user that they have complete control of a server.
- Blade server. A blade server is a server chassis housing multiple thin, modular electronic circuit boards, known as server blades. Each blade is a server in its own right, often dedicated to a single application.
- File server. This is a computer responsible for the central storage and management of data files so that other computers on the same network can access and share files.
- Policy server. This is a security component of a policy-based network that provides authorization services and facilitates tracking and control of files.
- Database server. This server is responsible for hosting one or more databases. Client applications perform database queries that retrieve data from or write data to the database that is hosted on the server.
- Print server. This server provides users with access to one or more network-attached printers. The print server acts as a queue for the print jobs that users submit. Some print servers can prioritize the jobs in the print queue based on the job type or who submitted the print job.
Server components
Servers are made up of several different hardware components and subcomponents as well as OS software.
Hardware
At the hardware level, servers typically have a rack mount chassis containing a power supply, a system board, one or more CPUs, memory, storage, a control panel up front, various connectors in the back and a network interface.
Most server hardware supports out-of-band management through a dedicated network port. Out-of-band management enables low-level management and monitoring of the server, independently of the OS. Out-of-band management systems can be used to remotely power the server on or off, to install an OS, and to perform health monitoring.
Operating system
A server OS, such as Windows Server 2022 or Linux Mint 22, acts as the platform that enables applications to run. The OS provides applications with access to the hardware resources they need and enables network connectivity.
Applications are what enable the server to do its job. For example, a database server runs a database application, and an email server runs a mail application.
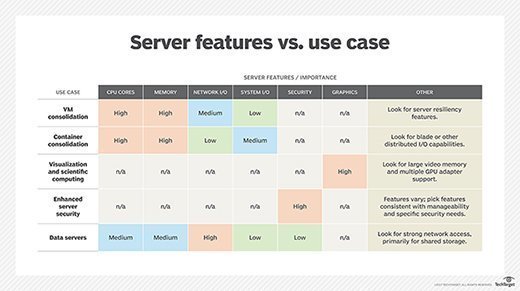
Choosing the right server
There are many factors to consider when buying a server, including VM and container consolidation. When choosing a server, evaluate the importance of certain features based on the use cases. Small businesses might have to consider some specific requirements.
Security capabilities are also important. There are a number of protection, detection and recovery features to consider, including native data encryption to protect data in transit and data at rest, as well as persistent event logging to provide an indelible record of all activity.
If the server will rely on internal storage, the choice of disk types and capacity is important because it can have a significant influence on input/output and resilience.
Many organizations are shrinking the number of physical servers in their data centers as virtualization enables fewer servers to host more workloads. The advent of cloud computing has also changed the number of servers an organization needs to host on-premises.
Packing more capability into fewer boxes reduces overall capital expenses, data center floor space, and power and cooling demands. However, hosting more workloads in fewer boxes increases risk, because more workloads will be affected if the server fails or needs to be offline for maintenance. Server OSes such as Windows Server 2022 include features to protect data and to ensure disaster recovery and resilience.
Considering the server options available, the following tips can facilitate the selection process:
- Ensure that senior management supports the need to modify server configurations and requirements and can provide the funding.
- Determine the workload requirements, including the number and types of applications, and the volumes and types of data being processed.
- Create a budget that includes the devices, software, power and HVAC requirements, spare parts, environment considerations, maintenance and support, and security.
- Determine production environment requirements, including the number of users and workloads, as well as the networking and operating environments.
- Choose an OS, factoring in current and anticipated workloads, system admin requirements, and training.
- If a physical computer server is selected, determine the form factor and where it's to be located, considering space, efficiency and security factors.
- Create a virtual server model to compare options or examine available physical servers.
Once installed, servers need routine maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Download our server maintenance checklist.