3D mesh
What is 3D mesh?
A 3D mesh is the structural build of a three-dimensional model consisting of polygons. 3D meshes use reference points in X, Y and Z axes to define shapes with height, width and depth.
A 3D mesh model is a 3D representation of an object. It consists of a collection of faces, edges and vertices that define the object's shape and structure in a fairly realistic way. Each edge connects two adjacent vertices, which are themselves coordinates or points in the 3D space.
The faces, called polygons, form the object's surface by enclosing the edges. The polygons used in a 3D mesh are typically quadrangles or triangles; these geometric shapes can be further broken down into vertices in X, Y, Z coordinates and lines.

Types of 3D mesh models
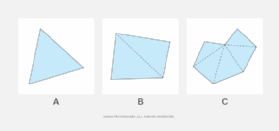
Triangle meshes, quad meshes, and n-gon meshes are all types of polygon 3D meshes. These models are the most used mesh models for a wide range of applications. Polygon models can be high poly, i.e., consisting of a high number of polygons, or low poly, created with fewer polygons.
High poly models are more detailed and effort-intensive. They are used in applications where model accuracy and detail are important. In contrast, low poly models are less detailed but easier to create. They are commonly used in applications where the fast rendering of 3D objects is of paramount importance. One example is gaming.
Triangles are the most used polygon in 3D mesh models (triangle mesh) because they can be used to model many kinds of objects easily and accurately. Quad meshes, consisting of quadrilaterals instead of triangles, are slightly more difficult to work with than triangle meshes. Even so, they are used in situations where a triangle mesh is insufficient to create models of certain object types.
The n-gon mesh is a type of 3D mesh consisting of polygons having more than four sides, such as a pentagon or hexagon. N-gon meshes are more difficult to work with than triangle or quad meshes but they are useful for modeling complex shapes.
Nonuniform rational B-spline or NURBS is another type of 3D mesh model. NURBS models produce smoother curves than polygon models since the latter consist exclusively of straight lines (edges). However, NURBS models are also more complex and require more computational effort and are usually used in situations where polygon models are insufficient or inaccurate.
A third type of 3D mesh model is the subdivision surface model. These models use both polygon and NURBS techniques to create detailed models of 3D objects with smooth surfaces.
Methods to create 3D mesh models
Most 3D meshes are created using modeling software packages -- commercial suites like Autodesk Maya, 3D Studio Max or the free open source Blender 3D. These products make it easy to create and edit the vertices, edges and faces of 3D mesh models.
3D scanning is another method to create 3D mesh models. This method uses a 3D scanner that scans the object, captures its surface, and uses this information to create the mesh. A third method is called sculpting, which involves shaping the mesh model by directly manipulating the object's surface. Finally, procedural modeling involves the use of algorithms and mathematical functions to create 3D mesh models.
The above methods can be combined to create complex, accurate, and realistic 3D models of all kinds of objects, including natural landscapes, clothing, furniture and fluids. Once the model is created, it can be modified by adding 2D images or textures. The optical properties of the object's surface can also be defined. The purpose of adding textures and defining optical properties is to make the model more detailed and realistic for its particular use case.
Advantages of 3D mesh models
It can take large numbers of polygons to make a 3D mesh photorealistic. However, these relatively simple shapes allow for faster processing than other techniques like NURBS, that produce smooth curves.
Reality capture, a newer process, creates accurate 3D models from point clouds, collections of 3D coordinates that define the shape of a physical system. These new processes and technologies make it easy to create accurate models of 3D objects for multiple design and engineering purposes.
Application areas of 3D mesh models
3D mesh models are a crucial element of 3D modeling, a technique used to create and visualize three-dimensional objects, scenes and spaces. 3D modeling, and by extension, 3D mesh models, are commonly used in areas like construction, architecture, interior design, product design, animation and film production.
3D meshes are also used for visualization and prototyping in these areas:
- Video games.
- Medical imaging (devices, diseases, treatments).
- Scientific research and analysis.
- Virtual reality and augmented reality.
Challenges in creating 3D mesh models
When models are created for animation, they require careful construction because odd deformations can happen -- unless polygons are carefully laid for continuous edge loops (a system connecting all edges) around areas that will be moved.
3D modeling can sometimes be a smooth process like working with clay. However, the necessity for edge loops often involves methodical and laborious placement of polygons. Some modeling software includes a process for defining the polygon layout separately from making the general shape.
3D technology is critical to VR worlds like the metaverse. Learn what marketers need to know about staying in front of target audiences in the metaverse. Explore where is 3D printing in manufacturing most useful.
