What is a motherboard?
A motherboard is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in a computer. The motherboard is a computer's central communications backbone connectivity point, through which all components and external computer hardware connect.
Motherboards can be found in virtually all computers, especially desktop computers and laptop PCs. The components that connect through them include chipsets, central processing units (CPUs) and memory. The external peripherals include Wi-Fi, Ethernet interfaces and graphics cards with a graphics processing unit (GPU).
Motherboard manufacturers include Acer, American Megatrends, ASRock, Asus, Biostar, EVGA Corporation, Gigabyte Technology, Micro-Star International (MSI) and Sapphire Technology.
How do motherboards work?
The PCB of a large motherboard can include six to 14 layers of fiberglass, copper connecting traces and copper planes for power and signal isolation. Other components get added to a motherboard through expansion slots. These include one or more CPU sockets; memory slots for dual in-line memory modules (DIMM); Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI), PCI Express (PCIe) and solid-state drive storage device M.2 slots; as well as power supply connections.

A heatsink and fan manage the heat generated by components such as the CPU. Typically, motherboards offer additional connectivity to peripheral devices through a Southbridge chip such as PCI, Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA), Thunderbolt (hardware interface), USB and other interfaces. A Northbridge chip connects the CPU, memory and storage components.
The CPU is generally connected to double data rate 3 (DDR3), DDR4, DDR5 or onboard low-power double data rate (LPDDRx ) RAM and PCIe. Connections are made through point-to-point interconnects, such as AMD HyperTransport bus architecture, Intel's QuickPath Interconnect (for CPUs) and Ultra Path Interconnect (superseded QuickPath Interconnect). Choosing a motherboard often determines many features a computer will be able to support.
Motherboard designs in desktop computers typically are the ATX motherboard, which is Intel's improved version of IBM's AT design. Other form factor designs include the following:
- Extended ATX.
- Mini-ATX.
- MicroATX.
- BTX.
- MicroBTX.
- Mini-ITX.
- Micro-ITX.
- Nano-ITX.
When determining a motherboard's form factor, check the technical specifications printed on its package, measure the board's dimensions, and examine the number of expansion slots.
Some memory controllers are now built into CPU functionality which eliminates the need for the Northbridge chips that provided memory management. Integrated video has moved from a motherboard slotted peripheral to graphics-enabled CPUs.
AMD's Ryzen has a system-on-a-chip (SoC) design that also makes the Southbridge chipset optional. This CPU integration has cut motherboard manufacturers' costs. They can offer base systems for workstations and entry-level computers and design customized implementations for various processors that enable platform upgrades.
Gaming motherboards are made for high-performance computers; they are more powerful and have more features than motherboards for desktop and laptop computers.
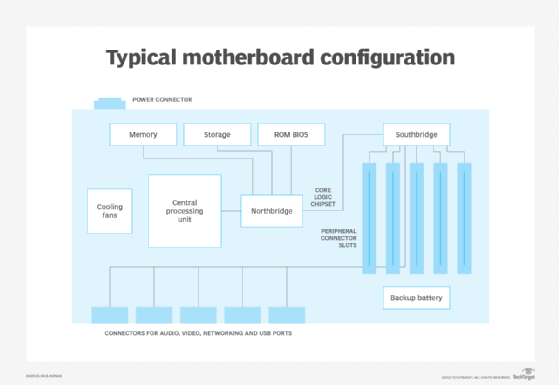
Motherboard components
Each motherboard is designed to support specific components, such as particular types of CPUs and memory modules. They can accommodate most types of hard drives and peripherals.
Motherboards include the following primary components:
- CPU with its logic circuitry that processes the instructions from programs, the operating system (OS) and other computer components
- Memory where instructions and data are temporarily stored and executed
- Storage interface for solid-state drives (SSDs) or hard disk drives (HDDs) for persistent data and application storage
- ROM BIOS providing non-volatile memory that stores firmware, such as the basic input/output system (BIOS)
- Northbridge chipset that connects CPU, memory, storage and other components
- Southbridge chipset that connects peripheral elements to the motherboard and connects to the Northbridge
- Cooling fans and heatsinks that maintain a suitable internal operating temperature
- Peripheral connector slots for plug-in peripheral cards, such as graphics and communications (e.g., Ethernet) adapters
- Connectors for peripheral devices such as USB ports and other connectors for external devices
- Backup battery that ensures key system configuration data is maintained when main power is unavailable
- Power connector that connects to an external power source
A typical motherboard comprises many other elements. For example, the system's front panel connects to the motherboard. A motherboard can be viewed as a large mosaic of electrical connections linking the various parts of a computer.
Pros and cons of motherboards
The principal benefit of having a motherboard is that without it, a PC or laptop probably wouldn't exist. It is the foundation component to which all other peripherals, CPU/memory and networking resources connect. The only downside to this product category is getting the wrong motherboard for the specific business or personal requirements.
The next section lists considerations to make when selecting a motherboard. It is important to follow the guidance as not doing so might result in paying too much for the wrong motherboard, loss of data, poor performance, lack of scalability for growth and even vulnerability to cyberattacks.
Things to remember when selecting a motherboard
At some point in time, it might be necessary to replace a motherboard. This can be the result of damage to an existing board or a change in use necessitating more power, for example. The following 12 items can serve as a good starting point.
- Determine which CPU and GPU will be used, as this can quickly identify options for motherboards that support the desired processors:
- For example, Intel CPUs require an Intel-compatible motherboard; the same is true if AMD CPUs are used.
- Motherboards must also be compatible with the processor generation to be used.
- Determine which motherboard size (e.g., ATX) will fit the device in question.
- Determine if the CPU and motherboard can accommodate overclocking, e.g., increasing the processor's speed above its factory setting.
- Determine if the motherboard supports connectivity ports, such as USB 3.1, 3.2 and 4.0, USB-C and Thunderbolt.
- Determine if the motherboard supports Wi-Fi connectivity.
- Determine which kinds of memory and storage slots are available, e.g., an M.2 slot for non-volatile memory express (NVMe).
- Determine if the motherboard supports the PCIe standard for connecting graphics cards, video cards, HDDs and SSDs, and network adaptors.
- Determine how many RAM slots are available.
- Determine how power is provided and if backup power is available on the motherboard.
- Compare costs.
Motherboards are available for many different use cases, such as general computing, gaming (typically more powerful than basic computer motherboards) and financial/scientific, which might require even more processing power.
Learn the essentials of buying server hardware, including what you need to know about server motherboards.
