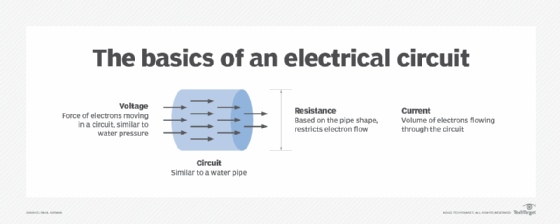
What is an inductor?
An inductor is a passive electronic component that temporarily stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through the inductor's coil. In its simplest form, an inductor consists of two terminals and an insulated wire coil. Inductors are also known as coils, chokes or reactors in older publications. Inductors help to handle fluctuations in an electric current running through a circuit.
When an electric current flows through a conductor such as copper wire, the current generates a small magnetic field around the wire. The magnetic field becomes much stronger if the wire is shaped into a coil. If the wire is coiled around a central core made up of a material such as iron, the magnetic field grows stronger still -- this is essentially how an electromagnet works. The strength of the magnetic field entirely depends on the electric current. Changing the electric current also changes that field.
Inductors use the relationship between the electric current and magnetic fields to compensate for changes in the current's flow by briefly storing electrical energy as magnetic force. When the current begins to pass through the inductor's coil, the magnetic field expands until it finally stabilizes. Until the magnetic field stabilizes, the coil inhibits the flow of current. After it stabilizes, the current flows through the coil normally.
Energy is stored in the magnetic field for as long as the current continues to run through the coil. When the current stops flowing, the magnetic field starts to collapse, and the magnetic energy is converted back into electrical energy, which continues to flow into the circuit until the magnetic field completely collapses.
Inductors and inductance
If the flow of current remains in a steady state, it passes through the inductor just like any wire without any reaction on the part of the inductor. However, if there are sudden changes in the current, the inductor tries to resist them.
An inductor causes the current to lag behind the voltage because of its magnetic field. When the current changes, the inductor's magnetic field changes -- increasing if the current increases, decreasing if the current decreases. Changes in the magnetic field cause changes to the magnetic flux, which in turn induce an electromagnetic field (EMF) that tries to oppose the change in current. If the current decreases, the EMF attempts to increase it. If the current increases, the EMF attempts to decrease it.
The inductor's ability to resist changes to the current is referred to as its inductance, which is the ratio of voltage to the current's rate of change within the coil. The standard unit of inductance is the henry (H). Because the henry is such a large unit, many inductors are measured in smaller quantities, such as the millihenry (1 mH equals 10-3 H) and the microhenry (1 µH equals 10-6 H). The nanohenry is occasionally used (1 nH equals 10-9 H).
Many factors can affect an inductor's level of inductance, including the number of coils, the length of the coiled wire, the material used for the core, and the size and shape of the core. If no core is used, then inductance also depends on the radius of the coil.
For a given coil radius and number of turns, air cores -- those without solid cores -- offer the least inductance. Materials such as wood, glass and plastic -- known as dielectric materials -- are essentially the same as air in terms of inductance. Ferromagnetic substances such as iron, laminated iron and powdered iron increase the inductance. In some cases, this increase is on the order of thousands of times. The shape of the core is also significant. Toroidal or donut-shaped cores provide more inductance for a given core material and number of turns than solenoidal or cylindrical cores.
Fabricating inductors onto integrated circuit (IC) chips is difficult, but it can be done, although they have a fairly low inductance. In some cases, inductance can be simulated by using transistors, resistors and capacitors fabricated onto IC chips.
Inductors share many elements in common with electrical transformers. They use wound coils and ferrous cores to create electromagnetic fields to store and convert electrical energy.
What are the differences between an inductor and a capacitor?
Inductors, capacitors and resistors make up the three fundamental passive components in circuits. Inductors and capacitors might at first seem like they serve the same function -- storing energy -- but their different electrical characteristics cause them to be used differently in circuits.
Inductors store energy as magnetic flux. Capacitors store energy as an electric field.
In an inductor, when a current is first applied, it resists the flow; when it is saturated, it allows the flow. In a capacitor, when a current is first applied, it allows the flow; once it is saturated, it resists the flow.
Inductors resist changes in current. This causes them to block high-frequency signals, and pass low-frequency signals and direct current. Capacitors resist direct current and low-frequency signals, and pass high-frequency signals.
What are inductors used for?
Inductors are most often used as filters to block unwanted high-frequency signals. For example, an inductor can filter out higher harmonics or noise in a power supply and leave a clean 50/60 Hz line frequency.
Inductors are often used with capacitors as a frequency band pass or a tuned circuit. By carefully selecting the inductance and capacitance, only a very specific frequency is allowed through. This is because the inductor blocks higher frequencies, and the capacitor blocks lower frequencies.
Band-pass circuits are widely used in wireless communications, audio systems, graphic equalizers and a range of other applications. For example, simple radios use a band-pass filter, with a variable capacitor, to select the station to listen to. These types of circuits can also be found in Wi-Fi and 5G radios to remove unwanted interference.
Switching power supplies use inductors in their design. The inductor can store power as the circuit switches on and off rapidly. By doing this, the resulting output voltage of the power supply can be controlled to be higher or lower than the input voltage. This also makes switching power supplies much more efficient than simpler passive power supplies.
Learn the main factors that can guide your uninterruptible power supply selection process and how to size a UPS unit. See what to know about managing power for edge devices and how to calculate data center cooling requirements.