What is virtual reality? How it's used and how it will evolve
What is virtual reality?
Virtual reality, or VR, is a simulated three-dimensional (3D) environment that lets users explore and interact with a virtual surrounding in a way that approximates reality, as it's perceived through the users' senses. The environment is created with computer hardware and software, although users might also need to wear devices such as goggles, headsets or bodysuits to interact with the environment.
The more deeply users can immerse themselves in a VR environment -- and block out their physical surroundings -- the more they can suspend their belief and accept it as real, even if it's fantastical in nature.
What are the main types of virtual reality?
The VR industry still has far to go before realizing its vision of a totally immersive environment that lets users engage multiple sensations in a way that approximates reality. However, virtual reality technology has come a long way in providing realistic sensory engagement and shows promise for business use in several industries.
VR systems can vary significantly, depending on their purpose and the technology used, although they generally fall into one of the following six categories:
Non-immersive
This type of VR typically refers to a 3D simulated environment that's accessed through a computer screen. The environment might also generate sound, depending on the program. The user has some control over the virtual environment using a keyboard, mouse or other device, but the environment doesn't directly interact with the user. A video game is a good example of non-immersive VR, as is a website that lets a user design a room's decor.
Semi-immersive
This type of VR offers a partial VR experience that's accessed through a computer screen or some type of glasses or headset. It focuses primarily on the visual 3D aspect of virtual reality and doesn't incorporate physical movement in the way that full immersion does. A common example of semi-immersive VR is a flight simulator, which airlines and militaries use to train their pilots.
Fully immersive
This type of immersive VR delivers the greatest level of virtual reality, completely immersing the user in the simulated 3D world. It incorporates sight, sound and, in some cases, touch. There have even been some experiments with the addition of smell. For example, Olorama technology offers a digital scent synthesizer olfactory device that can be used to diffuse scents in various full-body immersive settings such as during movies, events and escape rooms. For fully immersive experiences, users wear special equipment, like headgear, goggles or gloves, to interact with the environment. The environment might also incorporate such equipment as treadmills or stationary bicycles to provide users with the experience of moving through the 3D space. Fully immersive VR technology is a field still in its infancy, but it has made important inroads into the gaming industry and to some extent the healthcare industry, and is generating a great deal of interest in others.
Collaborative VR
This is sometimes cited as a type of virtual reality. In this model, people from different locations come together in a virtual environment to interact with one another, with each person represented by a projected 3D character. Users typically communicate through microphones and headsets.
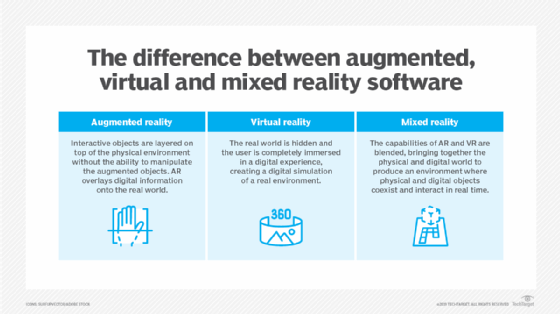
Augmented reality
AR is also sometimes referred to as a type of virtual reality, although many would argue that it's a separate but related field. With augmented reality, virtual simulations are overlaid with real-world environments to enhance or augment those environments. For example, a furniture retailer might provide an app that lets users point their phones at a room and visualize what a new chair or table might look like in that setting.
Mixed reality
This category blends the physical and virtual worlds into a single space. Like augmented reality, however, it's more often considered a separate but related field. In fact, there's been a growing consensus to group virtual reality, augmented reality and mixed reality under the umbrella term extended reality, which provides a handy way to reference all three, while still distinguishing among them.
Today's VR technologies and applications have inspired multiple companies and experts to advocate for advanced uses of the metaverse, which encompasses diverse digital realities, platforms and experiences, forming an interconnected network of virtual realms.
Features of virtual reality
Virtual reality has several essential features that make it an immersive and interactive medium. Unlike traditional interfaces, VR positions the user inside the virtual environment, delivering a truly immersive experience.
The primary characteristics and features of virtual reality include the following:
Immersion
By immersing users in a computer-generated world that seems and feels genuine, VR seeks to evoke a feeling of immersion. The level of immersion can vary depending on the type of VR system and the quality of the content. By donning and using wearable technology interactive gear -- such as data gloves, motion controllers, game consoles and head-mounted displays, like Meta Quest 2 -- viewers can fully immerse themselves in the virtual world.
Interaction
Virtual reality is a highly interactive experience where people can interact with various elements realistically. The elements of interaction depend on range, speed and mapping, letting users manipulate and control objects, navigate through virtual space and engage in activities within the virtual world.
Realistic visuals
High-resolution monitors and sophisticated graphics rendering techniques are used in VR to produce vivid, lifelike images. This includes realistic lighting and textures, realistic 3D visuals and stereoscopic imaging for depth perception.
Spatial audio
Spatial audio technology offers realistic sound effects positioned physically within the virtual environment. By producing an audio experience that corresponds with the user's visual environment, VR increases the user's sensation of presence and immersion.
Multi-sensory haptic feedback
Advanced virtual reality systems can also include haptic feedback, which gives tactile sensations to the users. This can involve force feedback, vibrations, or even full-body haptic suits that let users experience real-world bodily sensations in a virtual setting.
Spatial collaboration
The capacity for individuals or groups to work together and communicate in a common virtual environment through the use of virtual reality technology is known as spatial collaboration. Regardless of where they're physically located, it lets users collaborate virtually on projects, exchange ideas and interact as if they were in the same space. For example, Vision Pro, which is Apple's first spatial computer, combines mixed reality and VR to create an immersive experience without completely obstructing the outside world.
Complete 360-degree views
With a full 360-degree spherical field of view that most VR systems offer, users can look in any direction and explore the virtual space from different perspectives, just as they would in the real world.
Adaptive environments
When generative AI is integrated with VR settings, the result is a responsive and personalized experience that can change dynamically in response to human inputs. AI-driven systems, for instance, can evaluate user behavior in real time, enabling virtual environments to adjust and react to the user's activities to create a genuinely personalized and engaging experience.
How can virtual reality be used?
Virtual reality is often associated with gaming because the industry has been at the forefront of the VR effort, as evidenced by the popularity of products such as Beat Saber, Minecraft VR and Skyrim VR. Even so, there has been a growing interest in the potential of VR across several other areas, including the following:
Training
VR makes it possible to train personnel safely, efficiently and cost-effectively. It can be especially beneficial to those in high-risk or highly specialized positions, such as firefighters, emergency medical responders, police officers, soldiers, surgeons or other medical personnel. The training sector has also begun to embrace the benefits that VR learning presents, with corporations such as Bank of America sourcing 10,000 headsets and Walmart providing VR training to its one million employees.
Education
VR offers educational institutions new methods for teaching and learning. It can provide students with intimate insights into environments that are typically inaccessible, while keeping them engaged in the learning process. For example, a history teacher might use VR to show students firsthand what life was like in ancient Greece or China.
Healthcare
VR has the potential to benefit individuals across the healthcare industry, including patients, practitioners and researchers. For example, VR shows promise in treating disorders such as anorexia, anxiety or post-traumatic stress disorder. On the other hand, doctors might be able to use VR when working with patients to explain diagnoses or treatment options. VR could also benefit individuals who have physical limitations.
Retail
VR has already made some inroads into retail, but the industry has only scratched the surface. Many apps now let customers virtually try on clothes, decorate their homes, experiment with hairstyles, test eyeglasses and in general make more informed decisions about products and services.
Real estate
VR benefits real estate in several ways. For example, architects can show detailed plans in 3D; home buyers can tour homes virtually; building engineers can tour heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems; and homeowners can see what their remodels would look like.
Entertainment
VR has already had an impact on gaming, but it also promises to transform the film and television industries, providing viewers with an immersive experience that puts them right into the scene. VR could also lead to an entire industry in virtual tourism, making it possible for people to experience places that they might never be able to see in person.
Architecture and design
Virtual reality lets architects and designers conduct virtual tours of structures and places before they're built and enables clients to see and feel the design in a more immersive and realistic way. For example, if someone wants to add an extension to their home, they might visualize the room and how it will appear before it's built and then make modifications in real time. This saves time and money for both the customer and the architect while also improving project satisfaction.
Sports
VR is transforming the sports industry and revolutionizing the way people experience sporting events. For example, fans can now watch basketball, football and other virtual reality games from several vantage points in the stadium as if they're actually there. Meta also expanded its partnership with the National Basketball Association in 2023, so fans can now watch live games with a Meta Quest VR headset on their social VR world known as Meta Horizons World.
The simplest form of virtual reality is a 3D image that can be explored interactively through a PC, usually by manipulating keys or the mouse so that the content of the image moves in some direction or zooms in or out. More sophisticated efforts involve such approaches as wraparound display screens, physical rooms augmented with wearable devices, or haptic devices that let users feel the virtual images.
Future of virtual reality: How will it evolve?
Virtual reality is progressing rapidly, with ongoing breakthroughs anticipated across diverse industries. According to a recent International Market Analysis Research and Consulting Group report, the global virtual reality market is expected to reach $313.5 billion by 2032.
The following are a few insights and predictions into the future of VR:
The future of VR is propelled by its growing accessibility. Previously confined to costly, specialized equipment, VR has become more attainable with the emergence of affordable headsets and the integration of VR features into mobile devices. This increased accessibility is creating new possibilities for VR applications across diverse industries, such as enterprise, healthcare and education. This affordability will also enable a wider audience to embrace this technology.
As the demand for VR grows, users can anticipate heightened levels of immersion by bringing them even closer to real-life. VR will keep its focus on creating hyper-realistic experiences by engaging multiple senses. With the rapid adoption of haptic gloves, suits and spatial audio, the exploration into incorporating smells into deep immersive experiences will gain momentum.
VR will enable virtual workplace communication that's just as effective as face-to-face engagement. Nvidia, for instance, is making it possible to have high-fidelity 3D video conferences utilizing merely consumer webcams and AI-mediated methods.
The integration of augmented reality with VR is expected to open up new possibilities. For example, AR glasses will soon be able to overlay directions, places of interest and pertinent data over the user's field of vision, making navigation easier and more natural. This technology is promising for the travel and tourism industry as well as for helping those with vision impairments.
Ensuring secure and age-appropriate virtual experiences is going to be a major worldwide concern in the future. Meta lowered the minimum age for Quest accounts in 2023, letting kids between the ages of 10 and 12 get a parent-managed account for age-appropriate VR experiences. As VR devices become even more popular with younger users, businesses and parents will be looking into strong controls for VR access.
Whether it's augmented reality, virtual reality or mixed reality, each immersive technology has the potential to enhance digital experiences for individuals. Examine how these three technologies differ from one another.