operating model
What is an operating model?
An operating model is a visual representation of how an organization delivers value to its internal and external customers. Operating models are created to help employees visualize and understand the role each part of an organization plays in meeting the needs of other components.
Operating models also help managers understand how changes to one part of the organization might affect the value that other parts deliver. Target operating models depict how a company aims to structure and manage operations in the future.
How does an operating model work?
An operating model provides a roadmap that shows how to execute an organization's Business model. It's usually organized from the top down and can be high level or granular. A large organization may find it necessary to create dozens of operating models to accurately capture the steps each department follows to meet the needs of other parts of the business and its customers.
In large organizations, internal design teams with visualization expertise typically document operating models. Smaller companies often use flowcharts to create their operating models. It can take a few days or a few months to document an operational model, depending on the complexity of the organization's strategic plan and the amount of detail required.
These models often evolve Ad hoc. However, they can also be designed using frameworks such as the Operating Model Canvas (OMC) developed by Andrew Campbell, director of the Strategic Management Centre, a strategy research group in London. OMCs capture six elements that play an important role in delivering value: processes, organization, locations, information, suppliers and management systems (POLISM).
What is included in an operating model?
Operating models include a variety of visual tools that explain to stakeholders how a company's capabilities and business processes align with its overall strategy and how that strategy delivers value. Operating models can include the following elements:
- Business capability models are a representation of what a business can do in a logical framework.
- Capability maturity models are a methodology used to develop and refine software development processes. CMMs are used over time.
- Management structures are org charts that depict the hierarchy of management.
- Resource portfolios provide a schedule of resources needed to meet service delivery obligations.
- Supplier matrices represent all suppliers as strategic assets and categorizes them.
- People models depict the type of people the organization aims to attract.
- IT priorities are laid out in an IT blueprint that shows an organization's IT goals, projects, staffing and other related initiatives.
- Location maps show where work assets are located and why they're positioned there. Locations may be logical or physical.
- Decision grids depict the decision-making process in an organization.
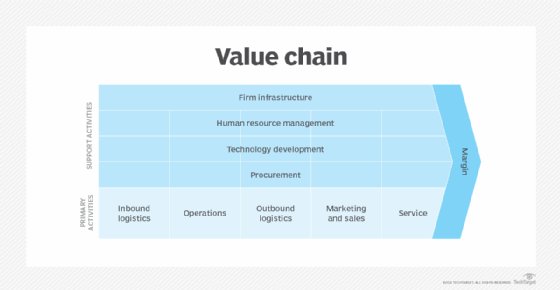
At their simplest, operating models are value delivery chains that describe the steps necessary to complete an organization's work and to deliver the desired business outcomes. Steps in the chain include the following:
- Inbound logistics. These are outside resources flowing in, which are also referred to as inputs.
- Operations. These are activities and processes that transform inputs into outputs. Value is added to outputs.
- Outbound logistics. This is when outputs are delivered to customers. Processes involve systems for storage, collection and distribution to customers.
- Marketing and sales. This involves activities such as advertising and brand building that increase visibility, reach a specific audience, and communicate why a consumer should buy a product or service.
- Service. These are activities related to maintaining the value of the product or service and might include things like customer support.
In a restaurant, for example, the steps in the value delivery chain might be the following:
- acquire ingredients,
- cook them,
- market to customers,
- serve customers and
- solicit customer feedback.
How do you create an operating model?
Operating models can be created using the POLISM framework, which involves the following six elements:
- Processes. These are the functions that deliver a company's value proposition. A value chain depiction is usually included in this portion.
- Organization. This consists of the people who do the work, the structure of logical units in the organization, and the decision-making requirements of those people and business units.
- Locations. This covers anywhere work is done and assets are stored. It can include both physical and logical locations.
- Information. Lots of data supports the work being done. It's often contained in software applications and databases.
- Suppliers. These include third-party partners that provide the organization with the resources to deliver on its value proposition and the business model associated with it.
- Management systems. These are used for budgeting, planning, performance management and people management processes that support the other five elements.
These six elements are set up on an OMC, which is a document that lays out the components of the organization that fall into each category. In the previous restaurant example, a value chain might be laid out in the P section of the OMC, while a list of the suppliers that deliver food to the restaurant would fall into the S section.
To incorporate each of the elements in POLISM, organizations need to do the following:
- Define the business strategy with input from stakeholders and the leadership team. One example of a corporate strategy would be to unify customer experience across all channels as part of a digital transformation effort.
- Create a list of processes and tools that deliver value for the business.
- Define the company's organizational structure, laying out the methodologies used to complete work.
- Determine success metrics for each role or department, and identify the technology needed to reach those goals and maintain operational excellence.
Operating model examples
The outdoor apparel brand Patagonia has an operating model that includes a value proposition to limit its environmental footprint while providing high-quality outdoor wear to customers. Customers feel they're contributing to a good cause when they buy Patagonia products. This differentiates the company from its competitors and gives it a competitive advantage.
Patagonia aligns its activities with environmental objectives, understanding that it might incur higher costs in doing so. To accommodate this operating model, the company had to align its mission statement to reflect its sustainability goals and use supply-chain partners to create more sustainable ecosystems and business processes. Some examples of sustainable processes include removing chlorine from wool products, printing paper catalogs on recycled paper and using renewable energy sources to power buildings.
Technology plays a role in developing a sound operating model that delivers value to customers. Learn why internet of things technology is vital to businesses, and how organizations can incorporate IoT to better deliver value to customers.
