privacy policy
What is a privacy policy?
A privacy policy is a legal document that explains how an organization handles any customer, client or employee information gathered in its operations. It will include how data is collected, stored, used, shared and protected and the user's rights in connection to the data. It is required by law in the European Union, the State of California and other jurisdictions.
A privacy policy might be required for privacy compliance.
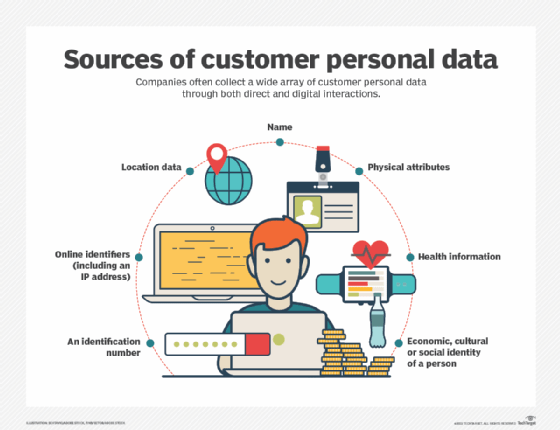
A privacy policy should specify any personally identifiable information (PII) that is gathered, such as name, address and credit card number, as well as other information like order history, browsing habits, uploads and downloads. The policy should also explain if data can be left on a user's computer, such as cookies. The policy should disclose if data can be shared with or sold to third parties and if so, what the purpose is.
For simple privacy policies, the first statement found in an online privacy policy is one to the effect that, by visiting the webpage (which you are doing if you're reading the policy), you agree to the details of the site's privacy policy. Some jurisdictions now require that the consumer give active consent, meaning that this type of clause is no longer binding.
Many sites now use a clickwrap (click through) agreement to prove user agreement to a privacy policy. These are much more defensible in court than policies that rely on passive agreement, such as by simply using a site. Clickwrap agreements often pop up at the bottom of a site with an accept or reject prompt. Adding a checkbox affirming that the consumer read and understood the terms of the privacy policy can further protect the organization. The date, time and identifying information of the acceptance should be tracked.
Privacy policy and cookie policy
A privacy policy covers all aspects of how a service collects and uses consumer data. A cookie policy only applies to website cookies, which can be used for consumer identification. It is now common for a service's privacy policy to also contain a cookie policy. These can be separate documents in some cases though.
What should a privacy policy include?
Privacy policies need to be written in simple-to-understand language. They should not use complicated legal terms and jargon. Most privacy policies are written and enforced in English, even if it is not the official language of the country. It is good practice though to provide high-quality translations of a privacy policy in every language in which a service is used.
A privacy policy should include the following information:
- Types of data collected -- name, date of birth, location, etc.
- How data is collected -- user entry, cookies, etc.
- How the data will be used -- marketing, usability, service functionality, etc.
- If the data will be shared or sold -- third-parties, partners, etc.
- How the data will be stored and protected -- service locality, encryption, etc.
- How to opt out and request deletion, including how to file requests and privacy questions.
- Date the policy comes into effect.
- Contact information for privacy-related requests.
- Other information that might be required according to the consumer's jurisdiction.
Privacy policy jurisdictions and enforcement
The United States currently has no federal laws that directly require or enforce privacy policies. The FTC (Federal Trade Commission) is promoting industry self-regulation and enforcement of current laws. Current U.S. laws mainly protect medical personal health information with HIPAA and children's privacy with COPPA (Children's Online Privacy Protection Act).
Several U.S. states have enacted laws protecting consumers' digital privacy. California has passed several such laws, such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
The European Union has passed many consumer data privacy laws. The most notable being the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This protects all EU citizens, even if the business is not located in the EU. It strictly defines how companies collect and store data and includes fines for non-compliance.
Other countries including Australia, Canada and India have laws that might require a privacy policy.
Even though they are not required for every country, it is now best practice for every service to have a public privacy policy to cover consumers in jurisdictions that require them. Privacy policies might include language to cover specific requirements of some of these laws and have sections dedicated to each of them.
Check out the top 10 customer data privacy best practices and how data anonymization best practices protect sensitive data. See how to use a data privacy framework to keep your information secure and overcome GDPR compliance challenges. Explore privacy controls to meet CCPA compliance requirements and how to comply with the CCPA.
