What is a programmable automation controller (PAC)?
Programmable automation controller (PAC) is a term that is loosely used to describe any type of automation controller that incorporates higher-level instructions. The systems are used in industrial control systems (ICS) for machinery in a wide range of industries, including those involved in critical infrastructure.
Uses of programmable automation controllers
For modern industrial applications that require advanced capabilities in addition to interfacing with signals from sensors and actuators, a controller that works on simple ladder logic, such as a programmable logic controller (PLC), is often insufficient. Also, PLCs handle discrete logic-based control of input/output (I/O) signals. Complex applications go beyond such traditional functions and often involve complex arithmetic operations and calculations.
There are three ways to satisfy the requirements of modern applications:
- Enhance the PLC with separate hardware cards, additional processors and middleware software running on a separate PC.
- Use an industrial PC that can perform PLC-like tasks, albeit with some expansions to support high-performance or deterministic industrial operations.
- Use a device that provides the benefits of both PLCs and PCs, i.e., deterministic process controls along with networking, data communications, enterprise integration and flexible configurations.
Option 3 refers to the use of PACs.
PACs are often the controller of choice for modern-day industrial applications (i.e., Industry 4.0) that require interfacing with signals from sensors and actuators in addition to advanced capabilities like control features, network connectivity and device interoperability.
Examples of such applications include:
- Vision-guided motion.
- Multi-axis, coordinated motion.
- Circular interpolation.
PACs are also used for applications that require integration between factory data and enterprise systems, I/O point monitoring and control, or data exchange via an OPC (Overall Line Efficiency for Process Control) server.
Additionally, functions like counting, latching, and PID loop control cannot be performed by simpler PLC-based control systems unless they are augmented with additional processing hardware. Such hardware devices are often very expensive. With PACs, these capabilities are built in, so separate components or devices are not required.
Key characteristics of programmable automation controllers
PACs feature an open, modular design and architecture, allowing for expandability and interconnectivity with other systems or devices. Simply put, PACs can easily interact and operate with other PACs, PLCs and human-machine interfaces to support industrial applications. The modular architecture also means that PACs can integrate with different networks and their functionality can be augmented - if required - with additional processors.
PACs are also known for their efficient processing and I/O scanning abilities. As a multifunctional device, a PAC can simultaneously monitor and control I/O signals from multiple sources. Moreover, it can handle three types of signals with ease:
- Digital, e.g., the on/off states of valves, switches, indicators and other monitored devices.
- Analog, e.g., temperature or pressure.
- Serial, e.g., data from inventory tracking equipment.
According to the ARC Advisory Group, the organization that originated the term PAC, a controller is a PAC if it has the following characteristics:
- Multi-domain functionality. PACs can operate in multiple domains such as logic, motion and process control using a single platform.
- A single development platform. A PAC uses common tagging and a single tag name database for all development tasks, regardless of the discipline it is employed for.
- Programmable with software. Various software tools are available to program PACs so that they can control processes and maximize process flows across multiple machines or units.
- Tight integration between controller hardware and software. Tight hardware/software integration helps improve the performance of the control system.
- Seamless operation in multi-vendor systems. PACs employ accepted standards for protocols (e.g., TCP/IP or Ethernet), network interfaces, and languages, enabling seamless data exchange within a networked multi-vendor system.
Benefits of programmable automation controllers
PACs can effectively satisfy complex industrial requirements, almost always without the need for extra components. This reduces total cost of ownership (TCO) and minimizes the time needed for programming and integration.
Also, the hardware and software in a PAC are tightly integrated, providing improved control system performance. All development tools share a single tag name database. This database is included in all the integrated development environments (IDEs) used to program and customize PACs. And programmers need to use only one software package to program the PAC's automation requirements., simplifying PAC programming.
The modular design of PACs allows for easy upgrades and replacements. This saves time and money and helps to maintain the PAC's operational performance and reliability.
Finally, unlike other types of controllers (e.g., PLCs), PACs incorporate modern networking and communication capabilities, plus versatile I/O options. These capabilities allow human operators to access accurate valuable production information in real-time (or near real-time). They can use this information to assess the health of the system or process and to make better data-driven decisions.
Advantages of programmable automation controllers over programmable logic controllers
PLCs were created in the 1960s as an improvement over relay-based systems. Although more advanced than relays, PLCs still functioned by simple ladder logic that resembled the appearance of wiring diagrams of relay systems.
In the beginning, PLCs had limited memory, required proprietary terminals and lacked remote I/O (input/output) capabilities. Additional abilities required adding hardware cards. PC-based programming of PLC was introduced in the 1980s and offered greater abilities, more memory and sequential control.
Early PACs came on the scene at the beginning of the 21st century. PACs offered a combination of the abilities and technologies of distributed control systems and remote terminal units as well as some of the abilities offered by PC control. A PAC makes it possible to provide more complex instructions to automated equipment, enabling much the same capabilities as PC-based controls in an all-in-one package like a PLC.
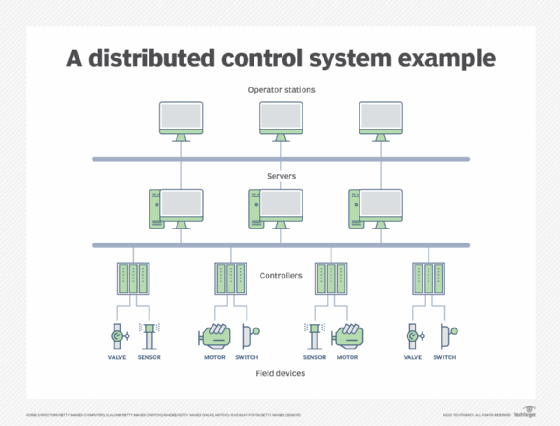
PACs also offered more connectivity options and broader control while maintaining smaller packaging and durability for environmental stresses and shock. With these new improvements, PACs were widely adopted in numerous industrial settings, although the use of PLCs continued for simple applications like single-axis motion control.
Controllers of both types have advanced since their creation. With the increased capabilities of PLC, the differentiating lines between the two have blurred. Higher-end PLCs with increased capabilities are often marketed as PAC.
Learn about how oil, energy and chemical companies are replacing expensive control systems with cheaper, more secure ones.
