scripting language
What is a scripting language?
A scripting language is a type of programming language in which the instructions are interpreted individually at runtime. With more conventional programming languages, such as C and C++, the code is compiled in advance and in its entirety. Scripting languages take a much simpler approach, which makes them easier to learn and faster to code. However, they're not as robust or efficient as the more structured conventional languages.
What is the difference between scripting and programming languages?
Scripting languages are often compared with programming languages as though they're opposite sides of the same coin. However, scripting languages are actually a subset of programming languages. All scripting languages are programming languages, but not all programming languages are scripting languages. More often than not, such comparisons are meant to distinguish scripting languages from conventional programming languages.
With conventional languages, the source code is compiled in its entirety prior to execution. Although languages take different approaches to preparing the code for processing, they typically start with human-readable source code, compile it into a lower-level code and eventually convert it into machine code. The machine code is specific to the platform architecture on which it runs. Machine code is sometimes submitted to the processor in the form of an executable file. In addition to the compiler, the preparation process might incorporate an assembler, linker, bytecode interpreter or other components.
In contrast to the conventional development approach, scripting languages are typically submitted to a translator at runtime. The translator converts the script into machine code and submits it to the processor. The script remains in its original human-readable form until the translator converts the instructions and submits them for processing.
The following figure provides a conceptual overview of how conventional programming languages compare with scripting languages when it comes to preparing the machine code. The conventional code is first submitted to the compiler, which converts it to object code, assembly code or intermediary code such as bytecode. If it's the latter, the code will then be passed to an interpreter at runtime.
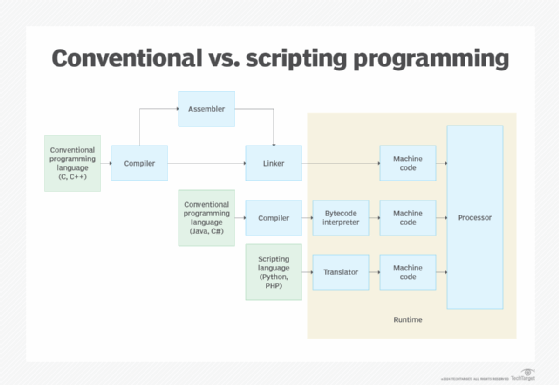
As the figure shows, conventional programming languages take different approaches to preparing the code. If the language is a conventional one such as C or C++, the code is first passed to the compiler for the initial transformation. The compiler will either transform it into object code and send it on to the linker, or turn it into assembly code and pass it on to the assembler. The assembler then converts it to object code and sends it on to the linker, which generates the executable code.
Not all conventional languages follow these approaches, however. If the language is one such as Java or C#, the compiler converts the code to an intermediary language, which is submitted to a virtual machine-based interpreter at runtime. The interpreter then generates the machine code and submits it to the processor.
These are not the only ways in which conventional programming languages are compiled and translated into machine code. However, the methods shown in the figure help to demonstrate how such languages differ from scripting languages. A scripting language, such as Python or Hypertext Preprocessor (PHP), remains in its raw form until runtime, at which point it is submitted to a translator. The translator interprets the commands one at a time, turning them into machine code that can be used by the processor.
Because scripting languages are not compiled in advance, they might not perform as well as conventional languages. However, scripting languages and translator software have steadily improved over time, helping to mitigate some of the concerns over performance.
Scripting languages and conventional programming languages differ in other ways as well. For example, scripting languages are dependent on other programs. You cannot use them to build independent applications like you can with conventional languages. In addition, scripting languages tend to provide less direct control over the hardware. With a conventional language, programmers can more easily manage processor, memory and input/output resources.
Scripting languages also tend to be loosely typed. This means that a variable's type is not defined within the code, but is determined at runtime and depends on the variable's value. In addition, a variable's type can sometimes change during the script's execution. For example, the following Python script initially defines a variable named scenery and assigns a short list of two values to the variable.
# create scenery variable and return value and type
scenery = ['mountains', 'trees']
print('\nThe value for "scenery" is', scenery)
print('The type for "scenery" is', type(scenery))
# assign scenery[1] value to scenery variable
scenery = scenery[1]
print('\nThe value for "scenery" is now', scenery)
print('The type for "scenery" is now', type(scenery), '\n')After defining the variable, the script prints the variable's original value and the variable's type. The script then assigns the list's second value, trees, to the variable. The script then prints the variable's new value and data type. The following result shows the output from each print command.
The value for "scenery" is ['mountains', 'trees']
The type for "scenery" is <class 'list'>
The value for "scenery" is now trees
The type for "scenery" is now <class 'str'>Conventional programming languages are strongly typed, which means that a type is assigned to the variable when it is defined. In this way, errors are more likely to get caught during compilation rather than at runtime, resulting in code that is more reliable. Strongly typed variables also mean that they cannot be inadvertently changed to the wrong type.
As scripting languages and their translators have evolved over time, the lines have begun to blur between what should and what should not be classified as a scripting language. Today, many believe that the classification should not be determined by the language itself, but rather by how the language is being used.
How are scripting languages used?
Scripting languages are often categorized as either server-side or client-side. Server-side scripting languages -- such as PHP, Ruby and Python -- are processed on the host server. Client-side scripting languages -- such as JavaScript, Hypertext Markup Language and Cascading Style Sheets -- are processed on the user's computer, typically within a browser. Client-side scripting reduces server and network loads. However, server-side scripts are not visible to the user and are generally considered more secure.
Scripting languages are used extensively in web applications to enhance their features and make them more dynamic. Although many scripts are processed on the server, client-side scripting -- particularly JavaScript -- is still used extensively in web development. For this reason, websites often require users to configure their browsers to permit client-side scripts to run. Otherwise, certain webpage features might not work.
Programmers also use scripting languages in other situations, such as multimedia and gaming. In addition, they might use scripting to automate tasks within their applications or to connect disparate system components.
When a scripting language is used to connect components, the language is sometimes referred to as a glue language. Glue languages often provide native support for specific aggregate data types such as arrays. They might also automate garbage collection to reclaim storage and prevent memory leaks.
Another common use of scripting languages is system administration. IT teams can use scripts to automate routine operations as well as to perform one-off tasks. For example, the following Python script loops through a directory on a macOS computer and returns a list of its subdirectories, along with the number of items in each one.
# import the os module
import os
# define target directory
path = '/users/mac3/documents/testdata/'
print('\npath:', path, '\n')
# retrieve subdirectory in target directory
for item in os.listdir(path):
sub = os.path.join(path, item)
# return only subdirectories
if os.path.isdir(sub):
size = len(os.listdir(sub))
# print info about each subdirectory
print(item + ': ' + str(size) + ' items')
print('\n')In this example, the script returns the following results, which include the name of the target directory, followed by the names of the subdirectories and number of items in each one.
path: /users/mac3/documents/testdata/
TestFolderH: 5 items
TestFolderA: 21 items
TestFolderF: 18 items
TestFolderG: 15 items
TestFolderI: 21 items
TestFolderK: 20 items
TestFolderL: 30 items
TestFolderE: 14 items
TestFolderB: 20 items
TestFolderC: 9 items
TestFolderD: 10 items
TestFolderM: 18 items
TestFolderJ: 0 itemsOf course, scripts can be far more complex, which can be especially useful for automating tasks. Programmers also use scripting languages for reporting, statistics, software extensions, text processing, back-end programming, embedded systems, software testing and numerous other use cases.
What are examples of scripting languages?
Scripting languages are generally easier to work with than conventional programming languages. The code is often simpler to read, write and maintain. For this reason, a wide range of scripting languages is now available, including the following examples:
- AppleScript. A scripting language developed by Apple for building small programs called applets that perform like bots. The applets can autonomously process and manage multimedia data, including digital video, text and web content.
- Bash. The free version of the Bourne shell distributed with Linux and GNU operating systems.
- Bourne shell. The original Unix shell, which is also known by its program name, sh.
- C shell. Shell script and platform that was invented for programmers who prefer a syntax similar to that of the C programming language.
- JavaScript. Scripting language developed by Netscape. It shares similar capabilities to those of Microsoft's Visual Basic, Sun's Tcl, Unix-derived Perl and IBM's Rexx.
- Korn shell. Shell script and platform that incorporates all the features of C shell, or csh, and Tab C shell, or tcsh. The Korn shell provides scripting features similar to the Bourne shell.
- LotusScript. Scripting language that supports object-oriented development for IBM software applications.
- Perl. Scripting language with syntax similar to the C language. Perl can optionally be compiled just before execution into either C code or cross-platform bytecode.
- PHP. General-purpose scripting language and interpreter that is freely available and widely used in web development, particularly for web applications hosted on Linux web servers.
- PowerShell. Scripting framework and language designed to perform and automate Windows system management tasks. PowerShell includes more than 130 standard command-line tools for functions that formerly required users to create scripts in Visual Basic, VBScript or C#.
- Python. A relatively simple scripting language that offers powerful features but is easier to learn than many other languages. Python is often used to add scripting capabilities to existing applications, although it supports a wide range of other use cases.
- Ruby. A dynamic, open source scripting language with a simple syntax that was partially inspired by the Ada and Eiffel languages. Ruby is a very readable language for anyone who is familiar with modern programming languages.
Choosing a programming language is often dictated by the problem the programmer wants to solve and the compute goal that a language is designed to achieve. Explore the differences between scripting and programming languages.
