Parallel ATA (Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment or PATA)
What is Parallel ATA (Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment or PATA)?
Parallel ATA (Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment or PATA) is a legacy standard for connecting internal floppy disks, hard disk drives (HDDs) and optical disk drives to older computer systems. ATA is sometimes known as AT Attachment.
As its name implies, PATA is based on parallel signaling technology, in which bits of data are sent simultaneously across multiple channels. PATA drives are no longer in widespread use in enterprise storage. They have been largely replaced by serial ATA (SATA) devices that use serial signaling technology to transfer one bit of data at a time across a single channel.

Is PATA the same as the IDE standard?
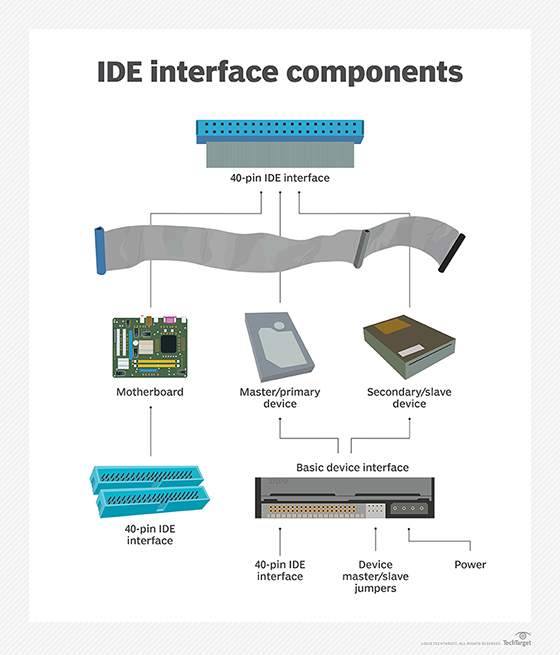
PATA was developed as a storage interface by Western Digital Corp. in 1999. The PATA acronym came later -- initially, the interface was called Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE), also known as enhanced IDE or EIDE. IDE specified how data transfer occurs between a motherboard and connected secondary storage devices, namely, by using a parallel communications channel.
IDE marked an important milestone in enterprise storage, as it standardized how vendors could package an integrated storage controller and drive as a single device. SATA drives are also designed on IDE technology.
What are PATA's benefits and drawbacks?
When introduced to the market, PATA drives intrigued enterprise users because of the ability to do the following:
- Simultaneously attach two devices to the same cable.
- Transfer multiple bits of data in parallel.
- Easily integrate with older computer operating systems and system hardware.
However, PATA lacks the features inherent in newer SATA technology. PATA does not support the following:
- Backward compatibility with SATA.
- Hot swapping of drives.
- Interfaces to access external drives.
- Native I/O command queuing.
How do PATA and SATA cables compare?
The connections for PATA devices were originally made using 40-conductor ribbon cables. These were later supplanted by 80-conductor cables in which every other conductor is grounded, minimizing mutual capacitance (and consequent crosstalk) between conductors.
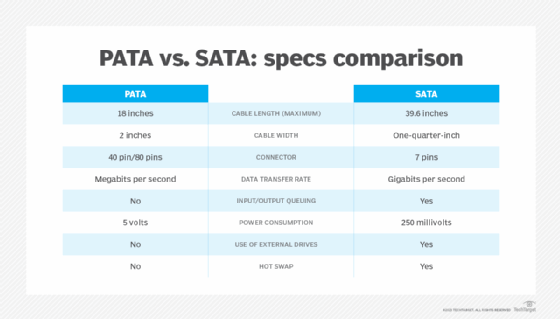
PATA cables are thick and flat with 40-pin connectors, divided into 20 pins on either side. The maximum workable cable length is 46 centimeters (about 18 inches). As a result, PATA cables potentially could restrict the airflow in a computer system, thus limiting its use to a limited number of internal drives.
Parallel ATA was originally called Advanced Technology Attachment until the first SATA drive standard was introduced in 2003. A SATA cable has seven conductors. These cables are more flexible than PATA cables and can be much longer, allowing a system designer more latitude in the physical layout of a system. Because there are fewer conductors, crosstalk is less likely to be troublesome with SATA. The signal voltage is lower as well (250 millivolts for SATA as compared with 5 volts for PATA).
What is PATA's future?
Western Digital, which helped spawn PATA, ceased selling PATA disk drives in 2013. Computer manufacturers generally ship new computers only with SATA connectors to storage devices. Older computers might have SATA ports along with a PATA port, typically designed to support an optical drive.
As noted, the emergence of SATA drives, along with serial-attached SCSI disk and flash drives have rendered PATA storage obsolete in most data centers.
Assess SATA vs. SAS HDD sustained data rates and block size and learn about HDD mean time to failure, annual failure rate and unrecoverable error rate.
