dark web monitoring
What is dark web monitoring?
Dark web monitoring is the process of searching for and continuously tracking information on the dark web. The information can be about an organization, its users or malicious actors on the dark web.
The dark web, sometimes called the dark net, is an encrypted part of the internet that is not indexed by search engines. Dark web content resides on an overlay network that requires a specific configuration to access. One well-known way to access the dark web is through the Tor browser. The Tor browser is a web browser designed for anonymized browsing. It uses multiple layers of encryption to conceal both the source and destination of web traffic.
Organizations can use dark web monitoring tools to find specific information such as corporate email addresses or information about the company. Dark web monitoring services scan multiple sources and index dark web data to make it searchable for users.
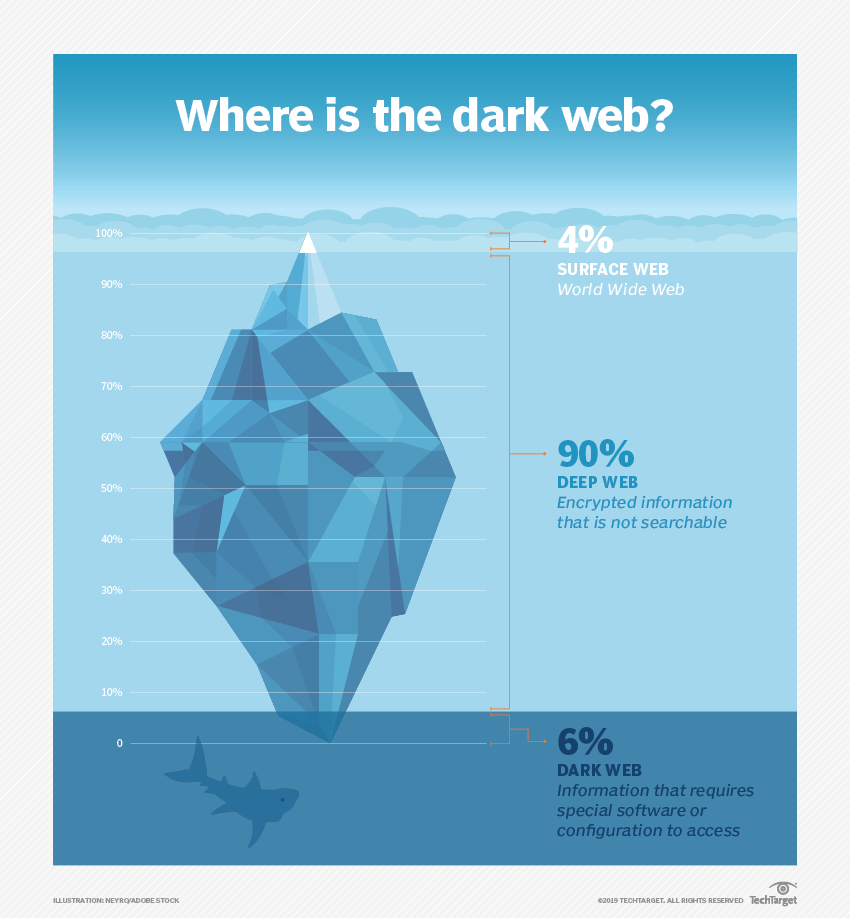
Dark web vs. deep web vs. clear web
The clear web, or surface web, is the part of the internet that is indexed by traditional search engines such as Google, Bing and Yahoo and can be accessed by standard web browsers. This is the part of the web that most users are accustomed to.
The deep web refers to the parts of the web that are not indexed by traditional search engines. The content of the deep web might not be explicitly hidden, just made not to be indexed. There are various ways a web page can be made unindexable. For example, a "noindex" meta tag can be used in the page's HTML, or the content can be password-protected or paywalled. Standard web browsers can access deep web content by searching the URL.
The dark web also refers to sections of the internet that are not indexed by traditional search engines. However, content on the dark web is usually intentionally hidden. This might be to hide illegal content like drug trafficking, identity theft or child exploitation. It might also be used for legal reasons, such as the exchange of proprietary business information or communication between political activists.
The dark web cannot be accessed by traditional web browsers and requires special tools to access it, such as Tor and a decryption key. One famous example of a dark website was the Silk Road marketplace, a black market (now defunct) that could only be accessed via Tor and a special URL.
Why is dark web monitoring important?
Dark web monitoring is important to both organizations and individuals for threat prevention and cybersecurity. Individuals can use dark web monitoring services to see if personal data such as social security numbers, login credentials or credit card numbers appear in illicit dark web marketplaces. Often, hackers gather personal or other sensitive information and sell it in bulk on the dark web, where it could be used for identity theft, phishing campaigns, ransomware or other exploits. These techniques are also used to retrieve personal data and post it on the dark web.
Businesses can use dark web monitoring to stay afoot of corporate data breaches that threaten to expose intellectual property or customer data to illicit marketplaces. Companies face reputation damage or compliance penalties if they fail to protect customer data.
Dark web monitoring can also be used to track the exchange of malware and attacker behavior, which can be useful in developing preventative cybersecurity strategies and faster incident response.
How does dark web monitoring work?
Enterprise dark web monitoring services often come as embedded features in larger security software-as-a-service products. The services monitor multiple sources on the dark web to report exposed assets or identities in real time. The services provide an added level of verification.
Users can configure alerts to let them know when relevant information has been exposed on the dark web. Some intelligence platforms with dark web monitoring capabilities also have intelligence databases and archives of hacker tactics that organizations can use to guide monitoring efforts, evaluate their security posture and enable faster incident response.
There are hundreds of data types that can be leaked on the dark web. Some of the more relevant ones include the following:
- Personally identifiable information (PII). This can include full names, social security numbers and home addresses.
- Financial information. This can include credit card numbers, transaction histories and PIN codes.
- Medical information. This can include medical records, prescription details or health insurance IDs.
- Credentials. This can include API keys, security questions and answers, usernames and passwords.
- Business data. This can include trade secrets, intellectual property and employee records.
- Educational data. This can include financial aid information, admission records and transcripts.
- Communication. This can include call and chat histories and business emails.
Benefits of dark web monitoring
Dark web monitoring offers organizations several core benefits:
- Threat detection. Businesses can use dark web monitoring to find out if they've been part of a corporate breach. The presence of proprietary information, business intelligence, business plans or customer data on the dark web means it might have been exposed.
- Data exfiltration. When exposed information is found via monitoring, organizations can alert users that their information has been compromised and work with them to secure their accounts, such as triggering a password reset.
- Compliance. Dark web monitoring can help companies avoid compliance penalties by preventing customer data breaches that put organizations in violation of privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation.
- Reconnaissance. Dark web monitoring lets companies gather information about the broader cyberthreat landscape. Security professionals can get insights into the tactics, trends and threats of cybercriminals, and proactively defend against attackers. Dark web monitoring can supplement other tools used to gather preemptive threat intelligence, such as the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
- Automation. Many dark web monitoring offerings scan automatically and continuously for information about the organization.
- User and enterprise versions. Dark web monitoring comes in security products for larger organizations as well as individual consumers.
Limitations of dark web monitoring
While there is valuable information on the dark web, such as activist communications or information about a company's brand, not all of it is exclusive to the dark web. Some of the information available on the dark web is also available on the clear web.
Also, hackers have other ways of sharing information privately. The dark web can be used for initial postings and trust building between hackers before they take more sensitive communications offline to private chat services such as Telegram, Discord and other encrypted chats. As organizations and law enforcement have gotten better at parsing the dark web, hackers have found other channels to share secret information.
Tips for dark web monitoring
Dark web monitoring should be used in conjunction with other traditional security practices to maintain a strong security posture. Other practices to be used in conjunction with dark web monitoring include:
- Identity management. Requiring multifactor authentication -- such as personal identification numbers (PINs) or biometric data -- for every user can help mitigate the risk of compromised credentials. Technology for identity threat protection can categorize identities and automatically implement conditional access based on risk. It can also swiftly remove access when threats are detected.
- Security culture. Chief information security officers can establish a strong security culture by improving security awareness among employees through trainings and creating a broad understanding that every employee have their share of responsibility for information security.
- Update security policies. It's important for companies to update security policies in line with the most recent threat trends. Also practice strong security hygiene by taking asset inventories and practicing vulnerability management.
- Patch management. Companies need to stay on top of patch management and software updates to fix vulnerabilities and protect data. However, companies should be aware of fake update messages in emails or pop-ups. Updates should always be run through the OS or choose to automatically update when available in the settings of the device.
