model-view-controller (MVC)
What is model-view-controller (MVC)?
In programming, model-view-controller (MVC) is an architectural design pattern that organizes an application's logic into distinct layers, each of which carries out a specific set of tasks. The layers also interact with each other to ensure that the application's functionality is delivered in a coordinated and consistent manner. The MVC methodology incorporates the entire application, from the user interface (UI) to the underlying data model.
The MVC system, which originated in the 1970s in connection with building graphical UIs, is widely used in program development, especially for today's web applications and object-oriented programming (OOP). Developers use a range of programming languages, including Java, Python, JavaScript, C#, Swift, Perl and PHP, to build applications based on MVC. Most of these languages also have MVC frameworks available to them to help streamline the development process. Popular MVC frameworks include Django, Ruby on Rails, Symfony, Catalyst and CherryPy, among many others.
MVC offers development teams important benefits. Programmers can build components simultaneously without stepping over each other's work, and they can reuse components. They can also deploy and maintain the components independently from others. MVC makes it easier to build large, complex applications, leading to faster, more efficient development efforts. In addition, MVC supports test-driven development, while making it possible to test and troubleshoot components individually.
MVC design layers
The MVC methodology separates an application's logic into three distinct layers:
- Model. The model layer is responsible for the application's data logic and storing and retrieving data from back-end data stores. The model layer might also include mechanisms for validating data and carrying out other data-related tasks. This layer is responsible for maintaining all aspects of the data and ensuring its integrity and accessibility.
- View. The view layer provides the UI necessary to interact with the application. It includes components needed to display the data and enables users to interact with that data. For example, the view layer might include buttons, links, tables, drop-down lists or text boxes.
- Controller. The controller layer contains the application logic necessary to facilitate communications across the application, acting as an interface between the view and model layers. The controller is sometimes viewed as the brains of the application, keeping everything moving and in sync.
It can be difficult to describe the three layers in specific terms because MVC can be implemented in different ways. For example, some developers use MVC frameworks to build their application, and these frameworks can differ from one product to the next in terms of how they implement MVC. In addition, each development team can have its own preferences for how it builds MVC-based apps, and those preferences can vary between development projects.
Conceptualizing model-view-controller
Conceptually, however, each approach to MVC development is similar in that they all attempt to follow the principle of separation of concerns (SoC), a design model that divides an application into distinct units with minimal overlap in functionality.
Figure 1 shows one way to conceptualize MVC. In this approach, the controller handles all user interaction, such as when the user clicks a button or selects a value from a list. The controller also feeds data to the view component in response to user requests. In addition, the controller interfaces with the model component, which sends updated data to the view element. The view component is concerned only with rendering the data provided by the controller, model or both.
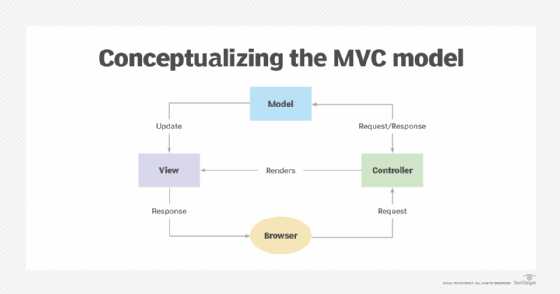
The amount of responsibility assigned to each component and the communication flow between them depend on the individual implementation. For example, the controller might handle data validation, or it might pass that responsibility onto the model. Or the controller might make all decisions about user input or let the view component perform the initial filtering, such as determining whether simple actions should be handled by the view component or the controller.
Development teams should have a good sense of how they conceptualize MVC before they start to design and build their applications. For example, in Figure 1, communication occurs between the view element and model and between the view component and controller. But not all teams plan their implementations this way. They might, for example, decide that the model should never communicate with the view or the entire structure should follow a strict linear process, as in Figure 2.
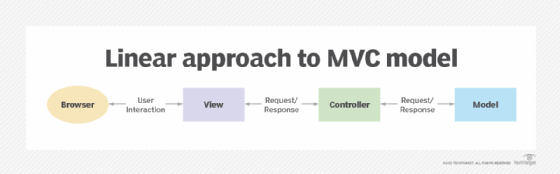
In this linear approach, users interact solely with the view element through a browser, the view interacts solely with the controller and the controller interacts solely with the model.
Each development team may have its own interpretation of how MVC should be implemented. If it's using an MVC framework, it might also need to work around how the framework structures an application. The important point is that the team adheres to the SoC principle when designing and building its applications, with each component responsible for a discrete set of tasks.
Learn about five types of software architecture design worth knowing, and compare the MVC vs. model-view-viewmodel architecture patterns for application modularity. Check out five proven patterns for resilient software architecture design.
