ESG vs. CSR vs. sustainability: What's the difference?
Environmental, social and governance and corporate social responsibility are related but different concepts that can be combined to boost corporate sustainability.
The terms environmental, social and governance and corporate social responsibility are being used more widely to describe how businesses can show their commitment to sustainability.
The terms have some overlapping meaning and are sometimes used interchangeably. But with tightening expectations on corporate practices and increasing concerns surrounding environmental sustainability, businesses should know what these terms mean, how they differ and where they overlap.
In recent years, environmental sustainability has become a top business focus, and for good reason. With growing fears about the state of the environment and the ability to prove ROI for sustainability practices, businesses are under increasing pressure to behave ethically and responsibly, and demonstrate they are doing so.
For example, the European Union's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) came into force in January 2023, introducing environmental, social and governance (ESG) reporting standards for about 50,000 companies. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) also enforced climate disclosure rules that resulted in new ESG reporting and compliance requirements for publicly traded companies.
This article is part of
ESG strategy and management guide for businesses
What is ESG?
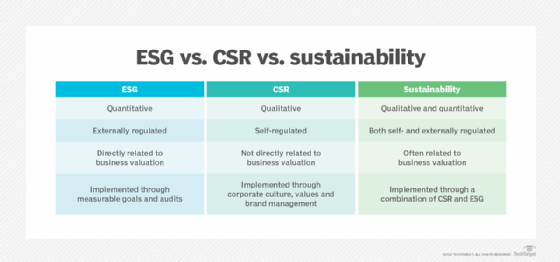
ESG is a quantifiable assessment of sustainability and business practices. ESG strategy focuses on reaching certain performance metrics, setting measurable goals for them and conducting audits to verify the metrics and related disclosures are accurate.
There are explicit criteria surrounding ESG. For example, ratings agencies like Bloomberg, MSCI, S&P Global and Morningstar's Sustainalytics subsidiary give companies ESG scores using different sets of performance criteria. Investors use these scores to evaluate businesses and, ultimately, inform their investment choices. Businesses create ESG reports to appeal to investors and other stakeholders and meet regulatory compliance requirements.
ESG encourages businesses to behave ethically, but it also helps define a company's financial value and its compliance record. In turn, it helps investors avoid losses when companies engage in risky behavior. Different investment firms may rate ESG criteria differently based on their own priorities.
The three aspects covered by ESG initiatives are the following:
- Environmental. These criteria might include corporate climate policies, energy use, waste management and treatment of animals.
- Social. These criteria cover the company's relationships with stakeholders other than investors, including employees and community members. Meeting ESG's social criteria might involve implementing diversity, equity and inclusion initiatives, making donations, encouraging employees to volunteer and engaging in supply chain sustainability and ethics practices.
- Governance. These criteria hold companies to ethical accounting and financial reporting standards, and include factors such as board diversity, executive compensation and rules on ethical business practices.
What is CSR?
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a self-regulating business model that aims to improve society and the environment. It's a loose, general framework for corporate behavior that can vary in terms of its implementation. The nature of CSR is qualitative, although the ISO 26000 voluntary standard does help companies define social responsibility and provides practical guidance for achieving it.
Good CSR helps companies maintain a positive brand image and boosts stakeholder morale. Companies usually highlight the achievements of their CSR efforts in annual reporting.
In one particularly notable example of CSR, Yvon Chouinard, the founder of apparel company Patagonia, pledged all of its future profits to an organization that fights the climate crisis in September 2022. Money not reinvested in running the business is now distributed to the charity. That amounts to about $100 million per year, according to Patagonia.
Other more conventional examples include Starbucks' commitment to eliminate plastic straws globally and Better World Books, an online used bookseller, which donates a book to someone in need for each book purchased.
What is sustainability?
In its broadest definition, sustainability refers to the ability to support and continue a process over time.
Corporate sustainability encompasses the practices that keep a business going and perpetuate its success. More specifically, it involves the coordination and management of environmental, social and financial demands to ensure a business is responsible, ethical and continually successful. Sustainability lets a company meet present needs without compromising its ability to meet its needs in the future.
Business sustainability, as it's also known, is often broken into three pillars:
- Economic, or profit.
- Social, or people.
- Environmental, or planet.
These three pillars are sometimes referred to as the triple bottom line -- a play on the traditional concept of the bottom line, which refers to immediate profit as the No. 1 priority for businesses. By comparison, the triple bottom line takes a broader view that includes the overall economic value created by companies and their social and environmental impact.
The term sustainability is often used in other, nonbusiness contexts to refer to environmental, social, policy or economic sustainability.
Where do ESG, CSR and sustainability overlap?
Sustainability is the umbrella that both ESG and CSR fall under and contribute to. ESG and CSR are both methods that businesses can use to demonstrate their commitment to sustainable business practices. CSR can be seen as the idealistic, big-picture perspective on sustainability, while ESG represents the practical, detail-oriented approach.
CSR can also be seen as the precursor to ESG. Companies self-regulate and commit to sustainable practices with the aim of making a positive effect on society. Then, the efforts undertaken in a CSR strategy can be refined and fit into ESG metrics. ESG data can then be publicly disclosed and shared through ESG reports. ESG puts a quantifiable stamp of credibility on the broad management philosophy of CSR. A business needs both practices in order to be truly sustainable.
How to implement each
ESG starts with CSR. For guidance on CSR, companies can consult voluntary standards, such as ISO 26000. When developing a CSR program, companies should consider the following:
- The company's core competencies. A core competency is something the company is uniquely good at. It could be buying power, product quality or innovation capabilities. For example, a company that excels at minimizing costs can direct money toward an environmental activism organization. Companies should strive to embed sustainability into existing processes.
- The issues customers care about. These could be environmental or social issues identified in a survey, or the aspects of the company or brand that resonate with customers. A company could survey customers about issues they care about most and align the results with a product they respond positively to.
- The issues employees care about. Companies can survey employees about what matters most to them and plan programs based on the results, while also offering volunteer opportunities.
- Quantifying the results of efforts tied to the bottom line. For example, a company that sets a goal to reduce waste might want to measure its progress to share with investors and other stakeholders in an ESG report later on.
- Current societal, industry and environmental trends. If a climate report has just been released, a company might align its goals with the data contained in the report. If a natural disaster has taken place, a company might align its CSR strategy with the discourse surrounding the disaster and participate in the recovery effort in some way.
When constructing an ESG strategy, companies should also consider the above factors. ESG strategies must also consider reporting laws and requirements, as well as investor interests, because ESG is more closely tied to compliance and stock performance.
There are many ESG reporting frameworks and standards that companies can consult when developing a strategy, including the following examples:
- United Nations (U.N.) Sustainable Development Goals.
- U.N. Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights.
- IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards, which are unified reporting standards developed by the International Sustainability Standards Board that build on existing ones, such as the SASB Standards and CDSB Framework.
- CDP, originally founded as the Carbon Disclosure Project.
- The Global Reporting Initiative's GRI Standards.
- Reporting recommendations from the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures.
- Workforce Disclosure Initiative.
Below are some general steps to begin formulating an ESG strategy:
- Assemble a qualified, cross-functional team of stakeholders.
- Perform a business impact analysis.
- Perform an ESG materiality assessment to determine what is important to the company.
- Define measurable goals.
- Develop a roadmap to meet goals.
- Implement action plans and report progress along the way.
Which approach is better?
ESG provides a clearer material path to business sustainability. However, a philosophy of CSR is necessary to implement an ESG plan effectively. ESG might also be considered better because it involves a more comprehensively designed and measurable plan regulated by outside forces -- not just the company carrying out a loosely defined CSR approach. Businesses will likely need the quantitative element of ESG to comply with the EU's CSRD regulations and the SEC's climate risk disclosure rule.
One area where CSR may have an advantage over ESG is in promoting elements of a corporation's sustainability goals to customers in order to boost employee morale and engagement. CSR is beneficial for fostering a company culture that empowers employees to participate in initiatives aimed at creating a positive social impact.
Ben Lutkevich is an editor for TechTarget's IT Infrastructure group. Previously, he wrote definitions and features for Whatis.com.