Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC)
What is Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC)?
Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC) is an eight-bit encoding scheme that standardizes how alphanumeric characters, punctuation and other symbols are interpreted by a computer's operating system (OS) and applications. The encoding scheme is typically referenced by the EBCDIC acronym, which is pronounced either "ehb-suh-dik" or "ehb-kuh-dik."
EBCDIC was developed by IBM in 1963 to complement the punched cards used for storage and data processing in the early days of computing. Although punched cards are now obsolete, the encoding scheme itself is still used today, primarily in IBM mainframe and midrange computers running the IBM Z/OS or IBM I operating systems. Some third-party systems also use the EBCDIC standard, such as Fujitsu Siemens mainframe computers running the BS2000 OS.
EBCDIC is similar to the American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) encoding scheme, although the two are incompatible. Because ASCII has become such a widely accepted standard, it is now used more extensively than EBCDIC. Operating systems that support EBCDIC invariably support ASCII as well, along with Unicode.

EBCDIC code pages
The EBCDIC encoding scheme is defined through multiple code pages that each map out a character set to meet specific requirements. A code page is identified through its Coded Character Set Identifier (CCSID). The page can contain up to 256 characters, with each character represented by an 8-bit binary value (a string of eight 0s or 1s). The first four bits indicate the type of character -- such as letter, number or symbol -- and the last four bits uniquely identify the character for the specific type.
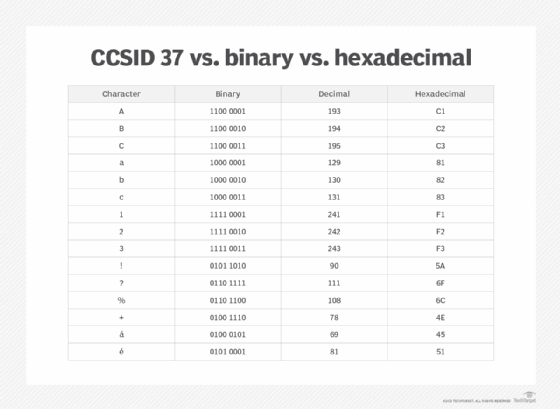
Each hexadecimal value in the EBCDIC character set has an equivalent binary value. The binary equivalent of the hex value A7 is 1010 0111. The first four bits, 1010, are equivalent to the hex value A and indicate that the character is a lowercase letter or some type of special character. Lowercase letters might also start with the binary value 1000 (hex 8) or 1001 (hex 9).
The second four bits for the letter x are 0111. This value is unique within the group of characters that start with 1010 (hex A), but it is not unique across the entire code page. For example, the uppercase P has a binary value of 1101 0111 (hex D7). Its last four binary digits are the same as the letter x.
The characters in an EBCDIC code page can also be represented by the decimal values 0 to 255. For example, the decimal value for the lowercase x is 167 and for the uppercase P is 215. Figure 3 shows a sample of characters in the CCSID 37 code page, along with their binary, decimal and hexadecimal equivalents.
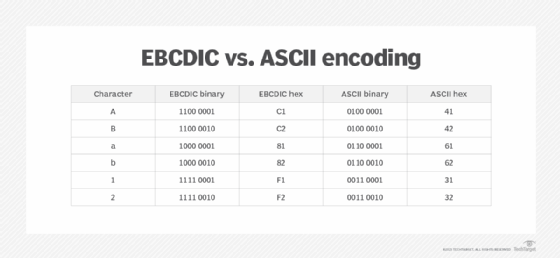
Although EBCDIC code pages are still in use, most of today's computers rely primarily on ASCII and Unicode encoding schemes, which have their own sets of codes pages. EBCDIC code pages are not compatible with other types of codes pages. Figure 4 lists several of the differences between EBCDIC and ASCII encoding. For example, EBCDIC assigns the binary value 1100 0001 (hex C1) to the uppercase letter A, and ASCII assigns the binary value 0100 0001 (hex 41).

Because different encoding schemes exist, it is sometimes necessary to convert code files from one scheme to another. Such conversions can be done using specialized conversion software or services. For instance, vEdit offers both conversion software and conversion services, and Microsoft's Azure Logic App makes it possible to convert EBCDIC to ASCII. In addition, Z/OS UNIX can automatically convert data from ASCII to EBCDIC.
See how to convert binary to decimal and vice versa, and learn about binary-coded decimal and how it is used.
