cluster
What is a cluster?
Clusters are typically defined as collections or groups of items with similar or different characteristics. The group or collection of items constitutes a cluster. The following are three definitions of a cluster related primarily to technology.
1. Enterprise computing. In a computer system, a cluster is a group of servers and other resources that act like a single system and enable high availability, load balancing and parallel processing. These systems can range from a two-node system of two personal computers (PCs) to a supercomputer that has a cluster architecture.
2. Personal computing. In PC storage technology, a cluster is the logical unit of file storage on a hard drive and is managed by the computer's OS. Any file stored on a hard disk takes up one or more clusters of storage. A file's clusters can be scattered among different locations on the drive. The clusters associated with a file are tracked in the hard disk's file allocation table (FAT). When a user reads a file, the entire file is obtained without the user knowing where it's stored.
Since a cluster is a logical rather than a physical unit – it's not built into the hard disk -- the size varies. The maximum number of clusters on a hard disk depends on the size of a FAT entry. DOS 4.0's FAT entries were 16 bits in length, allowing for a maximum of 65,536 clusters. Windows 95 OSR2 supported a 32-bit FAT entry, allowing enough clusters to support up to 2 TB of data, assuming the hard disk has enough capacity.
In a cluster, the smallest file -- or even a directory -- takes up the entire cluster. Thus, a 10 byte file will take up 2,048 bytes if that's the cluster size. Many OSes set the cluster size default at 4,096 bytes or 8,192 bytes. Until Microsoft Windows 95 OSR2, the largest hard disk that could be supported in a single partition was 512 MB. Larger hard disks could be divided into up to four partitions, each with a FAT capable of supporting 512 MB of clusters.
3. Terminals and workstations. In some products, a cluster is a group of terminals or workstations attached to a common control unit.
Applications and benefits of clustering
Clustering apps, whether resident in the OS or as a separate tool, support many important user requirements, and fall into the following categories:
High-performance computing
High performance computing (HPC) is achieved by using the performance capabilities of multiple processing nodes in the cluster and adding devices to a system. Clustering software ensures added resources meet user requirements for high speed and storage capacity.
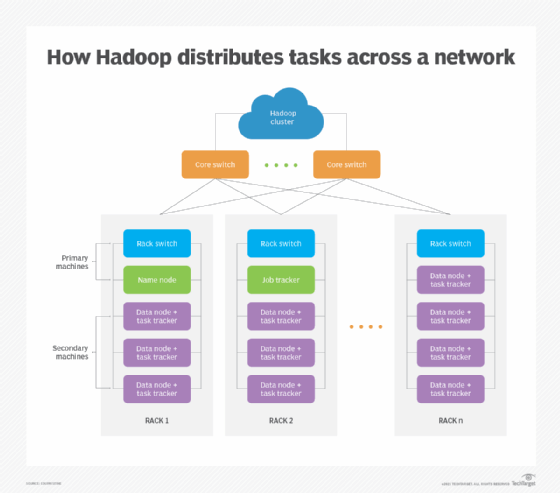
High availability
High availability of processor and storage resources -- also called fault tolerance -- ensures that a loss of or disruption to a processing or storage element in a computer cluster won't disrupt overall production. Members of the cluster can be designated as backup if another device fails. When this happens, cluster failover software quickly shifts processing or storage to the backup or standby system.
High-availability CPU and storage capabilities boost redundancy across a cluster, while operational reliability relies on all cluster members as needed. Clustering multiple devices ensures availability; enough resources to limit the negative effects of a disruption provides resilience.
Load balancing
Load balancing spreads processing activities across cluster nodes to optimize performance and spread workloads evenly across devices. Load balancing clusters improves performance and use among single nodes in a cluster. Processing activities spread across multiple systems achieves active/active processing and economies of scale.
Resource scalability
Computing and storage are expanded or scaled in two ways:
- vertically, where more storage or processing is added to the primary device; or
- horizontally, where more devices are added to the cluster itself.
Each approach is used for different user applications. Clustering software accommodates both types of scaling.
Container management
Containers combine all the resources needed to run an application into a single package. Clustering software is used to manage individual containers as if they were members of a cluster.
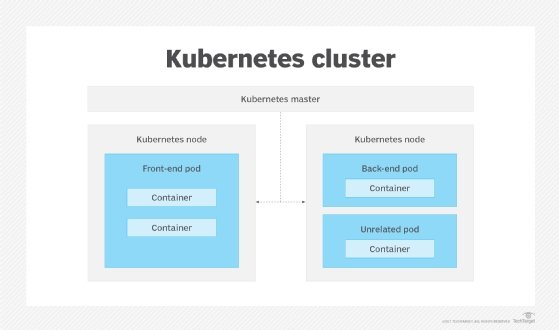
Kubernetes open source software facilitates the preparation, organization, scaling and deployment of container-based applications. Kubernetes clusters containing multiple containers, or pods, handle functions such as resource management, load sharing, fault tolerance and security requirements.
Managing cloud resources in clusters
Clustering isn't limited to on-premises data centers. It can be used with cloud computing and storage resources. Clusters are extended beyond the data center into a cloud provider's resources, with a set of storage and compute nodes implemented on VMs.
Clustering plays a key role in high-availability computing. Find out about the three best practices required for high-availability computing.
