corporate division
What is a corporate division?
A corporate division, or a business division, is a discrete part of a company that may operate under the same name and legal responsibility or as a separate corporate and legal entity under another business name.
Corporate divisions are an integral part of modern business, and for enterprise resource planning purposes allowing companies to structure their operations effectively and allocate resources efficiently.
Types of corporate divisions
In the realm of corporate architecture, there are various types of divisions that play pivotal roles in shaping and steering the operations of a business entity.
Strategic business units
Strategic business units (SBUs) represent semi-autonomous entities within an organization that operate as distinct businesses with their strategic direction and management. The primary purpose of SBUs is to allow companies to focus on specific market segments, products or services, thereby facilitating a more targeted and responsive approach to diverse business components.
For example, in the automotive industry, a car manufacturer might establish different SBUs for luxury vehicles, electric cars and commercial vehicles. Similarly, in the consumer goods sector, a multinational corporation may have SBUs dedicated to personal care, home care, and food and beverages.
These distinct SBUs enable companies to tailor strategies and planning, resources, operational tactics and processes to the unique demands of each market segment, enhancing their competitive edge.
Business segments or units
Business segments or units are structured divisions within an organization that are primarily aligned with specific operational functions, such as sales, marketing, research and development, or customer support. These units play a pivotal role in streamlining and optimizing the internal processes and workflows related to their respective functions.
Business units contribute to the overall organization by serving as specialized hubs that cater to the diverse needs of the enterprise. For instance, a dedicated marketing unit focuses on crafting and implementing promotional strategies, while a research and development unit drives innovation and product enhancement. These specialized units collectively bolster the operational efficiency and holistic functioning of the company.
Divisions by product or service lines
Companies often create divisions that are dedicated to specific product lines or service offerings, allowing for a more concentrated approach to innovation, marketing and strategic development within those domains.
The divisional structure based on product or service lines offers the advantage of focused attention and targeted resource allocation to drive innovation and growth within specific business domains. However, this structure can potentially lead to challenges related to inter-divisional coordination and resource sharing, which businesses must carefully manage to ensure optimal integration and operational fluidity among corporate divisions.
Advantages of corporate divisions
In organizational management, corporate divisions serve as indispensable assets, offering many advantages that elevate modern enterprises' operational capabilities and strategic acumen.
Increased focus and efficiency
Corporate divisions play a pivotal role in streamlining operations by enabling focused attention on specific market segments, product lines or operational functions. By delineating clear boundaries of responsibility and authority within divisions, organizations can achieve greater operational efficiency through targeted resource allocation, specialized expertise and streamlined decision-making processes.
Notable examples of companies benefiting from a divisional structure include conglomerates like General Electric and Procter & Gamble. These industry giants have used divisional setups to effectively manage diverse business vertical markets, drive innovation within specialized units and adapt swiftly to changing market dynamics by tailoring strategies to individual divisional needs.
Greater flexibility and adaptability
One of the key advantages of corporate divisions is their ability to respond to market changes independently. By granting divisions a degree of autonomy, organizations empower them to adapt swiftly to evolving market trends, customer demands and competitive landscapes.
This agility in response allows divisions to pivot strategies, innovate rapidly and capitalize on emerging opportunities with precision.
Decentralization in decision-making facilitated by corporate divisions accelerates the responsiveness of organizations to dynamic market conditions. Empowering divisions to make localized decisions based on their unique market insights and operational needs not only expedites the decision-making process but also fosters a culture of innovation, accountability and strategic alignment at all levels of the organization.
Improved performance evaluation and accountability
Through the lens of corporate divisions, organizations can enhance the granularity of performance evaluation by assessing the contributions and outcomes of individual divisions within the broader context of the company. This targeted evaluation allows for a more nuanced understanding of operational effectiveness, resource utilization and strategic impact, thereby enabling informed decision-making and continuous improvement initiatives -- for example, using the Kaizen method.
Setting division-specific goals is instrumental in aligning the efforts and objectives of each division with the overarching strategic planning and direction of the company. By defining clear and measurable targets for each division, organizations not only enhance accountability and performance tracking but also foster a sense of ownership, purpose and motivation within divisional teams, driving collective success and organizational alignment.
Implementing and managing corporate divisions
Transitioning from the conceptual realm to practical implementation, the efficacy of corporate divisions hinges on a meticulous blend of structural considerations, cross-functional team collaboration frameworks and effective evaluation mechanisms.
Within this framework, the interplay between overarching strategic vision and divisional autonomy sets the stage for a strategic choreography that harmonizes diverse capabilities, nurtures innovation and propels organizational resilience in the face of dynamic market forces.
Structural considerations
Designing an organizational structure conducive to effective divisions involves establishing clear lines of authority, delineated responsibilities and optimized resource allocation. This could entail a mix of functional, divisional or matrix structures tailored to the organization's unique needs and strategic imperatives.
It's important to align the structure with the company's overarching strategic objectives while ensuring that divisions have the autonomy and resources required to fulfill their designated roles.
Establishing solid reporting relationships and communication channels is also pivotal for ensuring coherence and cohesion among corporate divisions. Clear reporting lines facilitate streamlined decision-making and coordination, while effective communication channels, such as regular meetings, digital collaboration platforms and cross-divisional task forces, promote cooperation and alignment across divisions.
Cross-functional collaboration
Promoting collaboration and cooperation among divisions is essential for harnessing collective expertise and resources dispersed across the organization. This can be achieved through initiatives such as cross-divisional project teams, knowledge-sharing platforms, and inter-divisional workshops aimed at fostering a culture of collaboration, innovation and shared strategic vision.
Despite the benefits, inter-divisional cooperation can present challenges however, ranging from conflicting priorities to resource allocation disparities. Overcoming these challenges necessitates strong leadership, transparent communication and a culture that values broader organizational goals over individual divisional interests.
Implementing effective conflict resolution mechanisms and fostering a spirit of empathy and mutual support can further bolster inter-divisional cooperation.
Evaluation and monitoring
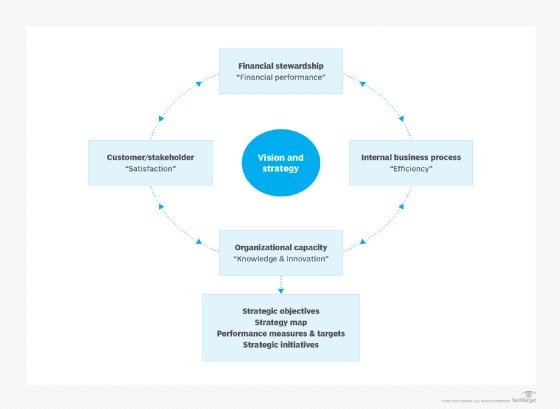
Measuring the success of divisions involves tracking a holistic set of business metrics, including financial performance, customer satisfaction, operational efficiency and strategic goal attainment. Using balanced scorecards or similar frameworks can provide a comprehensive view of divisional performance against predetermined targets and strategic milestones.
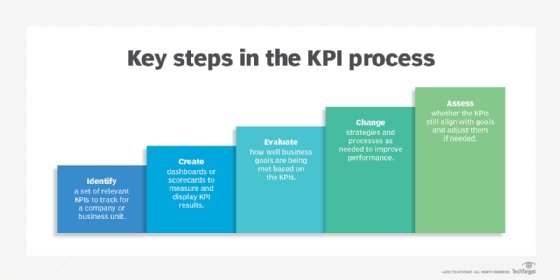
Identifying pertinent key performance indicators (KPIs) enables organizations to gauge the effectiveness and impact of divisions. These KPIs may encompass revenue growth, market share, customer retention rates, innovation pipeline strength and operational efficiency indices, offering a multifaceted view of divisional contributions to the organization.
Looking forward for corporate divisions
Corporate divisions serve as essential organizational constructs that yield myriad benefits, including enhanced focus, flexibility and performance evaluation. By effectively implementing and managing these divisions, organizations can navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape with agility and strategic clarity.
The future of corporate divisions is poised to witness further evolution, shaped by advancements in digital team collaboration tools and technologies, adaptive organizational structures and a heightened focus on cross-functional integration and strategic alignment.
Explore the four leading team collaboration tools and some of their competitors. See how to turn customer feedback into actionable insights. Read how to set business goals in this step-by-step guide.
