open system
What is an open system?
In computing, an open system is a platform that can be modified and extended and has freely available documentation. An open system might also be called open architecture or open source. Its opposite would be a closed system, sometimes called proprietary or closed source.
Characteristics of open systems include making available the source code, which can be used for understanding and possible modification or improvement; portability, which allows the system to be used in a variety of environments; and interoperability, which allows the system to function with other systems. Open systems are usually modular, which allows for portions to be added, removed or modified as needed without affecting other portions.
The term open system was first used in the 1980s. It was applied to the Unix operating system, which had well-documented programming interfaces and hardware compatibility. This contrasted with the popular mainframes or personal computers that used proprietary hardware and software.
The Linux operating system fully exemplifies the open system model.
Today, the term open source is more commonly used to refer to open systems. This is even true for open hardware standards. For example, the Tesla motor's charge port has been released as an open standard, now called the North American Charging Standard.
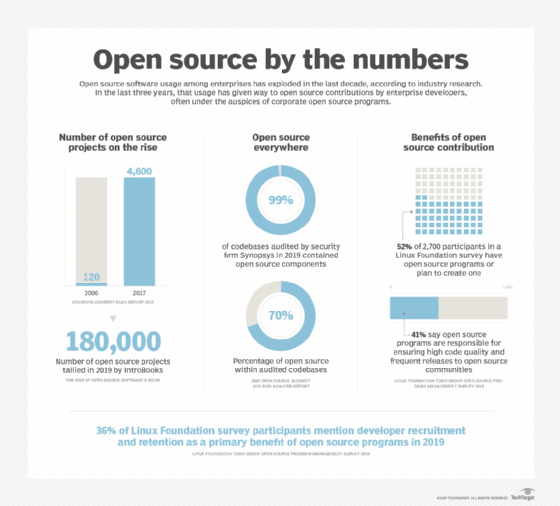
What is an open system in systems theory?
In systems theory, an open system is a system that interacts with other systems by having inputs or outputs. A closed system is one that is totally self-contained and does not input or output anything.
As an example of an open system, consider the human body. It requires the inputs of food and oxygen to continue to function, and it outputs carbon dioxide and other waste, which must be handled by other systems. Earth, as a whole, can be considered a closed system, as nothing generally enters or leaves it except the energy from the sun.
The concept of an open or closed system can also have value in business and software design. The inputs and outputs of a company or process can be analyzed. Software can be designed to be entirely self-reliant or to exchange data with external programs and sources.
An open system might also be fully transparent, or open to inspection by outsiders. For example, in an open government, all government documents are available to the public, and anyone can attend or view meetings of the legal bodies.
Consider these open source cloud platforms and tools and these open source cloud monitoring tools. Learn the difference between open core vs. open source.
