Basel II
What is Basel II?
Basel II is an international business standard that requires financial institutions to maintain enough cash reserves to cover risks incurred by their operations. The Basel accords are a series of recommendations on banking laws and regulations issued by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. The name for the accords is derived from Basel, Switzerland, where the committee that maintains the accords meets.
Basel II was released in 2004 and improved on Basel I, which was released in the 1988. Basel II offers more complex models for calculating regulatory capital.
Essentially, the accord mandates that banks holding riskier assets should have higher capital requirements than those maintaining safer portfolios. Basel II also requires companies to publish both the details of risky investments and risk management practices.
The full title of the accord is Basel II: International Convergence of Capital Measurement and Capital Standards: A Revised Framework.
What are the 3 pillars of Basel II?
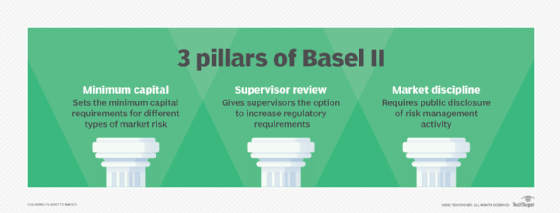
Basel II addresses the following three areas:
- Minimum capital. Basel II introduced a tiered system for different types of capital. It set regulatory minimums for each tier based on the quality of capital. Tier 1 capital is the highest quality of capital, such as shareholder equity. Tier 2 and tier 3 are lower quality capital, such as subordinated loans. Basel II mandates that institutional managers must be more risk sensitive with capital allocations.
- Supervisor review. National banking regulations require banks to enforce risk ratings and capital assessment processes. This supervisory review reduces the scope of regulatory arbitrage by attempting to align the real or economic risk precisely with regulatory risk assessment.
- Market discipline. This sets the disclosure requirements for individual banks. Banks must disclose all information related to risk management policies, and individual regulators are assigned to enforce the rule.
Basel II also mandated a standardized approach to how operational risk, market risk and credit risk are separated and quantified. Banks must meet minimum capital requirements against all three types of risk and exposures. Because operational risk is hard to quantify, gross income is generally used as a proxy for it.
Pros and cons of Basel II
Basel II expanded upon Basel I to help regulators handle the financial innovations and new financial products that came about since the inception of Basel I in the 1980s. For example, Basel II required that banks maintain a capital reserve equal to at least 8% of their risk weighted assets.
Basel II attempted to discourage risky behavior, but it also resulted in several strategies banks used to make risky investments. Among these strategies were ones that resulted in the emergence of the subprime mortgage market and moving higher-risk assets to unregulated parts of holding or parent companies. Another tactic was to transfer the risk directly to investors by securitization, which is the process of taking a nonliquid asset or groups of assets and transforming them into a security that can be traded on open markets.
Some experts contend that the risky behavior Basel II enabled was in part responsible for the subprime mortgage meltdown and accompanying Great Recession of 2008.
Basel III vs. Basel IV
In 2009, after the subprime mortgage meltdown, the Basel committee began working on Basel III. A key goal of Basel III was to institute an output floor -- lower limits on a bank's capital requirements -- to address comparability and consistency issues across banking systems.
The original 2015 implementation date for Basel III was repeatedly pushed back. The final Basel III reform package, which the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision passed in 2017, is now known as Basel IV. It is expected to be implemented Jan. 1, 2023.
One requirement of Basel II was for banks to provide regulatory risk assessments. Learn how and why the costs of risk assessments vary.
