What is SRAM (static random access memory)?
SRAM (static RAM) is a type of random access memory (RAM) that retains data bits in its memory as long as power is being supplied. Unlike dynamic RAM (DRAM), which must be continuously refreshed, SRAM does not have this requirement, resulting in better performance and lower power usage. However, SRAM is also more expensive than DRAM, and it requires a lot more space.
SRAM is a category of volatile RAM that uses flip-flops rather than capacitors to store data -- in the form of binary digits (bits). This inherent design feature means that constant refreshing is not needed to retain the data in SRAM. The term static in its name comes from the fact that no action is needed to keep the data intact.
By eliminating the need for time-consuming refresh cycles, SRAM reduces latency and facilitates faster data access. These capabilities can be particularly critical for key components, like speed-sensitive central processing unit caches. In general, SRAM is better able to improve the speed and performance of computing systems due to its ability to facilitate fast information retrieval by processors.
What is SRAM used for?
SRAM typically isn't used for a computer's main memory because of its cost and size. Most computers use DRAM instead because it supports greater data densities at a lower cost per megabyte.
That said, SRAM is often used for other purposes. For example, it might be part of a RAM digital-to-analog converter on a computer's video or graphics card. It might also be used in a disk drive as buffer cache; in a peripheral, such as a printer or liquid crystal display; or in a network device, such as a router or switch. Two of the most common uses of SRAM are for a computer's cache memory, such as a processor's L2 or L3 cache, and in high-speed registers.
SRAM can be found in other devices as well.
For example, SRAM chips are often used in cellphones, wearables and other consumer electronics. They might also be embedded in medical products, which can include anything from hearing aids to body area networks that comprise multiple devices embedded in the body. In all those devices, fast data access is imperative, making SRAM more suitable than DRAM or non-volatile flash memory. In addition, SRAM is used in toys, appliances, automobiles, industrial equipment and a wide range of internet of things (IoT) devices.
Types of SRAM
Over the years, many types of SRAM have been developed with different designs and to suit different applications.
The most common type is binary SRAM, where a memory cell stores a bit in one of two binary states: 0 or 1. This SRAM is best for applications that require low latency and fast data access. Ternary SRAM stores three states per cell, providing higher data density and more efficient read/write operations.
SRAM is also available in synchronous and asynchronous variants. Synchronous SRAM is synchronized to the system clock, whereas asynchronous SRAM works out of sync with the system clock. The former is suitable for high-speed digital signal processing in digital communications and other applications where data timing must be precisely coordinated between SRAM and the system clock. The latter is best for high-speed applications. Quad data rate SRAM is a specific type of synchronous SRAM that provides high speed and efficiency by synchronizing data access with the rising and falling edges of the system clock signal.
Low-power SRAM is also available. This type of SRAM consumes less power than other types, particularly in active and standby modes. It is suitable for portable devices where such modes are common occurrences.
What are the primary advantages of SRAM?
Speed is the biggest advantage of SRAM. As long as power is supplied, SRAM retains data. Also, since it does not require time-consuming refresh cycles, SRAM enables fast data access and offers lower latency. Those two qualities make SRAM ideal for applications where speed is essential.
Data integrity is another area where SRAM has an advantage over some other memory types. The integrity of data is consistently maintained because SRAM does not use capacitors and, again, because it does not require constant refreshing.
Modern SRAM is now available that uses techniques like power gating and dynamic voltage scaling. As a result, it consumes less power -- both in active and standby modes -- making it more energy-efficient than its predecessors. Even so, SRAM is best suited for applications where power efficiency is less of a priority than high access speeds and responsiveness -- ideally real time -- low latency and data integrity.
SRAM also generates less heat and is more resistant to radiation.
Drawbacks of SRAM
SRAM devices are low-density devices with a small memory capacity, making them unsuitable for applications that require high capacity. Complexity and bigger size are other drawbacks of SRAM, both of which result in higher cost. For these reasons, SRAM is preferred for high-speed cache memory rather than low-speed main memory for which DRAM is usually the preferred choice.
SRAM is also volatile memory, i.e., it loses data when not connected to a power source. This is why it is typically used in applications where its volatility may be acceptable in exchange for faster data access and high data transfer rates. Examples include consumer devices, medical devices, network switches and routers, processor registers, graphics processing units, network devices, programmable logic devices and IoT devices.
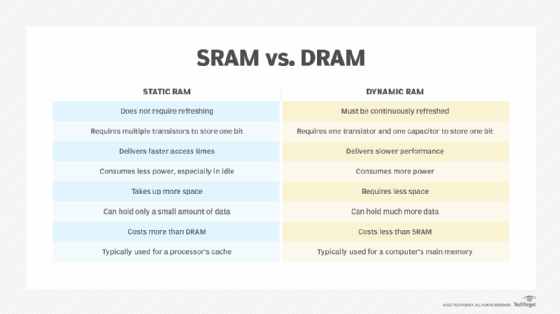
Static RAM vs. dynamic RAM
Both SRAM and DRAM are types of volatile memory, which means they lose their data if they are powered down or if the power goes out. Despite this similarity, they differ in important ways. Much of this difference lies in how they are constructed.
SRAM uses a flip-flop circuit to store each data bit. The circuit delivers two stable states, which are read as 1 or 0. To support these states, the circuit requires six transistors -- four to store the bit and two to control access to the cell. Because of all these transistors, an SRAM chip has a much lower capacity than a DRAM chip of comparable size.
At the same time, the use of multiple transistors and a flip-flop circuit removes the need for periodic refreshing, which is what speeds up data transfers and access. For read/write operations, the data is located through the address bus to access the specific memory cell.
DRAM requires only one transistor and one capacitor to store a bit. The capacitor holds the electrons that determine whether the bit is a 0 or 1. The transistor acts as a switch for reading and changing the capacitor's state. DRAM capacitors have a tendency to leak electrons and lose their charge, so they must be refreshed periodically to retain their data, which can affect access speeds and increase power usage.
Because of the different architectures, SRAM tends to perform better and require less power, especially when it sits idle. However, it cannot store as much data as DRAM, and it is more expensive.
SRAM, DRAM and other memory types
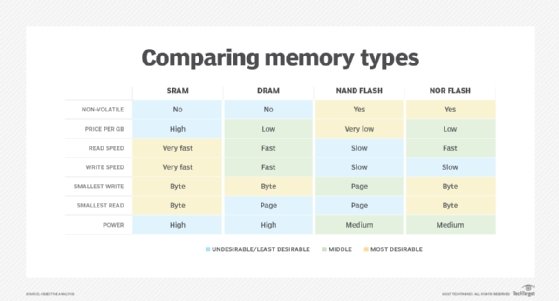
Both SRAM and DRAM easily outperform most of today's non-volatile memory, even the latest generation of flash drives and storage class memory devices. Computer systems are likely to rely on SRAM and DRAM for some time to come, although there is a great deal of research underway looking into alternatives to both solid-state memory and storage.
Until then, SRAM and DRAM offer individual advantages that make them best suited for specific use cases. As such, DRAM is used for a computer's memory, and SRAM is used for its cache, which requires the fastest possible access speeds. In fact, SRAM could potentially benefit any type of device in which performance and power usage are of primary concern.
Check out the guide to flash memory architecture, types and products. Learn about current use cases for the technology, and explore future directions.