second-level address translation (SLAT)
What is second-level address translation (SLAT)?
Second-level address translation (SLAT) is a hardware virtualization technology that reduces hypervisor overhead. SLAT is now available in many kinds of processors, including those from Intel and Advanced Micro Devices (AMD).
SLAT is a hardware mechanism in computer processors that is required when installing Microsoft Hyper-V, a virtualization product that is used to create and run a software version of a computer. This version, called a virtual machine (VM), runs an operating system (OS) and programs just like a physical machine, providing users with greater flexibility when utilizing required computing resources.
SLAT is used with virtualization products, known as hypervisors, such as Hyper-V, as a way to reduce the overhead that typically results when translating physical guest addresses to real physical addresses, which are required to set up the VM. To do so, SLAT reduces the inefficiencies associated with looking up virtualized memory addresses in software shadow volumes as processes such as applications or OS software seek to address system resources.
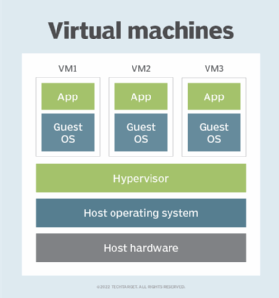
Importance of SLAT
Virtualization is a core technology for many data centers, but the software layer introduced by a hypervisor imposes computing overhead that reduces the resources available to VMs. Physical computing resources must be presented to VMs as virtualized resources. This is the essence of abstraction, which insulates workloads from the underlying computing hardware.
When resources are retrieved from SLAT rather than through a standard lookup operation, performance is enhanced because the memory address is stored on the processor. In addition, the hypervisor uses SLAT to reduce the overhead of translating guest physical addresses to real physical addresses.
This significantly reduces the hypervisor central processing unit (CPU) time, and more memory is saved for each VM. Latency is also reduced, and the system only goes through one memory lookup operation rather than two. SLAT is also used to perform VM memory management functions.
How SLAT works
SLAT technology exists as a CPU feature: an added translation lookaside buffer (TLB) that contains a real-time updated cache of virtualized memory addresses and their corresponding physical addresses. Simply put, the TLB supports the translation of virtual memory addresses to physical memory addresses. As a cache on the processor, the TLB contains recently used mappings from the page table. It checks whether the required mapping information is available each time a virtual-to-physical address translation is to be performed.
As memory is addressed in a virtualized system, the values for the referenced address are added to SLAT. The TLB holds recent page table mappings generated by the hypervisor. When a virtual-to-physical address translation is requested, the hypervisor queries the TLB for mapping information.
If there's a match, the physical address is returned to the hypervisor -- without the memory and CPU resources that are required for translation. This is the "second level" of address translation. If there is no match, the hypervisor checks the traditional page table and performs the normal address translation. The hypervisor then saves the new translation to the TLB for future reference. Because the TLB is involved in holding address mapping information, address translation and data access, it substantially decreases the hypervisor's overhead.
SLAT in different processors and hypervisors
Both Intel and AMD support SLAT, although the companies label the technology differently. Multiple generations of Intel Core i3, i5, i7 and i9 support what Intel calls their SLAT technology: Extended Page Table (EPT).
Other Intel processor families that support SLAT and EPT include the following:
- Intel Xeon W.
- Intel Xeon E3/E5/E7.
- Intel Celeron.
- Intel Pentium.
- Intel Core X-series.
AMD processors have included SLAT since their Barcelona architecture. AMD calls its SLAT implementation Rapid Virtualization Indexing (RVI).
Both approaches can offer performance increases of up to about 40% in heavy virtualization situations and even up to 600% in microbenchmarks.
There are a number of hypervisors that support SLAT apart from Microsoft Hyper-V, including kernel-based VM since version 2.6.26, VirtualBox 2.0.0 and later, VMware ESXi version 3.5 and later, and Xen 3.2.0 and later. Bhyve and Qubes OS not only support SLAT, but require it. Open source hypervisors, like ACRN and QEMU, also support SLAT.
How to check if a Windows computer supports SLAT
Before installing a hypervisor on a Windows system, it's important to check if the processor supports SLAT. This can be done in one of two ways.
1. Download Coreinfo from Microsoft
Coreinfo is a command-line utility from Microsoft that provides insights into the system's processor and cache topology. When used with the right parameter (-v), Coreinfo dumps the processor's virtualization-related features, including whether it supports SLAT.
Microsoft provides Coreinfo as a ZIP file, which must be unzipped. Its executable file should then be copied to the root of the system's C drive. To see the virtualization-related features, the following steps must be followed after copying Coreinfo.exe to the C drive:
- Open a command prompt as an administrator.
- Navigate to the root of the C drive in the command prompt using the command cd C:\.
- Run the command coreinfo –v.
For Intel processors that support SLAT, the command-line prompt shows an asterisk in the EPT row. Similarly, for AMD processors that support SLAT, the command-line prompt shows an asterisk in the RVI row. If either type of processor does not support SLAT, the command-line prompt shows a dash in the EPT or RVI rows.
2. Turn Windows features on and off
Control Panel in Windows 10 and 11 systems includes a feature called Turn Windows features on and off. When the panel opens, it shows an option for Hyper-V that can be expanded. If the option for Hyper-V Platform is greyed out, the system and processor do not support SLAT.
Choosing the right CPU for virtual infrastructures depends on many factors, including feature sets and hardware specs. See how to choose the best CPU for virtualization.
