stacked ranking (stack ranking)
What is stacked ranking (stack ranking)?
Stacked ranking (stack ranking) is an employee evaluation method that slots a certain percentage of employees into each of several levels of performance. The goal is to separate out the high-performing employees from the low-performing employees in order to reward the former and, ultimately, cultivate a high-performance workforce.
Stacked ranking is an employee performance management approach in which high-performing employees are differentiated from their low-performing colleagues based on certain metrics and a bell curve ranking system. Employees whose performance is better than their peers are considered top-tier performers and awarded higher ranks.
Low performers receive lower ranks. Employees with the lowest ranks may be laid off. This knowledge is meant to motivate all employees to do better than their colleagues so the organization can create a high-performance workforce.
The stacked ranking model of performance appraisals is also known as stack ranking, employee stack ranking, forced ranking and rank and yank. And, because the ranking is inherently somewhat arbitrary, the model is also sometimes referred to as a forced distribution.
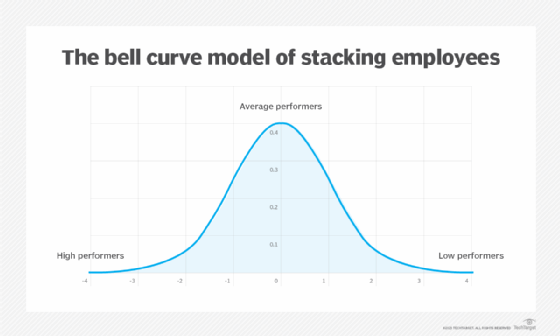
How stacked ranking works
A stacked ranking model might assume a normal distribution or bell curve. A majority of employees fall in the middle part of the bell curve with small minorities on either side. The percentage distribution of the top-middle-bottom performers can be something like 10-70-20, 10-80-10, 20-70-10, etc.
For example, the minority may represent 10% of employees who are labeled "high achievers," 80% are satisfactory and valuable, and 10% are detrimental to the company. When evaluating the staff, administrators, such as managers or human resources (HR) personnel, assign individuals to those categories in such a way that the percentages assigned to each category remain constant.
Companies have different ways of determining the next steps for the employees in each group. For instance, one company may fire the low performers, while others may place them on a performance improvement plan. Similarly, one company may promote high performers, while another may reward them with a performance bonus.
Companies that use -- or used -- stacked ranking
One of the first companies to adopt the stacked ranking model was General Electric (GE). The model was pioneered by the company and its then-CEO Jack Welch in the 1980s. It was then adopted by many other companies.
Companies that use -- or did use -- stacked ranking include Dow Chemical, Enron, Motorola, IBM, and Yahoo. Microsoft followed the stacked ranking model for years but abandoned it in 2013 in response to employee complaints about the system.
Tech giants, like Amazon and Google, have also used stacked ranking -- or a modified version of it -- to appraise employee performance and try to maintain their workforce's overall performance levels. Google used stacked ranking to determine who should be promoted, while Amazon has since abandoned the model in favor of a less contentious continuous feedback employee appraisal model.
What is an example of stacked ranking?
One of the best-known stacked ranking systems is Welch's vitality curve. Welch explained the concept in his 2001 book, Jack: Straight from the Gut.
The vitality curve is also known as the 20-70-10 system. This is because it assigns high-achieving employees, whom Welch called "A players," to the top 20%; normally productive employees (B players) to the middle 70% level; and unproductive employees (C players) to the bottom 10% rank.
According to Welch, the top employees are passionate about and committed to their work and of the greatest use to the organization. They should, therefore, be further motivated with bonuses and other rewards. On the other hand, the bottom 10% are the "nonproducers" and Welch believes that they should be fired.
The middle-of-the-path B players are not as effective or as beneficial as the A players; neither are they as expendable as the C players. However, they constitute the majority of the workforce, are vital to the organization's business continuity and success and should, therefore, be retained and encouraged to improve.
Controversy erupted around the vitality curve after it was first proposed, which explains why GE has since moved away from the practice. However, several companies still follow the model, albeit covertly to avoid criticism from customers, the public and other stakeholders.
Pros and cons of stacked ranking
Proponents of stacked ranking claim that it motivates midrange employees to aspire to top-level ranking by clearly highlighting their weaknesses and areas of improvement. It also helps companies to clearly identify and weed out underperformers, which enables them to create a high-performing workforce that benefits the firm. In doing so, the model can help them increase their productivity, which can then positively impact profits.
Critics of the model argue that it is too cutthroat and "me-focused" and discourages cooperation and collaboration. For the same reasons, they believe that it encourages unethical behaviors, especially among employees who aspire to join the ranks of the A players and also among employees who are already ranked A players and are desperate to remain in that group.
Another criticism of stacked ranking is that it hampers staff cohesiveness and morale since it encourages competitiveness over teamwork. It can also lead to bullying and blaming of so-called low-performers, thus creating a toxic workplace culture, instead of a culture that encourages innovation and learning through experimentation.
Yet another problem with the stacked ranking model is that it is associated with threats of probation and termination that can demotivate low-ranked employees instead of encouraging them to improve their performance. Low motivation levels among staff can affect their workplace engagement, which then adversely impacts the company's overall productivity and, eventually, its profitability and competitiveness.
A stacked ranking appraisal system also prioritizes performance at all costs over healthy habits related to mental health and work-life balance. Consequently, it creates teams who are high-performing but, at the same time, highly burned out. Overwhelmed, highly burned out employees are more likely to be absent or to quit entirely, increasing the company's turnover problems.
See how to solve the biggest employee retention challenges. Read this guide to build an effective employee experience strategy. Explore performance appraisal types for HR leaders to consider and top performance review questions and answers.