
What is named entity recognition (NER)?
Named entity recognition (NER) is a natural language processing (NLP) method that extracts information from text. NER involves detecting and categorizing important information in text known as named entities. Named entities refer to the key subjects of a piece of text, such as names, locations, companies, events and products, as well as themes, topics, times, monetary values and percentages.
NER is also referred to as entity extraction, chunking and identification. It's used in many fields in artificial intelligence (AI), including machine learning (ML), deep learning and neural networks. NER is a key component of NLP systems, such as chatbots, sentiment analysis tools and search engines. It's used in healthcare, finance, human resources (HR), customer support, higher education and social media analysis.
What is the purpose of NER?
NER identifies, categorizes and extracts the most important pieces of information from unstructured text without requiring time-consuming human analysis. It's particularly useful for quickly extracting key information from large amounts of data because it automates the extraction process.
NER delivers critical insights to organizations about their customers, products, competition and market trends. For example, companies use it to detect when they're mentioned in publications. Healthcare providers use it to extract key medical information from patient records.
This article is part of
What is enterprise AI? A complete guide for businesses
As NER models improve their ability to correctly identify important information, they are helping improve AI systems in general. These systems are enhancing AI language comprehension capabilities in areas such as summarization and translation systems and the ability of AI systems to analyze text.
How does NER work?
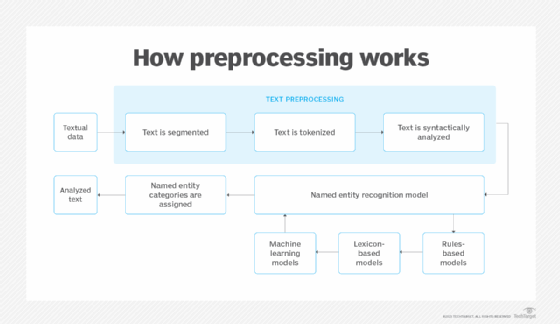
NER uses algorithms that are based on grammar, statistical NLP models and predictive models. These algorithms are trained on data sets labeled with predefined named entity categories, such as people, locations, organizations, expressions, percentages and monetary values. Categories are identified with abbreviations; for example, LOC is used for location, PER for persons and ORG for organizations.
Once trained on textual data and entity types, an NER learning model automatically analyzes new unstructured text, categorizing named entities and semantic meaning based on its training. When the information category of a piece of text is recognized, an information extraction utility extracts the named entity's related information and constructs a machine-readable document that other tools can process to extract meaning.

What are the four types of NER?
The four most used types of NER systems are the following:
- Supervised ML-based systems use ML models trained on texts humans have prelabeled with named entity categories. Supervised machine learning approaches use algorithms such as conditional random fields and maximum entropy, two complex statistical language models. This method is effective for parsing semantic meanings and other complexities, though it requires large volumes of training data.
- Rule-based systems use rules to extract information. Rules can include capitalizations or titles, such as "Dr." This method requires a lot of human intervention to input, monitor and tweak the rules, and it might miss textual variations not included in its training annotations. It's thought that rule-based systems don't handle complexity as well as machine learning models.
- Dictionary-based systems use a dictionary with an extensive vocabulary and synonym collection to cross-check and identify named entities. This method might have trouble classifying named entities with variations in spellings.
- Deep learning systems are the most accurate of the four. The use of neural networks, such as recurrent neural networks and transformer architectures, to examine the syntax and semantics of sentence structures. This approach is considered an upgrade from traditional machine learning because it can handle large data sets of text better and automatically learn features and attributes of input data.
NER methods
There are several methods available for implementing NER. Each is a type of tool trained to perform specific NER tasks. They are best described as follows:
- Unsupervised machine learning systems. These models use ML systems that aren't already pretrained on annotated text data. Unsupervised learning models are thought to be capable of processing more complex NER tasks than supervised systems.
- Bootstrapping systems. Also known as self-supervised, these systems categorize named entities based on grammatical characteristics, such as capitalization, parts-of-speech tags and other pretrained and predefined categories. A person then fine-tunes the bootstrap system, labeling its predictions as correct or incorrect and adding the correct ones to a new training set.
- Neural network systems. These build an NER model using neural networks; bidirectional architecture learning models, such as Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT); and encoding techniques. This approach minimizes human interaction.
- Statistical systems. These systems use probabilistic models trained on textual patterns and relationships to predict named entities in new input text data.
- Semantic role labeling systems. These preprocess an NER model with semantic learning techniques to teach it the context and relationships between categories.
- Hybrid systems. These use aspects of multiple systems in a combined approach.
Who uses NER?
Various industries and applications use NER in different ways. Each use case simplifies searching for and extracting important information from large data volumes so people can spend time on more valuable tasks. Examples include the following:
- Chatbots. OpenAI's generative AI, ChatGPT, Google's Bard and other chatbots use NER models to identify relevant entities mentioned in user queries and conversations. This helps them understand the context of a user's question and improves chatbot responses.
- Customer support. NERs organize customer feedback and complaints by product name and identify common or trending complaints about specific products or branch locations. This helps customer support teams prepare for incoming queries, respond faster and establish automated systems that route customers to relevant support desks and sections of FAQ pages.
- Finance. NER extracts figures from private markets, loans and earnings reports, increasing the speed and accuracy of analyzing profitability and credit risk. NER also extracts names and companies mentioned in social media and other online posts, helping financial institutions monitor trends and developments that could affect stock prices.
- Healthcare. NER tools extract critical information from lab reports and patients' electronic health records, helping healthcare providers reduce workloads, analyze data faster and more accurately, and improve care.
- Higher education. NER lets students, researchers and professors quickly summarize volumes of papers and archival material, as well as find relevant subjects, topics and themes.
- HR. These systems streamline recruitment and hiring by summarizing applicants' resumes and extracting information, such as qualifications, education and references. NER also filters employee complaints and queries to the relevant departments, helping organize internal workflows.
- Media. News providers use NER to analyze the many articles and social media posts they need to read and to categorize the content into important information and trends. This helps them quickly understand and report on news and current events.
- Recommendation engines. Many companies use NER to improve the relevancy of their recommendation engines. For instance, companies like Netflix use NER to analyze users' searches and viewing histories to provide personalized recommendations.
- Search engines. NER helps search engines identify and categorize subjects mentioned on the web and in searches. This lets search platforms understand the relevancy of subjects to a user's search and provide users with accurate results.
- Sentiment analysis. NER is a key component of sentiment analysis. It extracts product names, brands and other information mentioned in customer reviews, social media posts and other unstructured text. The sentiment analysis tool then analyzes the information to determine the author's feelings about a product, company or other subject. NER is also used to analyze employee sentiment in survey responses and complaints.
NER benefits and challenges
There are several benefits and challenges relevant to NER.
NER benefits
Named entity recognition provides a range of advantages when used appropriately:
- Automates the information extraction of large amounts of data.
- Analyzes key information in unstructured text.
- Facilitates the analysis of emerging trends.
- Eliminates human error in analysis.
- Is used in almost all industries.
- Frees up time for employees to perform other tasks.
- Improves the precision of NLP tasks and processes.
NER challenges
NER also comes with its own set of issues:
- Has difficulty in analyzing lexical ambiguities, semantics and evolving usages of language in text.
- Runs into problems with spelling variations.
- Doesn't know all foreign words.
- Can have issues with spoken word text, such as telephone conversations.
- Leads to many state-of-the-art NER models reporting limited performance measures.
- Can require large volumes of training data or a lot of human intervention.
- Can be prone to bias in results if the ML algorithm has hidden bias.
NER best practices
Enterprises should follow a set of best practices when training, using and maintaining their NER systems. These practices include:
- Using the correct tools. Various providers offer tools tailored to NER tasks. These include language models and libraries such as BERT, Stanford NER tagger, Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) and SpaCy.
- Clearly labeling and annotating data. It's important to clearly define entity types and have an annotation scheme that NER models will abide by when performing tasks. This is necessary when preparing the data used to train NER models.
- Feature engineering. To fine-tune an NER model, feature engineering is used to provide important features, such as part-of-speech tagging and word embedding. It also does tasks such as representing words as numerical values so computer systems can process and understand them in context.
- Continuous model evaluation. Continuous reevaluation of NER models is necessary after implementation. For example, analyzing performance over time to identify errors will determine areas for improvement.
Natural Language Toolkit vs. SpaCy
NLTK and SpaCy are two NER programs with unique differences. NLTK is based on Python's NLP library and provides several algorithms. NLTK is often used for teaching NLP to beginners, as well as researchers building applications from the ground level. It uses strings as inputs and outputs in preprocessing. It provides tokenization, stemming, part-of-speech tagging and parsing and can be trained on customized data.
SpaCy, on the other hand, is open source and uses a single stemmer algorithm suited for concrete tasks. It's often used for building professional NLP applications and is object-oriented in preprocessing. SpaCy is also able to handle large data volumes, extract relationships between entities and offer support for word vectors. It's considered faster than NLTK.
Named entity recognition is a critical part of natural language processing. Learn how NLP augments enterprise analytics.