digital wallet
What is a digital wallet?
A digital wallet is an online payment tool or software application that serves as an electronic version of a physical wallet. Also known as an electronic wallet, e-wallet or mobile wallet, it enables users to securely store digital versions of payment methods -- credit and debit cards, gift cards, cryptocurrency, boarding passes, event tickets, passwords and coupons -- to use on the go with their smartphones or smartwatches.
A customer can use a digital wallet to make purchases at stores, online or through digital wallet apps. For in-store purchases, they generally use a contactless payment terminal by tapping their contactless credit card or a payment-enabled smartphone or smartwatch over the contactless payment terminal.
Not all retailers accept mobile payments, so a user must look for the contactless payment symbol on the retailer's point of sale (PoS) system or card reader. The contactless symbol resembles a sideways Wi-Fi icon.

How does a digital wallet work?
Digital wallets employ several technologies -- including mobile apps, mobile hardware devices, near-field communication (NFC) and security methods such as tokenization -- to create a user-friendly, mobile and ostensibly secure payment experience.
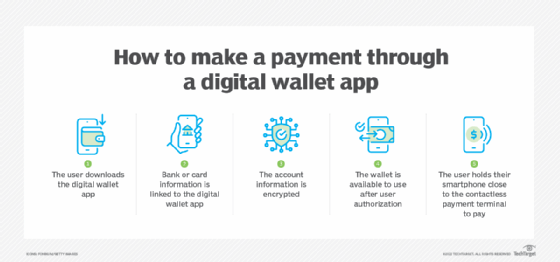
To use a digital wallet, a user enters their card information into the digital wallet app or site. The information is encrypted and the wallet is available for use once the device is unlocked and the user authorizes the wallet. To make a mobile payment, the user holds their smartphone close to the contactless terminal.
The most popular technologies digital wallets use include the following:
Quick response (QR) codes. These barcodes encode information into a black and white pattern that a user can access with a smartphone camera or their digital wallet's scanning system to initiate a payment. Payment apps can encode information, including the transaction amount and the intended recipient. For example, in the PayPal app, a QR code can be generated that enables shoppers to use their accounts to pay for items in store.
NFC. This wireless data transfer technology uses electromagnetic signals to enable smartphones, tablets, laptops and other devices to share and transfer data when in close proximity. Generally, two devices need to be within an inch and a half of each other to connect.
Magnetic secure transmission (MST). This mobile payment technology enables smartphones to transact wireless payments with both traditional pre-chip magnetic stripe systems and modern no-swipe credit card terminals. It generates a magnetic signal similar to when someone swipes the magnetic stripe on a credit card reader. MST enables customers and retailers to transact securely without having to upgrade their equipment.
Examples of digital wallets
Fueled by the convenience factor, more consumers are transitioning to digital wallets. According to the "2022 Global Payments Report" by Worldpay from FIS, by 2025, digital wallet use will account for over 52.5% of e-commerce transactions globally, as compared to 48.6% in 2021.
There are a variety of digital wallet options, but which one a consumer uses boils down to the type of smartphone they use and their needs. Apple Pay, for example, is only used with an iPhone and can't be used on an Android phone.
Notable examples of digital wallets include the following:
Apple Pay. Apply Pay provides a safe and contactless way for users to make payments through iOS, iPadOS and watchOS apps and on websites through the Safari browser. Apple Cash and any debit or credit card number that a customer adds to their Apple Wallet can be used for making Apple Pay transactions. Payments made with Apple Pay are verified using a passcode set on the device and optionally through touch or Face ID.
Google Wallet. Although Google Wallet replaces Google Pay in many countries, the two apps remain separate. Google Wallet uses NFC technology, enabling users to pay with a fingerprint or password. Using NFC in conjunction with cloud technology enables customers to use Google Wallet to make secure and fast digital payments by tapping their phone on any NFC-enabled POS terminal upon checkout.
Samsung Wallet. Samsung Wallet is formerly known as Samsung Pay. In July 2022, it was re-released and merged with Samsung Pay and Samsung Pass. It uses NFC technology to transfer card information to an NFC-enabled payment terminal. However, it provides limited usage as it's only compatible with Samsung devices and isn't yet set up to manage payments on websites.
PayPal. PayPal is one of the oldest peer-to-peer (P2P) money transfer services used for online and in-app purchases, personal money transfers and e-commerce. Individuals can send money to each other through a linked debit or credit card or a bank account. Users can also link PayPal with other digital wallets, including Apple Pay.
PayPal One Touch. This extension of the services provided by PayPal enables users to skip logging in with their email and password when making payments or transferring funds. PayPal One Touch speeds up transactions while keeping a user's financial information secure by ensuring they're always using the same device and browser combination. If the user tries to update their personal information, they're prompted to login again.
Venmo. Venmo is a subsidiary of PayPal and initially started as a money-sharing app. It made it easier to request money from friends, split bills or share a portion of rent with roommates. Over time, Venmo has grown into a complete financial platform that enables users to shop online and in person with participating retailers.
CashApp. This P2P payment platform enables users to send and receive money through their mobile devices. CashApp also offers users the option to purchase stock and Bitcoin and file taxes through its CashApp Taxes feature.
Types of digital wallets
There are three types of digital wallets -- closed, semi-closed and open.
- Closed wallet. This wallet is restricted to certain individuals. For example, a company selling products and services can develop a closed wallet just for its customers. The money from returns and cancellations is stored in this wallet and users can only transact with the issuer of that wallet. Amazon Pay is an example of a closed wallet.
- Semi-closed wallet. With a semi-closed wallet, users can make transactions at listed merchants and locations. The payment information is stored in a centralized location for safety purposes, but a user may need to share a key or a password with another person before making a transaction. A semi-closed wallet provides ease of use by storing multiple public addresses while keeping private keys offline.
- Open wallet. Open wallets can be used to manage and track payment information online. Operating as easy-to-use online applications, a user can download an open wallet to any device or browser with an internet connection. Open wallets are compatible across all platforms and users can transact anytime and from anywhere.
Advantages of digital wallets
While many factors are driving the growth of digital wallets, the COVID-19 pandemic helped skyrocket their use due to a surge in online shopping and contactless transactions.
The following are the main benefits of using digital wallets:
- Streamlined customer experience. Digital wallets streamline and expedite the checkout process, as customers aren't required to fill out lengthy checkout pages or forms. This is a win-win for everyone, as faster checkouts discourage customers from abandoning their shopping carts, which in turn increases the conversion rates for businesses.
- Security. Digital wallet providers, including Apple Pay and Google Wallet, use tokenization, which masks credit card details and is transaction-specific to prevent hackers from gaining access to consumers' data. Digital wallets also employ biometrics, including fingerprint and facial recognition technology, which prevents the account information from being stolen. For example, if a person drops a physical card or a wallet, their personal information can be easily stolen; whereas digital wallets add layers of security through features such as Face ID or two-factor authentication, which makes it more difficult for anyone to access the stolen information.
- Contactless payments. Contactless payments enable consumers to make payments without having to carry a card or search for one inside their physical wallets. Users can simply use touch or Face ID on their phones to confirm payment during the checkout process.
- Valuable customer insights. Digital wallets help extract real-time data for valuable insights into a customer's shopping habits, including their shopping history and preferences. This helps businesses create targeted marketing campaigns as well as helps with inventory management and budget creation.
- Access to rewards and offers. With digital wallets, consumers are often rewarded with special promotions and offers, such as cashback, coupons and loyalty programs from their favorite brands and retailers.
Disadvantages of digital wallets
Digital wallets offer great convenience, but they also come with a few inherent risks. The following are a few disadvantages of using digital wallets:
- Safety and privacy concerns. While digital wallets offer transaction security, there's always a risk of getting hacked if the device gets lost or is stolen. If hackers get access to a device with the digital wallet app, they could potentially get their hands on the device owner's account and transaction history.
- Limited merchants. Even with the wide acceptance of digital wallets among consumers, not all merchants -- especially small shop owners -- support it. This means people still need to carry cash and credit cards for certain transactions.
- Security and budgeting. Many people who are used to using cash and credit cards find it difficult to adopt contactless payment methods. Some might even believe that carrying physical money is safer or that paying cash might help them control their spending habits.
- Device dependency. A digital wallet works on accessible devices only. This means that if a person misplaces their device or the device's battery dies, they won't have access to their digital wallet for payments.
Digital wallets are revolutionizing the customer experience by offering greater security, accessibility and convenience. Here's a look at the eight popular digital wallet companies and what they offer.