What is HTTP and how does it work? Hypertext Transfer Protocol
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is a set of rules that govern how information will be transferred between networked devices, specifically web servers and client browsers.
First developed between 1989 and 1991 by Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web, HTTP is an application layer protocol whose older versions (prior to HTTP/3) ran on top of the TCP/IP (transmission control protocol/internet protocol) suite of protocols. HTTP, TCP and IP form the foundation of the modern-day internet.
The latest version of HTTP is HTTP/3, which was published in 2021. It is a major upgrade to its predecessor, HTTP/2, although HTTP/2 is still used by many websites, and many browsers still support it.
What is HTTP used for?
When a user surfs the internet, their web browser requests certain information or webpages. So, as soon as a user opens their web browser, they are indirectly using HTTP. The information requested by the browser may include many kinds of files or resources, such as text, images, sound, video and other multimedia files, all of which are transferred by HTTP over the web and displayed in the user's web browser. HTTP facilitates communications between web browsers and web servers in a standardized way, thus providing the foundation for information exchange on the world wide web.
Different versions of HTTP remain in use today. Tim Berners-Lee and his team developed HTTP to facilitate secure data transmissions over the internet. HTTP/2, the successor to HTTP/1.1 that was first published in 2015, offers significant performance improvements over its predecessors in terms of webpage loading speeds. This is a particularly useful benefit for complex web applications and pages.
Since June 2022, many web servers and browsers have adopted HTTP/3, the successor of HTTP/2. HTTP/3 offers even better performance, speed and reliability of web content delivery than HTTP/2. Additionally, it offers stronger security and enhanced user experience while using the world wide web. Third, it helps site owners to simplify website maintenance and optimize the usage of network resources.
How does HTTP work?
Through the HTTP protocol, resources are exchanged between client devices -- specifically the web browsers used on the clients -- and web servers over the internet.
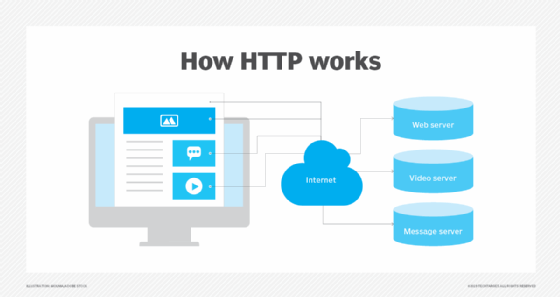
A web server delivers website content to a user's web browser upon receiving such requests from the browser. A web browser is an HTTP client that sends requests for information to servers. The request -- which contains specific information, such as the HTTP version type, an HTTP method, HTTP request headers and HTTP body (optional) -- happens when the browser user enters file requests by either opening a web file by typing in a URL or clicking on a hypertext link. The browser builds the HTTP request and sends it to the Internet Protocol address (IP address) indicated by the URL.
The web server contains an HTTP daemon, a program that waits for HTTP requests and handles them when they arrive. The daemon in the destination server receives the request from the browser and sends back the requested file or files associated with the request as its answer or HTTP response. Like the request from the browser, the response from the server also contains valuable information, including HTTP response headers, an HTTP status code and HTTP body (again, optional).
Requests and responses share subdocuments -- such as data on images, text, text layouts, etc. -- which are pieced together by a client web browser to display the full webpage file.
HTTP example
Suppose a user wants to visit https://www.techtarget.com. They type in the web address in the browser's address bar or simply type TechTarget or TechTarget.com in a search engine like Google. Either way, the computer sends a GET request to a web server that hosts that address. That GET request is sent using HTTP and tells the TechTarget server that the user is looking for the HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) code used to structure and give the login page its look and feel.
The text of that login page is included in the HTML response, but other parts of the page -- particularly its images and videos -- are requested by separate HTTP requests and responses. The more requests that are made -- for example, to call a page that has numerous images -- the longer it will take the server to respond to those requests and for the user's browser to load the page.
HTTP requests and responses
Client devices submit HTTP requests to servers, which reply by sending HTTP responses back to the clients. Requests state what information the client is seeking from the server in order to load the website; responses contain code that the client browser will translate into a webpage.
These requests and responses that servers and clients use to share data with each other consist of ASCII code. Also, each interaction between the client and server is called a message, so HTTP messages can be either requests or responses.
HTTP request
The request from a client device, such as an internet browser, provides the server with the desired information it needs to tailor its response to the client device. Each HTTP request contains encoded data, with information such as the following:
- The specific version of HTTP in use. HTTP, HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 are the versions currently available.
- A URL. The URL points to the resource, i.e., a specific website accessible via the web.
- An HTTP method. The method indicates the specific action the request expects to receive from the server when it responds.
- HTTP request headers. Request headers include data such as the type of browser being used and what data the request is seeking from the server. It can also include cookies, which show information previously sent from the server handling the request.
- An HTTP body. This is optional information the server needs from the request, such as user forms -- username/password logins, short responses and file uploads -- that are being submitted to the website.
HTTP response
The HTTP response message is the server's reply to an HTTP request from a client device. The information contained in the response is tailored to the context the server received from the request, and may include the following data:
- HTTP status code. This indicates the status of the request to the client device. Responses may indicate success, an informational response, a redirect or errors on the server or client side.
- HTTP response headers. These send information about the server and requested resources.
- HTTP body (optional). If a request is successful, the body contains the requested data in the form of HTML code, which is translated into a webpage by the client browser.
HTTP status codes
In response to HTTP requests, servers often issue response codes, indicating the request is being processed, there was an error in the request or that the request is being redirected. Here are some common response codes:
- 200 OK. This is one of the most common response codes; it means that the request, such as GET or POST, worked and is being acted upon.
- 300 Moved Permanently. The URL of the requested resource has been changed permanently.
- 401 Unauthorized. The client, or user making the request of the server, has not been authenticated to allow access to the requested information.
- 403 Forbidden. The client's identity is known but has not been given access authorization.
- 404 Not Found. The 404 error code means the URL is not recognized or the resource at the location does not exist.
- 500 Internal Server Error. The server has encountered a situation it doesn't know how to handle.
HTTP, TCP and QUIC
Traditional HTTP (HTTP versions before HTTP/3) used TCP as the transport layer protocol. When request/response pairs are being sent by the web server and web client via the older versions of HTTP, they use TCP/IP to reduce and transport information in small packets of binary sequences of ones and zeros. These packets are physically sent through electric wires, fiber optic cables and wireless networks.
Since TCP is connection-based and includes error-checking mechanisms, it helped ensure the reliable delivery and correct display of web content. Additionally, TCP takes care of data transmission complexities, allowing HTTP to focus on formatting, interpreting and displaying web resources in response to a client's request to a server.
The latest version of HTTP/3, uses the Quick UDP Internet Connections (QUIC) protocol rather than TCP. Developed and deployed by Google in 2012, QUIC provides numerous advantages over TCP, including faster connection establishment, traffic congestion control, lower latency and built-in security. QUIC allows disruption-free migrations between networks, which is a useful capability for users who use many types of devices and frequently switch networks, and also to support the connection needs of highly networked IoT devices. Additionally, it supports high-transaction connections with minimal disruptions or slowdowns, can reduce device energy consumption and improves the performance of web applications.
Proxies in HTTP
Proxies, or proxy servers, are the application-layer servers, computers or other machines that go between the client device and the server. Proxies relay HTTP requests and responses between the client and server. Typically, there are one or more proxies for each client-server interaction.
Proxies may be transparent or non-transparent. Transparent proxies do not modify the client's request but rather send it to the server in its original form. Non-transparent proxies will modify the client's request in some capacity. Non-transparent proxies can be used for additional services, often to increase the server's retrieval speed.
Web developers can use proxies for the following purposes:
- Caching. Cache servers can save webpages or other internet content locally, for faster content retrieval and to reduce the demand for the site's bandwidth.
- Authentication. A proxy may be used to control access privileges to applications and online information.
- Logging. Logs are used to store historical data, such as the IP addresses of clients that sent requests to the server.
- Web filtering. Filtering controls access to webpages that can compromise security or include inappropriate content.
- Load balancing. Client requests to the server can be handled by multiple servers using load balancing rather than just one.
What is the difference between HTTPs and HTTP?
Developed in 1994 by the now-defunct firm Netscape Communications as the SSL 1.0 (Secure Sockets Layer) protocol, HTTPS is the more secure version of HTTP. The S following HTTP stands for "secure." In 2000, HTTPS was formally added to the Internet Engineering Task Force's (IETF) RFC 2818, a document that describes how to use Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure HTTP connections over the internet.
HTTPS refers to the use of SSL or TLS protocols as a sublayer under regular HTTP application layering. Strictly speaking, HTTP/TLS is conceptually similar to HTTP/TCP. However, where HTTP transmits unencrypted data, HTTPS encrypts and decrypts user HTTP page requests as well as the pages that are returned by the web server. Such encryptions account for the more secure nature of HTTPS in comparison to HTTP. Data encryption prevents third parties from intercepting and/or reading (eavesdropping) the information sent from a browser. In addition, HTTPS provides protection from man-in-the-middle attacks.
Since HTTPS offers an added layer of security and trust, it provides a way to safeguard user data. This allows businesses (website owners) to earn users' trust. Adopting HTTPS can also positively impact a site's search engine optimization (SEO) by boosting its ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs). For all these reasons, migrating from HTTP to HTTPS is considered beneficial for site owners.
Learn the differences between Web 3.0, Web 2.0 and Web 1.0 to see how the original web laid the groundwork for the internet's future. Ranking high on SERPs is the goal of search engine optimization. Explore the top SEO marketing challenges and some ways to address them.