What is the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) is the ongoing transformation of how people live, work and relate to one another through the fusion of technologies that blur the lines between the physical, digital and biological spheres.
Building on the digital advancements of the Third Industrial Revolution, this new era is marked by rapid technological breakthroughs in fields such as AI, robotics, the internet of things (IoT), quantum computing, biotechnology and more.
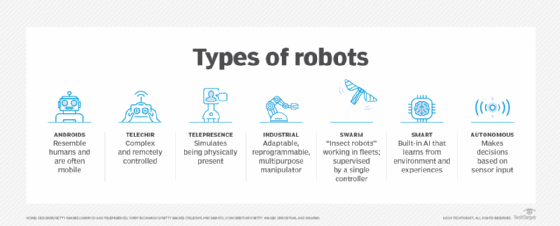
A brief history of industrial revolutions
To better understand the Fourth Industrial Revolution, it helps to view it in the context of the previous three revolutions:
- The First Industrial Revolution, in the late 18th to early 19th century, introduced mechanization through steam engines and waterpower, shifting economies from agrarian to industrial.
- The Second Industrial Revolution, in the late 19th to early 20th century, brought electricity, mass production and the rise of factories.
- The Third Industrial Revolution, in the mid-20th century, marked the digital revolution, ushering in computers, IT and early automation.
Defining characteristics of the Fourth Industrial Revolution
According to Klaus Schwab, founder of the World Economic Forum and author of The Fourth Industrial Revolution, 4IR is distinguished not just by emerging technologies, but by the speed, scope and systemic impact of these changes. Unlike previous industrial revolutions, the fourth is evolving at an exponential rather than linear pace and affects virtually every industry in every country.
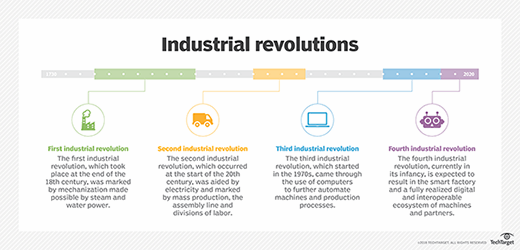
Core technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution
The Fourth Industrial Revolution includes the integration and advancement of numerous technologies:
- AI and machine learning.
- IoT, including the industrial internet of things (IIoT).
- Robotics and autonomous machines.
- Virtual reality and augmented reality.
- Blockchain and distributed ledger technology.
- Cloud computing and edge computing.
- 3D printing or additive manufacturing.
- Quantum computing.
- Biotechnology and gene editing, e.g., CRISPR.
- Cyber-physical systems and smart factories.
Industry 4.0 and manufacturing
A major subdomain of 4IR is Industry 4.0, which refers to the use of smart technology in manufacturing environments. Smart factories use IoT devices, real-time data analytics and automation to create self-optimizing systems that increase efficiency, reduce waste and enable mass customization.
Societal and economic implications
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is not only transforming business models, but also reshaping job markets, education systems and government policies. Key areas of impact include the following:
- Job displacement and creation. While automation might eliminate certain jobs, it also creates new roles requiring advanced technical and soft skills.
- Privacy and data security. The proliferation of connected devices raises concerns about surveillance, cybersecurity threats and data governance.
- Ethical challenges. Questions around AI bias, digital inclusion and biotechnology call for new ethical frameworks.
- Global inequality. Countries and individuals lacking digital infrastructure might fall behind, increasing the risk of a widening digital divide.
Preparing for the Fourth Industrial Revolution
To adapt to this new era, individuals, businesses and governments must take proactive steps, such as the following:
- Investing in education and lifelong learning, especially in STEM and digital literacy.
- Developing ethical AI and data governance frameworks.
- Promoting public-private partnerships to build inclusive digital economies.
- Creating resilient regulatory systems that can keep pace with rapid innovation.
Embracing the Fourth Industrial Revolution requires more than just adopting new technologies -- it demands a mindset of continuous learning, ethical innovation and cross-sector collaboration. By preparing today, individuals and organizations can help shape a more inclusive, resilient and technologically empowered future.
Learn ways to reduce machine learning bias in its different forms. Explore ways in which AI and IoT technologies work together and how AI supercharges existing IoT systems for the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Check potential IIoT use cases and its advantages and challenges.